Android进程间通信之AIDL工作原理初探
我们新建了AIDL文件后,再build一下项目,就会生成编译后的AIDL,如:
// IMyAidlInterface.aidl
package com.wong.remoteservice;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
interface IMyAidlInterface { // 服务端数据 String getString();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
编译后得到的 IMyAidlInterface.java:
/*
* This file is auto-generated. DO NOT MODIFY.
*/
package com.wong.remoteservice;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
public interface IMyAidlInterface extends android.os.IInterface
{
/** Default implementation for IMyAidlInterface. */
public static class Default implements com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface
{ // 服务端数据 @Override public java.lang.String getString() throws android.os.RemoteException { return null; } @Override public android.os.IBinder asBinder() { return null; }
}
/** Local-side IPC implementation stub class. */
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface
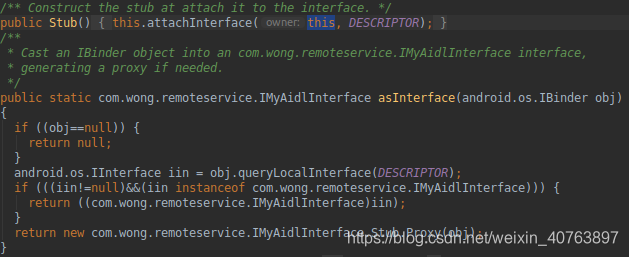
{ private static final java.lang.String DESCRIPTOR = "com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface"; /** Construct the stub at attach it to the interface. */ public Stub() { this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR); } /** * Cast an IBinder object into an com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface interface, * generating a proxy if needed. */ public static com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj) { if ((obj==null)) { return null; } android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR); if (((iin!=null)&&(iin instanceof com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface))) { return ((com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface)iin); } return new com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface.Stub.Proxy(obj); } @Override public android.os.IBinder asBinder() { return this; } @Override public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException { java.lang.String descriptor = DESCRIPTOR; switch (code) { case INTERFACE_TRANSACTION: { reply.writeString(descriptor); return true; } case TRANSACTION_getString: { data.enforceInterface(descriptor); java.lang.String _result = this.getString(); reply.writeNoException(); reply.writeString(_result); return true; } default: { return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags); } } } private static class Proxy implements com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface { private android.os.IBinder mRemote; Proxy(android.os.IBinder remote) { mRemote = remote; } @Override public android.os.IBinder asBinder() { return mRemote; } public java.lang.String getInterfaceDescriptor() { return DESCRIPTOR; } // 服务端数据 @Override public java.lang.String getString() throws android.os.RemoteException { android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain(); android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain(); java.lang.String _result; try { _data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR); boolean _status = mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_getString, _data, _reply, 0); if (!_status && getDefaultImpl() != null) { return getDefaultImpl().getString(); } _reply.readException(); _result = _reply.readString(); } finally { _reply.recycle(); _data.recycle(); } return _result; } public static com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface sDefaultImpl; } static final int TRANSACTION_getString = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 0); public static boolean setDefaultImpl(com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface impl) { if (Stub.Proxy.sDefaultImpl == null && impl != null) { Stub.Proxy.sDefaultImpl = impl; return true; } return false; } public static com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface getDefaultImpl() { return Stub.Proxy.sDefaultImpl; }
}
// 服务端数据 public java.lang.String getString() throws android.os.RemoteException;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
我们来仔细分析一下,这个编译后的AIDL。整体结构是这样的:
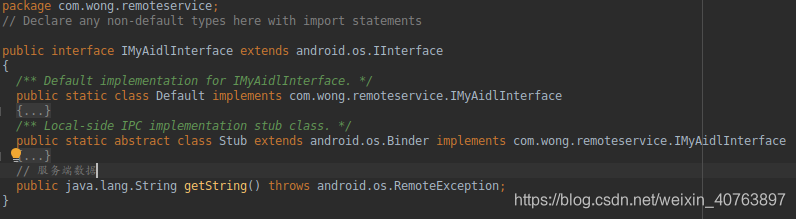
IMyAidlInterface继承了IInterface接口,IInterface接口:
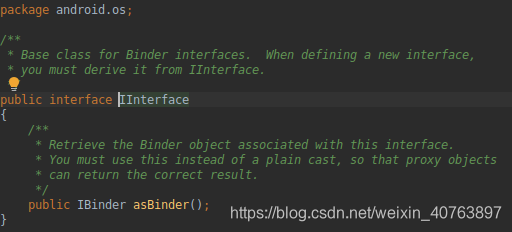
IBinder是用于远程对象的基础接口。轻量级远程调用机制的核心部分,为提高在进程内和跨进程调用的性能而设计。 这个接口描述了与远程对象交互使用的抽象协议,不要直接实现这个接口,而是通过继承Binder来完成。在Android中,实现远程对象(服务)的调用,就是靠Binder来实现的。
(1)Default类,提供了默认实现。
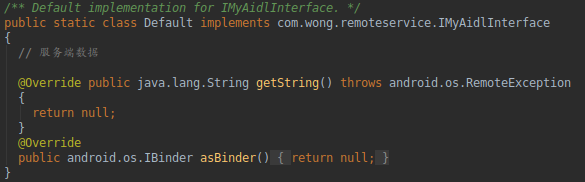
(2)我们自己定义的接口getString,这个接口要在服务端实现,最终也是通过这个接口向外提供服务的。
(3)为了获得实现了getString接口的对象,我们现在要介绍最重要的Stub类:
/** Local-side IPC implementation stub class. */
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface
{ private static final java.lang.String DESCRIPTOR = "com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface"; /** Construct the stub at attach it to the interface. */ public Stub() { this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR); } /** * Cast an IBinder object into an com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface interface, * generating a proxy if needed. */ public static com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj) { if ((obj==null)) { return null; } android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR); if (((iin!=null)&&(iin instanceof com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface))) { return ((com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface)iin); } return new com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface.Stub.Proxy(obj); } @Override public android.os.IBinder asBinder() { return this; } @Override public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException { java.lang.String descriptor = DESCRIPTOR; switch (code) { case INTERFACE_TRANSACTION: { reply.writeString(descriptor); return true; } case TRANSACTION_getString: { data.enforceInterface(descriptor); java.lang.String _result = this.getString(); reply.writeNoException(); reply.writeString(_result); return true; } default: { return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags); } } } private static class Proxy implements com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface { private android.os.IBinder mRemote; Proxy(android.os.IBinder remote) { mRemote = remote; } @Override public android.os.IBinder asBinder() { return mRemote; } public java.lang.String getInterfaceDescriptor() { return DESCRIPTOR; } // 服务端数据 @Override public java.lang.String getString() throws android.os.RemoteException { android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain(); android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain(); java.lang.String _result; try { _data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR); boolean _status = mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_getString, _data, _reply, 0); if (!_status && getDefaultImpl() != null) { return getDefaultImpl().getString(); } _reply.readException(); _result = _reply.readString(); } finally { _reply.recycle(); _data.recycle(); } return _result; } public static com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface sDefaultImpl; } static final int TRANSACTION_getString = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 0); public static boolean setDefaultImpl(com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface impl) { if (Stub.Proxy.sDefaultImpl == null && impl != null) { Stub.Proxy.sDefaultImpl = impl; return true; } return false; } public static com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface getDefaultImpl() { return Stub.Proxy.sDefaultImpl; }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
Stub的结构如下:
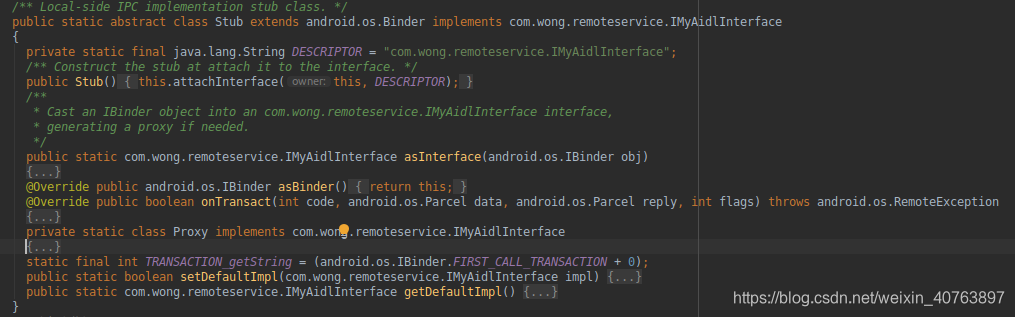
- Stub类是一个抽象类实现了IMyAidlInterface接口,但Stub并不实现getString这个方法,留给真正要对外服务的子类来实现。
- Stub类继承了Binder,使得Stub具有访问远程对象的能力。
- asInterface接口:

在客户端获取服务端的数据是这样获得的:
private IMyAidlInterface myBind;
private ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection() { @Override public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) { myBind = IMyAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface(service); } @Override public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) { } };
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
由调用方式IMyAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface(service)可知,Stub没有被初始化,因此执行了:
return new com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface.Stub.Proxy(obj);
- 1
返回了一个代理Proxy对象,那么我们看看定义在Stub类里的内部类Proxy:
private static class Proxy implements com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface { private android.os.IBinder mRemote; Proxy(android.os.IBinder remote) { mRemote = remote; } @Override public android.os.IBinder asBinder() { return mRemote; } public java.lang.String getInterfaceDescriptor() { return DESCRIPTOR; } // 服务端数据 @Override public java.lang.String getString() throws android.os.RemoteException { android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain(); android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain(); java.lang.String _result; try { _data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR); boolean _status = mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_getString, _data, _reply, 0); if (!_status && getDefaultImpl() != null) { return getDefaultImpl().getString(); } _reply.readException(); _result = _reply.readString(); } finally { _reply.recycle(); _data.recycle(); } return _result; } public static com.wong.remoteservice.IMyAidlInterface sDefaultImpl; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
从这个代理可知,当我们要调用getString方法获得服务器数据时,它就会通过Binder对象的transact,向服务端请求数据。通过这种方式来完成跨进程的通信。
boolean _status = mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_getString, _data, _reply, 0);
- 1
以上就是关于AIDL的通信原理的一部分知识。
谢谢阅读
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:WongKyunban,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/weixin_40763897/article/details/103867859
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)