【强化学习】gym简介
什么是gym?
gym可以理解为一个仿真环境,里面内置了多种仿真游戏。比如,出租车游戏、悬崖游戏。不同的游戏所用的网格、规则、奖励(reward)都不一样,适合为强化学习做测试。同时,其提供了页面渲染,可以可视化地查看效果。
安装gym
pip install gym
- 1
gym的常用函数解释
生成仿真环境
gym.make(‘环境名’)
例如:选择Pong-v0这个环境
env = gym.make(‘Pong-v0’)
重置仿真环境
env.reset()
重置环境,回到初始状态。
渲染环境
env.render()
渲染当前环境,可视化显示
环境执行一步
env.step():
step()用于执行一个动作,最后返回一个元组(observation, reward, done, info)
observation (object): 智能体执行动作a后的状态,也就是所谓的“下一步状态s’ ”
reward (浮点数) : 智能体执行动作a后获得的奖励
done (布尔值): 判断episode是否结束,即s’是否是最终状态?是,则done=True;否,则done=False。
info (字典): 一些辅助诊断信息(有助于调试,也可用于学习),一般用不到。
列出所有环境
envs
from gym import envs
names = [env.id for env in envs.registry.all()]
print('\n'.join(names))
- 1
- 2
- 3
案例:出租车问题
下面通过gym来生成并可视化出租车问题(Taxi-v2)
可视化环境
import gym
# 生成仿真环境
env = gym.make('Taxi-v2') # 这里若不存在Taxi-v2,可以改为Taxi-v3
# 重置仿真环境
obs = env.reset()
# 渲染环境当前状态
env.render()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
列出状态数量和动作数量
m = env.observation_space.n # size of the state space
n = env.action_space.n # size of action space
print("出租车问题状态数量为{:d},动作数量为{:d}。".format(m, n))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
出租车问题状态数量为500,动作数量为6。
规则解释
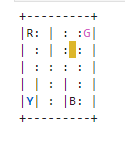
图上有四个位置:R,G,B,Y,蓝色代表乘客当前位置(上车位置),红色代表乘客目的地(下车位置),这两个位置会在四个位置在中随机选取。黄色框代表出租车,它会在广场任意位置随机生成。图中,竖线代表不可穿越的墙壁,虚线代表可以穿过的马路。当出租车接上乘客,再将乘客送往目的地之后,游戏结束。
动作:
有6个离散的确定性动作:
- 0:向南移动
- 1:向北移动
- 2:向东移动
- 3:向西移动
- 4:乘客上车
- 5:乘客下车
奖励:
每次行动奖励-1,解除乘客安全奖励+20。非法执行“载客/落客”行为的,奖励-10。
颜色:
- 蓝色:乘客
- 洋红:目的地
- 黄色:空出租车
- 绿色:出租车满座
状态空间:
状态空间表示为:
(出租车行、出租车列、乘客位置、目的地)
英文官方解释:
The Taxi Problem
from "Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning with the MAXQ Value Function Decomposition"
by Tom Dietterich
Description:
There are four designated locations in the grid world indicated by R(ed), B(lue), G(reen), and Y(ellow). When the episode starts, the taxi starts off at a random square and the passenger is at a random location. The taxi drive to the passenger's location, pick up the passenger, drive to the passenger's destination (another one of the four specified locations), and then drop off the passenger. Once the passenger is dropped off, the episode ends.
Observations:
There are 500 discrete states since there are 25 taxi positions, 5 possible locations of the passenger (including the case when the passenger is the taxi), and 4 destination locations.
MAP = [
"+---------+",
"|R: | : :G|",
"| : : : : |",
"| : : : : |",
"| | : | : |",
"|Y| : |B: |",
"+---------+",
]
Actions:
There are 6 discrete deterministic actions:
- 0: move south
- 1: move north
- 2: move east
- 3: move west
- 4: pickup passenger
- 5: dropoff passenger
Rewards:
There is a reward of -1 for each action and an additional reward of +20 for delievering the passenger. There is a reward of -10 for executing actions "pickup" and "dropoff" illegally.
Rendering:
- blue: passenger
- magenta: destination
- yellow: empty taxi
- green: full taxi
- other letters (R, G, B and Y): locations for passengers and destinations
actions:
- 0: south
- 1: north
- 2: east
- 3: west
- 4: pickup
- 5: dropoff
state space is represented by:
(taxi_row, taxi_col, passenger_location, destination)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
2022.4.10更
程序代码
Q学习实际上就是离轨策略的时序差分(TD)方法,相关的理论看参考本专栏的这篇博文【强化学习】迷宫寻宝:Sarsa和Q-Learning
完整代码:
import gym
import numpy as np
# 生成仿真环境
env = gym.make('Taxi-v3')
# 重置仿真环境
obs = env.reset()
# 渲染环境当前状态
env.render()
m = env.observation_space.n # size of the state space
n = env.action_space.n # size of action space
# Intialize the Q-table and hyperparameters
# Q表,大小为 m*n
Q = np.zeros([m, n])
# 回报的折扣率
gamma = 0.97
# 分幕式训练中最大幕数
max_episode = 1000
# 每一幕最长步数
max_steps = 100
# 学习率参数
alpha = 0.7
# 随机探索概率
epsilon = 0.3
for i in range(max_episode):
# Start with new environment
s = env.reset()
done = False
counter = 0
for _ in range(max_steps):
# Choose an action using epsilon greedy policy
p = np.random.rand()
# 请根据 epsilon-贪婪算法 选择动作 a
# p > epsilon 或尚未学习到某个状态的价值时,随机探索
# 其它情况,利用已经觉得的价值函数进行贪婪选择 (np.argmax)
if p > epsilon:
a = env.action_space.sample() # 随机探索
else:
Q_list = Q[s, :]
maxQ = np.max(Q_list)
action_list = np.where(Q_list == maxQ)[0] # maxQ可能对应多个action
a = np.random.choice(action_list)
# env.step(action) 根据所选动作action执行一步
# 返回新的状态、回报、以及是否完成
s_new, r, done, _ = env.step(a)
# 请根据贝尔曼方程,更新Q表 (np.max)
if done:
Q[s, a] = (1 - alpha) * Q[s, a] + alpha * r # 无下一个状态的情况
else:
Q[s, a] = (1 - alpha) * Q[s, a] + alpha * (r + gamma * np.max(Q[s_new, :]))
print(Q[s, a], r)
s = s_new
if done:
break
s = env.reset()
done = False
env.render()
# Test the learned Agent
for i in range(max_steps):
a = np.argmax(Q[s,:])
s, _, done, _ = env.step(a)
env.render()
if done:
break
rewards = []
for _ in range(100):
s = env.reset()
done = False
# Test the learned Agent
for i in range(max_steps):
a = np.argmax(Q[s,:])
s, r, done, _ = env.step(a)
rewards.append(r)
if done:
break
r_mean = np.mean(rewards)
r_var = np.var(rewards)
print("平均回报为{},回报的方差为{}。".format(r_mean, r_var))
env.close()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
文章来源: zstar.blog.csdn.net,作者:zstar-_,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:zstar.blog.csdn.net/article/details/121464508
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)