【语音识别】基于matlab GUI声纹识别【含Matlab源码 1022期】
一、声纹识别简介
本文基于Matlab设计实现了一个文本相关的声纹识别系统,可以判定说话人身份。
1 系统原理
a 声纹识别
这两年随着人工智能的发展,不少手机App都推出了声纹锁的功能。这里面所采用的主要就是声纹识别相关的技术。声纹识别又叫说话人识别,它和语音识别存在一点差别。

b 梅尔频率倒谱系数(MFCC)
梅尔频率倒谱系数(Mel Frequency Cepstrum Coefficient, MFCC)是语音信号处理中最常用的语音信号特征之一。
实验观测发现人耳就像一个滤波器组一样,它只关注频谱上某些特定的频率。人耳的声音频率感知范围在频谱上的不遵循线性关系,而是在Mel频域上遵循近似线性关系。
梅尔频率倒谱系数考虑到了人类的听觉特征,先将线性频谱映射到基于听觉感知的Mel非线性频谱中,然后转换到倒谱上。普通频率转换到梅尔频率的关系式为:
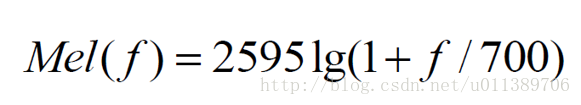
c 矢量量化(VectorQuantization)
本系统利用矢量量化对提取的语音MFCC特征进行压缩。
VectorQuantization (VQ)是一种基于块编码规则的有损数据压缩方法。事实上,在 JPEG 和 MPEG-4 等多媒体压缩格式里都有 VQ 这一步。它的基本思想是:将若干个标量数据组构成一个矢量,然后在矢量空间给以整体量化,从而压缩了数据而不损失多少信息。
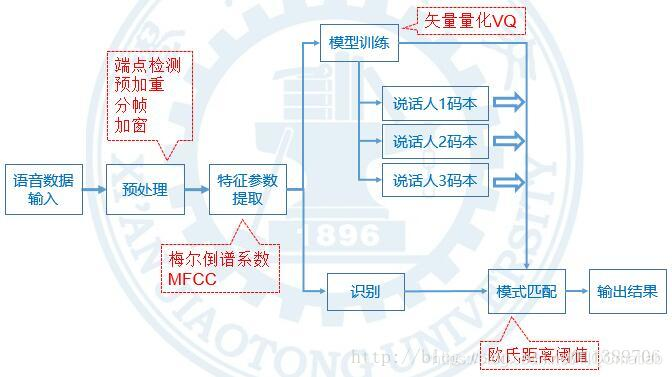
3 系统结构
本文整个系统的结构如下图:
3.1 训练过程
首先对语音信号进行预处理,之后提取MFCC特征参数,利用矢量量化方法进行压缩,得到说话人发音的码本。同一说话人多次说同一内容,重复该训练过程,最终形成一个码本库。
3.2 识别过程
在识别时,同样先对语音信号预处理,提取MFCC特征,比较本次特征和训练库码本之间的欧氏距离。当小于某个阈值,我们认定本次说话的说话人及说话内容与训练码本库中的一致,配对成功。
二、部分源代码
function varargout = GUI(varargin)
% GUI MATLAB code for GUI.fig
% GUI, by itself, creates a new GUI or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = GUI returns the handle to a new GUI or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% GUI('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in GUI.M with the given input arguments.
%
% GUI('Property','Value',...) creates a new GUI or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before GUI_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to GUI_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help GUI
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 15-Mar-2021 17:37:45
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @GUI_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @GUI_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before GUI is made visible.
function GUI_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to GUI (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for GUI
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes GUI wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = GUI_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
fprintf('\n识别中...\n\n');
%加载训练好的GMM模型
load speakerData;
load speakerGmm;
waveDir='trainning\'; %导入测试集
Test_speakerData = dir(waveDir); %获取测试集中的结构体数据,这是一个char类型的结构体
Test_speakerData(1:2) = [];
Test_speakerNum=length(Test_speakerData);
Test_speakerNum
count=0;
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%for i=1:Test_speakerNum
%%%读取语音
[filename,filepath]=uigetfile('*.wav','选择音频文件');
set(handles.text1,'string',filepath)
filep=strcat(filepath,filename);
[testing_data, fs]=audioread(filep);
sound(testing_data, fs);
save testing_data
load testing_data
y=testing_data
axes(handles.axes1)
plot(y);
xlabel('t');ylabel('幅值');
title('时域图');
%频域
%幅频图
N=length(y);
fs1=100; %采样频率
n=0:N-1;
t=n/fs; %时间序列
yfft =fft(y,N);
mag=abs(yfft); %取振幅的绝对值
f=n*fs/N; %频率序列
axes(handles.axes2)
plot(f(1:N/2),mag(1:N/2)); %绘出Nyquist频率之前随频率变化的振幅
xlabel('频率/Hz');
ylabel('振幅');title('频域图');
%相谱
A=abs(yfft);
ph=2*angle(yfft(1:N/2));
ph=ph*180/pi;
axes(handles.axes3);
plot(f(1:N/2),ph(1:N/2));
xlabel('频率/hz'),ylabel('相角'),title('数字0-9的相位谱');
% 绘制功率谱
Fs=1000;
n=0:1/Fs:1;
xn=y;
nfft=1024;
window=boxcar(length(n)); %矩形窗
noverlap=0; %数据无重叠
p=0.9; %置信概率
[Pxx,Pxxc]=psd(xn,nfft,Fs,window,noverlap,p);
index=0:round(nfft/2-1);
k=index*Fs/nfft;
plot_Pxx=10*log10(Pxx(index+1));
plot_Pxxc=10*log10(Pxxc(index+1));
axes(handles.axes4)
plot(k,plot_Pxx);
title('数字0-9的功率谱');
axes(handles.axes5)
surf( speakerData(1).mfcc); %绘制MFCC的三维图
title('第一个人语音的三维MFCC'); %第一个人说话的mfcc的特征 mfcc是指梅尔倒谱系数
%绘制第一个人的MFCC的全部二维图
axes(handles.axes6)
for i=1:speakerNum
fprintf('\n为第%d个语者%s训练GMM……', i,speakerData(i).name(1:end-4));
[speakerGmm(i).mu, speakerGmm(i).sigm,speakerGmm(i).c] = gmm_estimate(speakerData(i).mfcc(:,5:12)',gaussianNum,20); %转置正确
end
fprintf('\n');
save speakerGmm speakerGmm; %保存样本GMM
% hObject handle to pushbutton5 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton6.
function pushbutton6_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
clc
close all
% hObject handle to pushbutton6 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
三、运行结果


四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1]韩纪庆,张磊,郑铁然.语音信号处理(第3版)[M].清华大学出版社,2019.
[2]柳若边.深度学习:语音识别技术实践[M].清华大学出版社,2019.
文章来源: qq912100926.blog.csdn.net,作者:海神之光,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:qq912100926.blog.csdn.net/article/details/118033436
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者



评论(0)