Python实现极限学习机ELM【hpelm库】
【摘要】 一直以为没有人做极限学习机的库,知道发现了hpelm库,才发现,针不戳!!!文末Python源代码自取!!! ELM简介在2004年,由南洋理工学院黄广斌教授所提出的极限学习机器(Extreme Learning Machine,ELM)理论可以改善这种情况。最初的极限学习机是对单隐层前馈神经网络(single-hidden layer feed-forward neural network...
一直以为没有人做极限学习机的库,知道发现了hpelm库,才发现,针不戳!!!
文末Python源代码自取!!!
ELM简介
在2004年,由南洋理工学院黄广斌教授所提出的极限学习机器(Extreme Learning Machine,ELM)理论可以改善这种情况。最初的极限学习机是对单隐层前馈神经网络(single-hidden layer feed-forward neural networks,SLFNs)提出的一种新型的学习算法。它随机选取输入权重,并分析以决定网络的输出权重。在这个理论中,这种算法试图在学习速度上提供极限的性能。
ELM的优势
ELM算法和神经网络算法我认为最大的区别在于:ELM不需要进行迭代,而是一次性通过标签计算出最后一层神经元的权重。而神经网络是通过梯度下降的方法,不断的根据loss值更新权重值。
因此ELM算法不适合构造出更深的网络结构,但是减少了计算量,少了机器开销。而DELM相对于ELM加入了正则项的限制,防止过拟合。
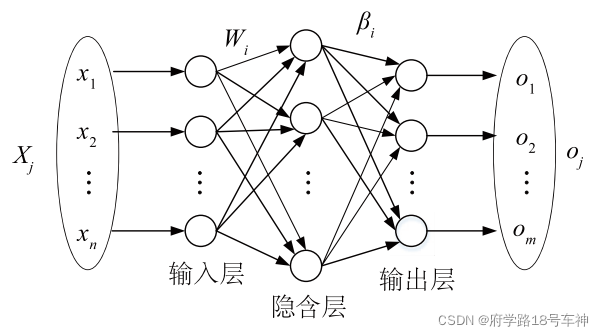
ELM原理
ELM是一种新型的快速学习算法,对于单隐层神经网络,ELM 可以随机初始化输入权重和偏置并得到相应的隐节点输出:


导入库
直接在PyCharm终端输入:
pip install hpelm
ELM线性回归Regression
以线性回归Regression为例,Python代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2021/12/27 11:02
# @Author : 府学路18号车神
# @Email :yurz_control@163.com
# @File : elm_regression.py
#Import libraries
import hpelm
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.utils import to_categorical
import numpy as np
from numpy import random
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#Lists to store results
Train_T = []
Test_E = []
##Load wine testing UCI data data
data = np.genfromtxt('winequality-white.csv', dtype = float, delimiter = ';')
#Delete heading
data = np.delete(data,0,0)
x = data[:,:11]
y = data[:,-1]
#Train test split
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.33,random_state=42)
#===============================================================
def calculateE(y,t):
#Calculate RMSE
return mean_squared_error(y, t)
#===============================================================
#Initialization
Lmax = 40
L = 0
E = 0
ExpectedAccuracy = 0
while L < Lmax and E >= ExpectedAccuracy:
#Increase Node
L = L + 1
#Calculate Random weights, they are already addded into model using hpelm library
w = random.rand(11,L)
#Initialize model
model = hpelm.ELM(11,1)
model.add_neurons(L,'sigm')
start_time = time.time()
#Train model
model.train(x_train,y_train,'r')
Train_T.append(time.time() - start_time)
#Calculate output weights and intermediate layer
BL_HL = model.predict(x_test)
#Calculate new EMSE
E = calculateE(y_test,BL_HL)
Test_E.append(E)
#Print result
print("Hidden Node",L,"RMSE :",E)
#===================================================================
#Find best RMSE
L = Test_E.index(min(Test_E)) + 1
print()
print()
print()
print()
#Define model
model = hpelm.ELM(11,1)
model.add_neurons(L,'sigm')
start_time = time.time()
model.train(x_train,y_train,'r')
print('Training Time :',time.time() - start_time)
start_time = time.time()
BL_HL = model.predict(x_train)
print('Testing Time :',time.time() - start_time)
#Calculate training RMSE
E = calculateE(y_train,BL_HL)
print('Training RMSE :',E)
print('Testing RMSE :',min(Test_E))
#===================================================================
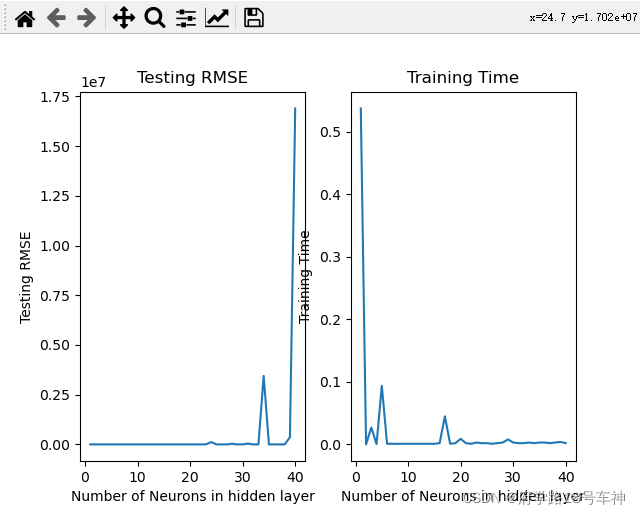
#Plot Data
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1) #Generate graph for ANN
plt.plot(range(1,Lmax+1),Test_E)
plt.title('Testing RMSE')
plt.xlabel('Number of Neurons in hidden layer')
plt.ylabel('Testing RMSE')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2) #Generate graph for CNN
plt.plot(range(1,Lmax+1),Train_T)
plt.title('Training Time')
plt.xlabel('Number of Neurons in hidden layer')
plt.ylabel('Training Time')
plt.show()
源代码
源代码及文件在这里:Python极限学习机ELM实现线性回归
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1b3yTQp5El-aNwvOT7vad-A
提取码:yyds
【声明】本内容来自华为云开发者社区博主,不代表华为云及华为云开发者社区的观点和立场。转载时必须标注文章的来源(华为云社区)、文章链接、文章作者等基本信息,否则作者和本社区有权追究责任。如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)