第04篇:Mybatis代理对象生成

作者: 西魏陶渊明
博客: https://blog.springlearn.cn/
西魏陶渊明
莫笑少年江湖梦,谁不少年梦江湖
一、架构分析
Mybatis中Mapper一般只是一个接口, 那么为什么能执行数据操作的呢? 那肯定是基于代理没得说。在了解Mybatis如何实现代理前, 我们先大概看下它的架构是什么样的, 对这些关键的类有个大概的认识, 知道它所处的位置在哪里。
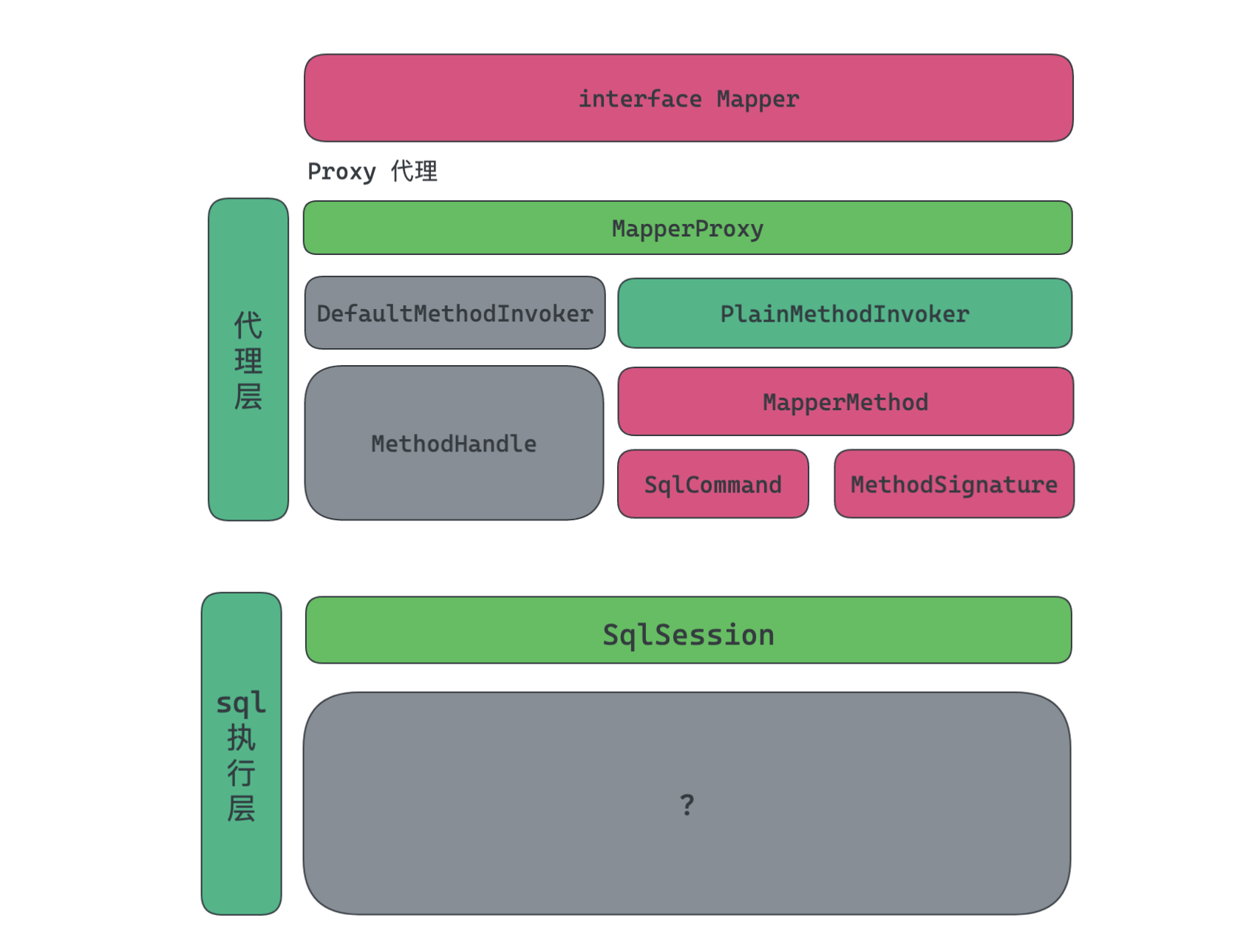
本篇我们只深入研究下代理层, 学习下mybatis是如何进行代理操作的, 而关于sql的最终执行, 放到下一篇执行流程中来研究。
二、源码分析
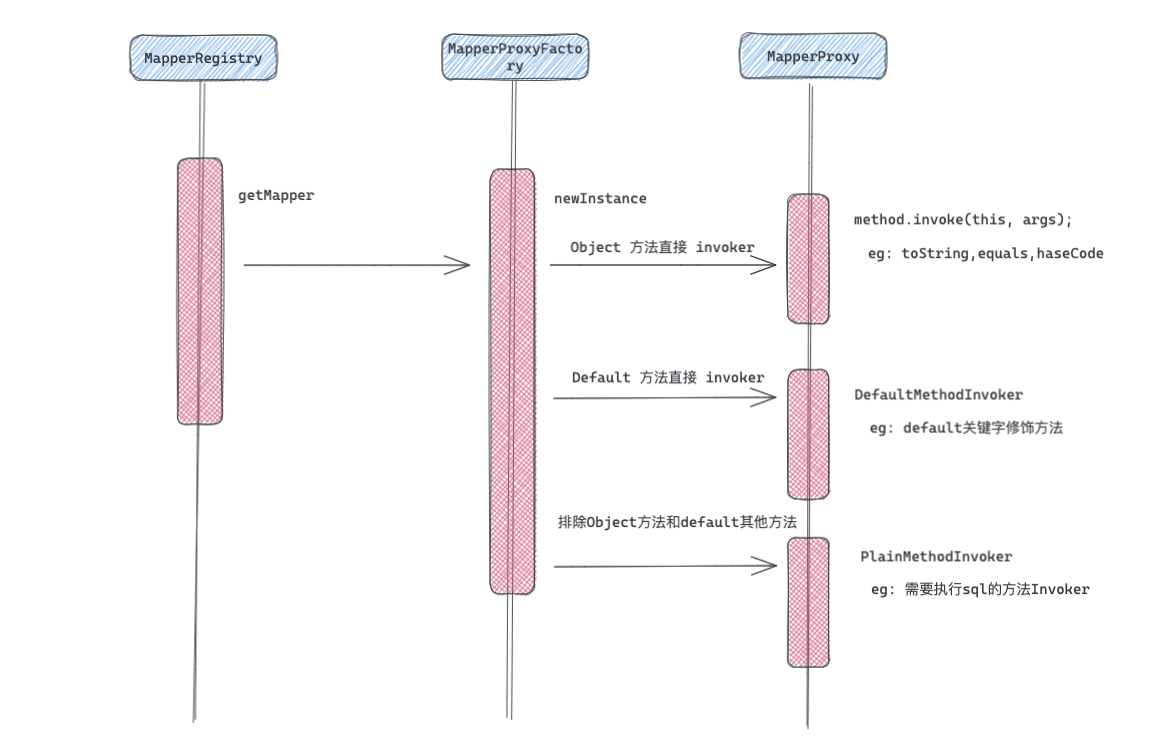
首先不要慌, 看上面这个图, Mybatis的代理流程还是比较简单的。下面主要看下每个核心的类是做什么用的。
2.1 MapperProxyFactory
- 代理工厂里面看代码是比较简单的, 就是利用Proxy创建代理对象。
- 对于已经生成的代理方法, 直接放到MethodCache缓存起来。
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// Jdk代理Proxy, 可以看到主要逻辑在MapperProxy中
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
2.2 MapperProxy
MapperProxy 的代理逻辑也非常简单, 就以下三个能力, 看图理解。
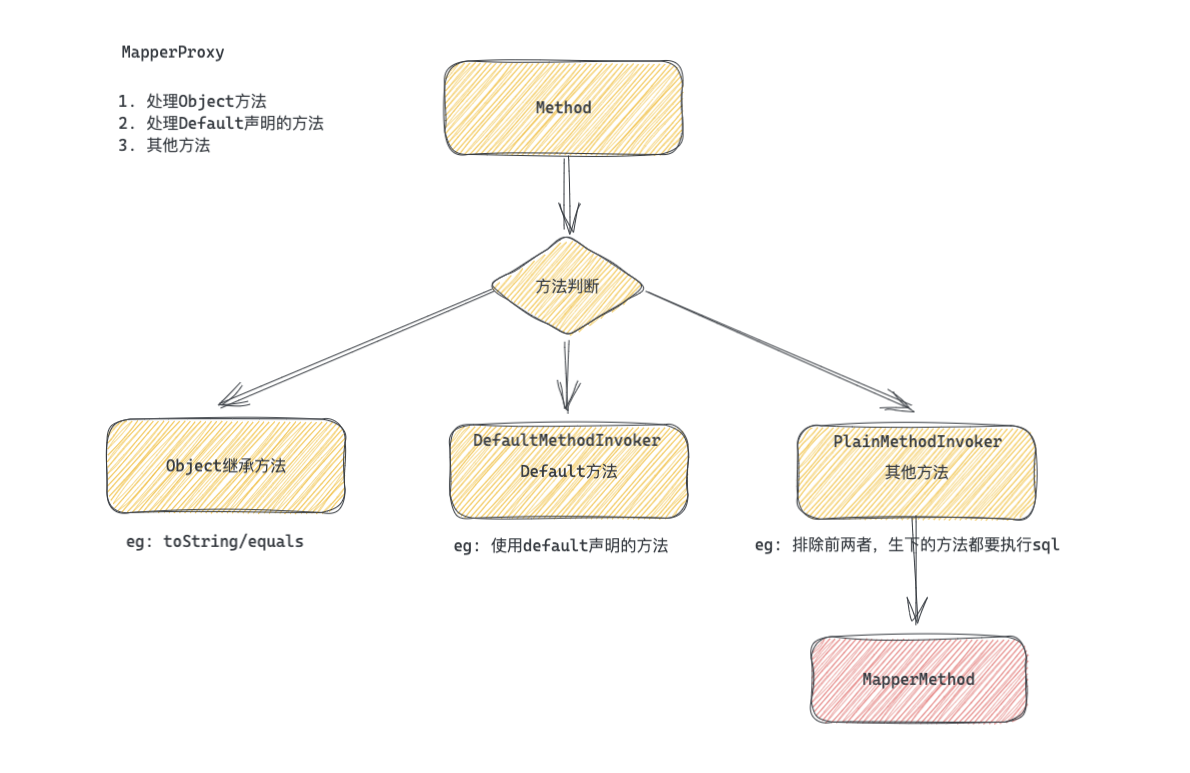
下面将核心的处理代码给挑选了出来, 增加了注释。
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// Object方法直接执行
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
// 其他方法生成代理方法
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {
try {
return MapUtil.computeIfAbsent(methodCache, method, m -> {
// 如果是默认方法
if (m.isDefault()) {
try {
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
// 生成java8的语法解析生成代理方法
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));
} else {
// // 生成java9的语法解析生成代理方法
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException | InvocationTargetException
| NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else {
// 不是默认方法, 生成代理方法 MapperMethod
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
});
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
Throwable cause = re.getCause();
throw cause == null ? re : cause;
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
2.3 PlainMethodInvoker
前面说了代理方法主要有三种场景。
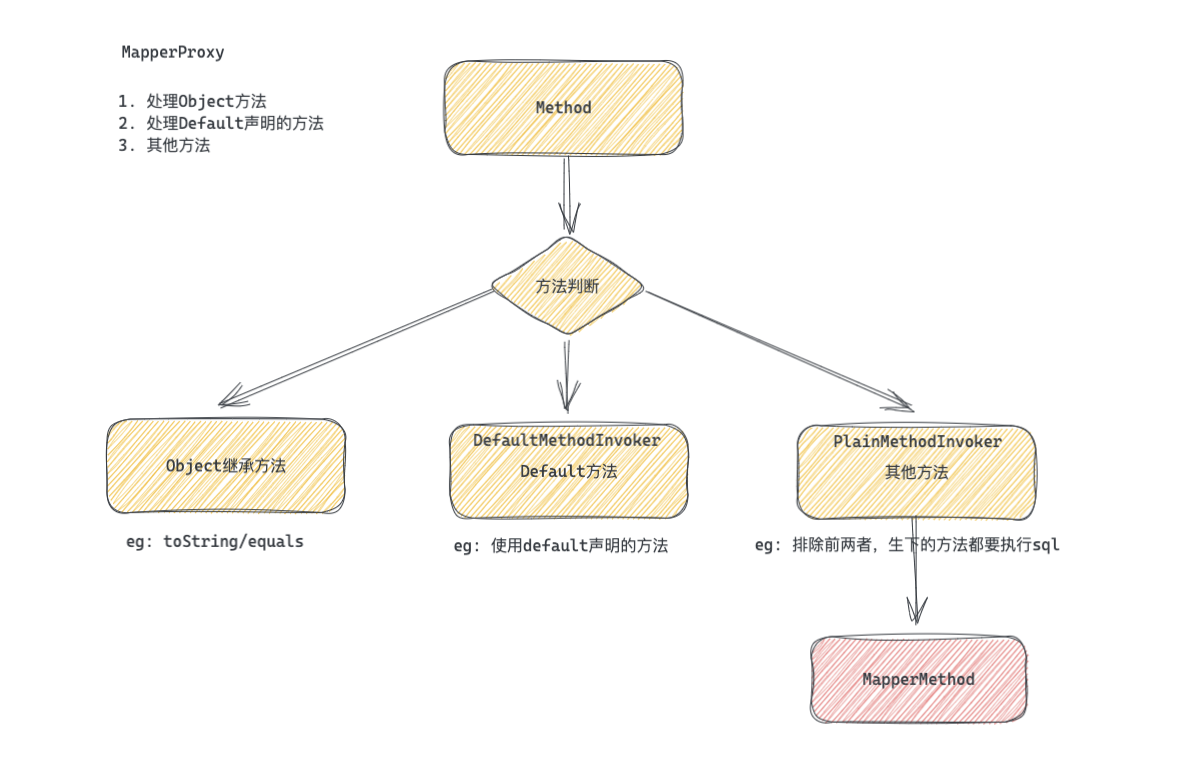
- Object方法直接method.invoker(this, args);
- default关键字修饰的方法, 是DefaultMethodInvoker
- 而更重要的要执行sql的代理Invoker是PlainMethodInvoker
PlainMethodInvoker 才是真正处理需要进行sql的具体实现类。真正的代理逻辑在 MapperMethod 中。
private static class PlainMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {
private final MapperMethod mapperMethod;
public PlainMethodInvoker(MapperMethod mapperMethod) {
super();
this.mapperMethod = mapperMethod;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
MapperMethod, 简单看下流程, 里面有2个重要的实现类, 分别用于判断sql类型, 处理方法参数(解析@Param参数)并最终交给SqlSession执行。到这里就把代理的
流程给搞清楚了。但是具体sql怎么组装参数, 如何调用数据库jdbc接口, 都还没有看到。这部分内容。我们放到下一篇 第05篇:Mybatis的SQL执行流程分析
public class MapperMethod {
private final SqlCommand command;
private final MethodSignature method;
public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
文章来源: springlearn.blog.csdn.net,作者:西魏陶渊明,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:springlearn.blog.csdn.net/article/details/125876443
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)