HDU 2586 How far away?(LCA使用详解)
题目:
Description
Input
For each test case,in the first line there are two numbers n(2<=n<=40000) and m (1<=m<=200),the number of houses and the number of queries. The following n-1 lines each consisting three numbers i,j,k, separated bu a single space, meaning that there is a road connecting house i and house j,with length k(0<k<=40000).The houses are labeled from 1 to n.
Next m lines each has distinct integers i and j, you areato answer the distance between house i and house j.
Output
Sample Input
2 3 2 1 2 10 3 1 15 1 2 2 3 2 2 1 2 100 1 2 2 1
Sample Output
10 25 100 100
题意:
n个房子用n-1条路连接起来(也就是一棵树),对于每一个询问,
求出2个房子直接的线路距离
思路:
这个题目只要建立一个树,然后查询任意2个点之间的距离,没有更新操作,所以可以用LCA来做。
LCA就是寻找最近公共祖先,这有什么用呢?
这是因为有一个性质,假设B和C的最近公共祖先是A,那么对于整个树的根节点D,
都有:|BD|+|CD|-|AD|*2=|BC|
也就是说,只要事先求出所有点到D的距离dist(dist的大小为n),
然后对于输入的B和C,只需要求出最近公共祖先,即可利用上式得到答案。
步骤:
1,存边
每次输入1条边,把2个点都存入对方的儿子列表中
因为儿子的数量未知,但是总数是2n-2,所以用向量数组v来存比较合适。(v的大小为n)
2,建树
建树的方法有很多,而且n个点都是可以用来当做根节点的。
这里我采用的是以第一个节点作为根节点,利用深度优先搜索建树
因为在计算dist之前需要找到根节点,所以需要1个数组fa记录父亲的标号(fa的大小为n)
3,深度优先搜索
既然有儿子列表,那么就可以深度优先搜索了。
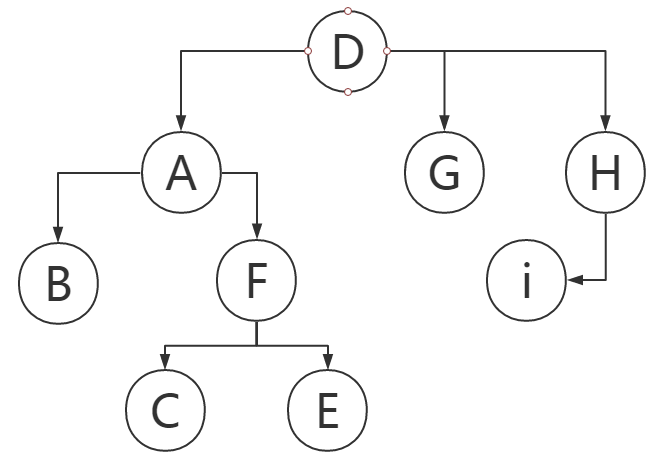
利用深度优先,把树映射到一维数组,这是哈希的一种。
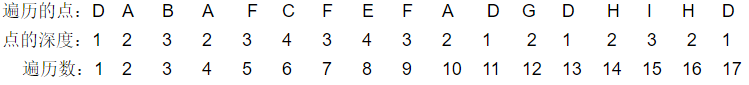
得到这个表有什么用呢?
也不知道是哪个神人想出来的,仅用这个表就可以得到最近公共祖先。
比如B的遍历数为3,C的遍历数为6,从3到6,深度依次为3 2 3 4,
最小的是2,对应的是A,所以A就是B和C的最近公共祖先。
注意,遍历数不一定是唯一的,比如求A和I的最近公共祖先,A有3个不同的遍历数,
但是不管选哪个,结果都是一样的。
所以说,只需要用动态规划的RMQ方法求出区间的最小值,即可求出公共祖先。
4,空间分析
首先,我们需要对每个点存1个遍历数,任选1个存起来即可。(visitn的大小为n)
然后,我们还需要把所有的遍历数对应的是哪个点存起来。
那么,一共有多少个遍历数呢?
规律很明显,总结如下:1个叶子节点只有1个遍历数,每个节点的遍历数等于出度加1
所以遍历数一共有:节点总数+出度总数=n+n-1(visitnum的大小为n+n-1)
(mins第一个维度的大小为n+n-1,第二个维度约为log2(n)+1)
上面的9个节点就有17个遍历数。
5,计算每个点到根节点的距离。
visit函数是一个递归调用的函数,用来实现深度优先搜索。
搜索的过程中,除了要计算visitn和visitnum,还要计算deep和dist(deep的大小为n)
(至此,7个数组的用途和大小都用蓝色粗体标注了)
deep和dist都可以利用递归的参数d和dis非常方便的计算出来。
6,RMQ
用RMQ求的是什么,这个倒是不要搞错了。
RMQ求的是visitnum数组的一段区间中,拥有最小deep的那个点对应的visitnum
而不是求deep的最小值,也不是求visitnum的最小值。
7,LCA
这个和RMQ对应,求的是visitnum数组的一段区间中,拥有最小deep的那个点对应的visitnum。
只需要根据visitnum便可知道到底哪个点是最近公共祖先
8,查询
输入x,y,取出他们的遍历数visitn,由此求出他们的最近公共祖先。
需要注意的是,因为遍历数有很多个,随便取一个存到visitn数组中,
那么x和y的遍历数谁大谁小就完全不知道了,需要判断。
代码:
-
#include<iostream>
-
#include<vector>
-
using namespace std;
-
-
struct node
-
{
-
int son;
-
int distance;
-
};
-
-
int n;
-
vector<node>v[40001];//存儿子标号
-
int deep[40001];//每个点的深度
-
int visitnum[80001];//遍历数是2*n-1
-
int visitn[40001];//每个点的任意一个遍历数
-
int vnum;
-
int mins[80001][18]; //区间最小值
-
int dist[40001]; //每个点到祖先的距离distance
-
int fa[40001];
-
-
void visit(int m, int d, int dis) //遍历重编号、计算distance
-
{
-
vector<node>::iterator p;
-
deep[m] = d;
-
dist[m] = dis;
-
for (p = v[m].begin(); p != v[m].end(); p++)
-
{
-
if (fa[(*p).son]>-1)continue;
-
fa[(*p).son] = m;
-
visitnum[vnum++] = m; //存入访问的第vnum个点是哪个点
-
visit((*p).son, d + 1, dis + (*p).distance);
-
}
-
visitn[m] = vnum; //注意这2句的顺序
-
visitnum[vnum++] = m;
-
}
-
-
void rmq() //计算区间最小值
-
{
-
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n - 1; i++)mins[i][0] = visitnum[i];
-
for (int j = 1; (1 << j) <= 2 * n - 1; j++)
-
{
-
for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n - 1; i++)
-
{
-
mins[i][j] = mins[i][j - 1];
-
int k = i + (1 << (j - 1));
-
if (k <= 2 * n - 1 && deep[mins[i][j]] > deep[mins[k][j - 1]])
-
mins[i][j] = mins[k][j - 1];
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
-
int lca(int x, int y) //求最近公共祖先
-
{
-
x = visitn[x], y = visitn[y];
-
if (x > y)x ^= y ^= x ^= y;
-
int j = 0;
-
while ((1 << j) <= y - x + 1)j++;
-
j--;
-
int min = mins[y + 1 - (1 << j)][j];
-
if (deep[min] > deep[mins[x][j]])min = mins[x][j];
-
return min;
-
}
-
-
int main()
-
{
-
int t, m, x, y, l;
-
cin >> t;
-
while (t--)
-
{
-
cin >> n >> m;
-
vnum = 1;
-
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
-
{
-
v[i].clear(); //初始化
-
fa[i] = -1;
-
}
-
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
-
{
-
scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &l);
-
node nod1, nod2;
-
nod1.distance = l, nod1.son = y;
-
v[x].insert(v[x].end(), nod1);
-
nod2.distance = l, nod2.son = x;
-
v[y].insert(v[y].end(), nod2);
-
}
-
fa[1] = 1;
-
visit(1, 1, 0);
-
rmq();
-
while (m--)
-
{
-
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
-
printf("%d\n", dist[x] + dist[y] - dist[lca(x, y)] * 2);
-
}
-
}
-
return 0;
-
}
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:csuzhucong,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/nameofcsdn/article/details/52230548
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)