大厂面试真题:Spring中Bean的生命周期
前言
这其实是一道面试题,是我在面试百度的时候被问到的,当时没有答出来(因为自己真的很菜),后来在网上寻找答案,看到也是一头雾水,直到看到了《Spring in action》这本书,书上有对Bean声明周期的大致解释,但是没有代码分析,所以就自己上网寻找资料,一定要把这个Bean生命周期弄明白!
网上大部分都是验证的Bean 在面试问的生命周期,其实查阅JDK还有一个完整的Bean生命周期,这同时也验证了书是具有片面性的,最fresh 的资料还是查阅原始JDK!!!
一、Bean 的完整生命周期
在传统的Java应用中,bean的生命周期很简单,使用Java关键字 new 进行Bean 的实例化,然后该Bean 就能够使用了。一旦bean不再被使用,则由Java自动进行垃圾回收。
相比之下,Spring管理Bean的生命周期就复杂多了,正确理解Bean 的生命周期非常重要,因为Spring对Bean的管理可扩展性非常强,下面展示了一个Bean的构造过程
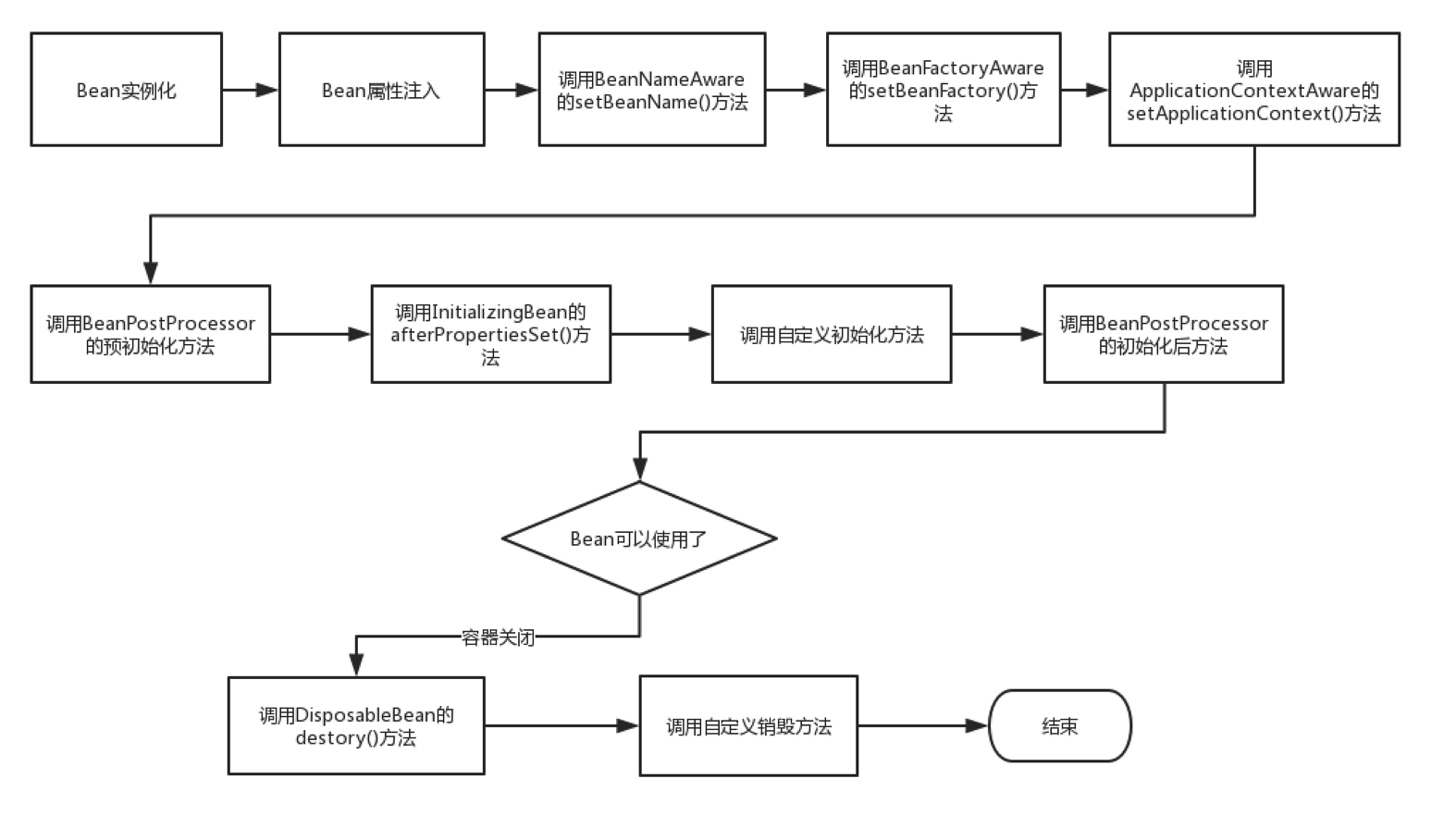
Bean 的生命周期
如上图所示,Bean 的生命周期还是比较复杂的,下面来对上图每一个步骤做文字描述:
- Spring启动,查找并加载需要被Spring管理的bean,进行Bean的实例化
- Bean实例化后对将Bean的引入和值注入到Bean的属性中
- 如果Bean实现了BeanNameAware接口的话,Spring将Bean的Id传递给setBeanName()方法
- 如果Bean实现了BeanFactoryAware接口的话,Spring将调用setBeanFactory()方法,将BeanFactory容器实例传入
- 如果Bean实现了ApplicationContextAware接口的话,Spring将调用Bean的setApplicationContext()方法,将bean所在应用上下文引用传入进来
- 如果Bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,Spring就将调用他们的postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法。
- 如果Bean 实现了InitializingBean接口,Spring将调用他们的afterPropertiesSet()方法。类似的,如果bean使用init-method声明了初始化方法,该方法也会被调用
- 如果Bean 实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,Spring就将调用他们的postProcessAfterInitialization()方法。
- 此时,Bean已经准备就绪,可以被应用程序使用了。他们将一直驻留在应用上下文中,直到应用上下文被销毁。
- 如果bean实现了DisposableBean接口,Spring将调用它的destory()接口方法,同样,如果bean使用了destory-method 声明销毁方法,该方法也会被调用。
上面是Spring 中Bean的核心接口和生命周期,面试回答上述过程已经足够了。但是翻阅JavaDoc文档发现除了以上接口外,还有另外的初始化过程涉及的接口:
摘自org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory, 全部相关接口如下,上述已有的就不用着重标注,把额外的相关接口着重标注下
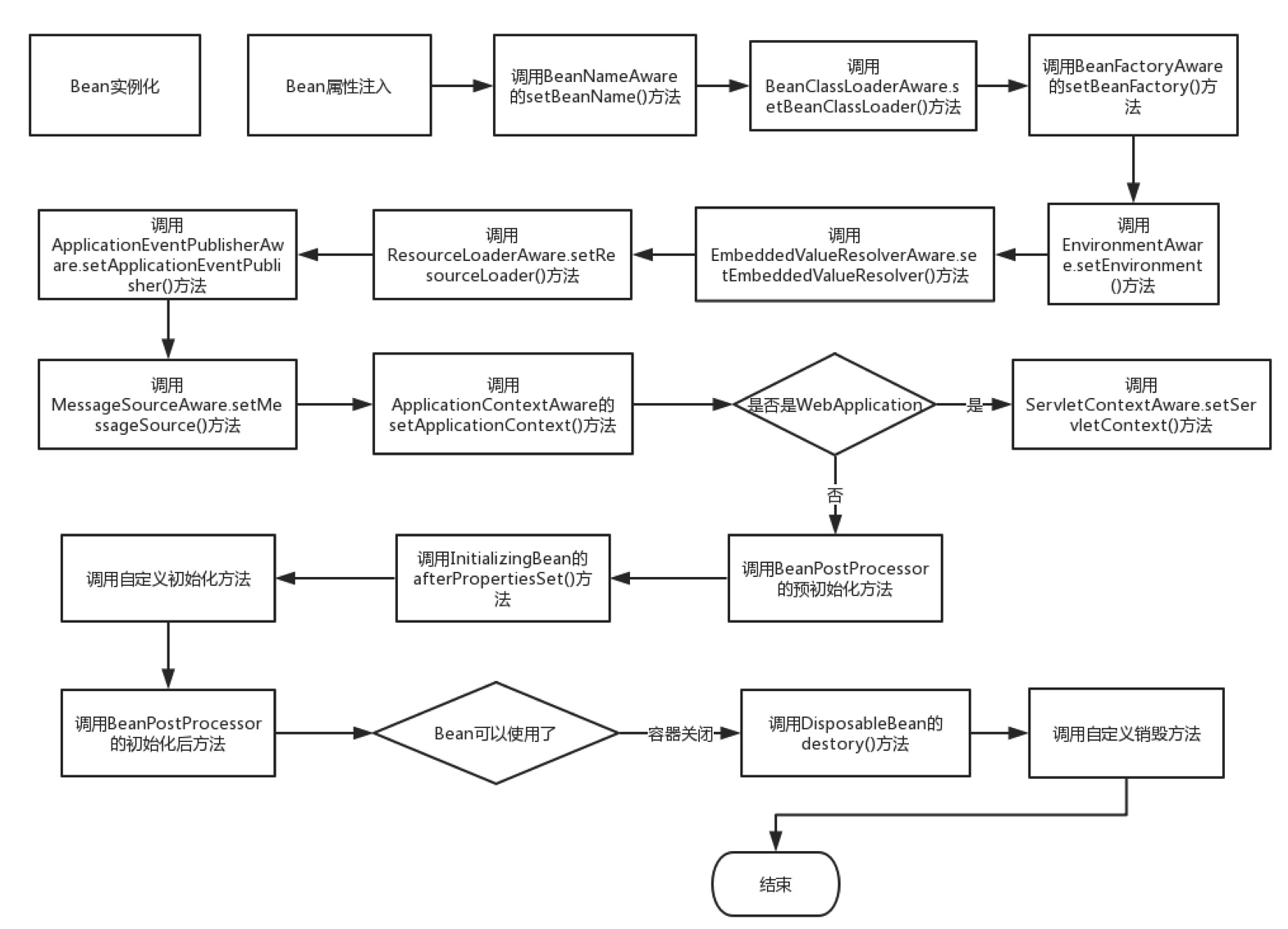
Bean 完整的生命周期
文字解释如下:
————————————初始化————————————
- BeanNameAware.setBeanName() 在创建此bean的bean工厂中设置bean的名称,在普通属性设置之后调用,在InitializinngBean.afterPropertiesSet()方法之前调用
BeanClassLoaderAware.setBeanClassLoader(): 在普通属性设置之后,InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()之前调用- BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory() : 回调提供了自己的bean实例工厂,在普通属性设置之后,在InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()或者自定义初始化方法之前调用
EnvironmentAware.setEnvironment(): 设置environment在组件使用时调用EmbeddedValueResolverAware.setEmbeddedValueResolver(): 设置StringValueResolver 用来解决嵌入式的值域问题ResourceLoaderAware.setResourceLoader(): 在普通bean对象之后调用,在afterPropertiesSet 或者自定义的init-method 之前调用,在 ApplicationContextAware 之前调用。ApplicationEventPublisherAware.setApplicationEventPublisher(): 在普通bean属性之后调用,在初始化调用afterPropertiesSet 或者自定义初始化方法之前调用。在 ApplicationContextAware 之前调用。MessageSourceAware.setMessageSource(): 在普通bean属性之后调用,在初始化调用afterPropertiesSet 或者自定义初始化方法之前调用,在 ApplicationContextAware 之前调用。- ApplicationContextAware.setApplicationContext(): 在普通Bean对象生成之后调用,在InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet之前调用或者用户自定义初始化方法之前。在ResourceLoaderAware.setResourceLoader,ApplicationEventPublisherAware.setApplicationEventPublisher,MessageSourceAware之后调用。
ServletContextAware.setServletContext(): 运行时设置ServletContext,在普通bean初始化后调用,在InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet之前调用,在 ApplicationContextAware 之后调用注:是在WebApplicationContext 运行时- BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization() : 将此BeanPostProcessor 应用于给定的新bean实例 在任何bean初始化回调方法(像是InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet或者自定义的初始化方法)之前调用。这个bean将要准备填充属性的值。返回的bean示例可能被普通对象包装,默认实现返回是一个bean。
- BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization() : 将此BeanPostProcessor 应用于给定的新bean实例 在任何bean初始化回调方法(像是InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet或者自定义的初始化方法)之后调用。这个bean将要准备填充属性的值。返回的bean示例可能被普通对象包装
- InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet(): 被BeanFactory在设置所有bean属性之后调用(并且满足BeanFactory 和 ApplicationContextAware)。
————————————销毁————————————
在BeanFactory 关闭的时候,Bean的生命周期会调用如下方法:
DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeDestruction(): 在销毁之前将此BeanPostProcessor 应用于给定的bean实例。能够调用自定义回调,像是DisposableBean 的销毁和自定义销毁方法,这个回调仅仅适用于工厂中的单例bean(包括内部bean)- 实现了自定义的destory()方法
二、Bean 的生命周期验证
为了验证Bean生命周期的过程,有两种形式:一种是为面试而准备的,一种是为了解全过程而准备的,下面来看代码:
- Book.class
public class Book implements BeanNameAware,BeanFactoryAware, ApplicationContextAware,InitializingBean,DisposableBean { private String bookName; public Book(){ System.out.println("Book Initializing "); } public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { System.out.println("Book.setBeanFactory invoke"); } public void setBeanName(String name) { System.out.println("Book.setBeanName invoke"); } public void destroy() throws Exception { System.out.println("Book.destory invoke"); } public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { System.out.println("Book.afterPropertiesSet invoke"); } public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { System.out.println("Book.setApplicationContext invoke"); } public String getBookName() { return bookName; } public void setBookName(String bookName) { this.bookName = bookName; System.out.println("setBookName: Book name has set."); } public void myPostConstruct(){ System.out.println("Book.myPostConstruct invoke"); } // 自定义初始化方法 @PostConstruct public void springPostConstruct(){ System.out.println("@PostConstruct"); } public void myPreDestory(){ System.out.println("Book.myPreDestory invoke"); System.out.println("---------------destroy-----------------"); } // 自定义销毁方法 @PreDestroy public void springPreDestory(){ System.out.println("@PreDestory"); } @Override protected void finalize() throws Throwable { System.out.println("------inside finalize-----"); }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 自定义实现BeanPostProcessor 的MyBeanPostProcessor:
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { // 容器加载的时候会加载一些其他的bean,会调用初始化前和初始化后方法 // 这次只关注book(bean)的生命周期 public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if(bean instanceof Book){ System.out.println("MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization"); } return bean; } public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if(bean instanceof Book){ System.out.println("MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization"); } return bean; }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 在resources 目录下新建Bean-Lifecycle.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 扫描bean --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.bean.lifecycle"/> <!-- 实现了用户自定义初始化和销毁方法 --> <bean id="book" class="com.bean.lifecycle.Book" init-method="myPostConstruct" destroy-method="myPreDestory"> <!-- 注入bean 属性名称 --> <property name="bookName" value="thingking in java" /> </bean> <!--引入自定义的BeanPostProcessor--> <bean class="com.bean.lifecycle.MyBeanPostProcessor"/>
</beans>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 做一个启动类的测试,新建SpringBeanLifecycleApplication
public class SpringBeanLifecycleApplication { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 为面试而准备的Bean生命周期加载过程 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Bean-Lifecycle.xml"); Book book = (Book)context.getBean("book"); System.out.println("Book name = " + book.getBookName()); ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) context).destroy(); }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
启动测试,输出结果如下:
Book Initializing
setBookName: Book name has set.
Book.setBeanName invoke
Book.setBeanFactory invoke
Book.setApplicationContext invoke
MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization
@PostConstruct
Book.afterPropertiesSet invoke
Book.myPostConstruct invoke
MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization
Book name = thingking in java
@PreDestory
Book.destory invoke
Book.myPreDestory invoke
---------------destroy-----------------
- 为了验证Bean完整的生命周期,需要新建一个SubBookClass 继承Book类
public class SubBookClass extends Book implements BeanClassLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware,EmbeddedValueResolverAware,ResourceLoaderAware, ApplicationEventPublisherAware,MessageSourceAware{ private String bookSystem; public String getBookSystem() { return bookSystem; } public void setBookSystem(String bookSystem) { System.out.println("设置BookSystem 的属性值"); this.bookSystem = bookSystem; } public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) { System.out.println("SubBookClass.setBeanClassLoader() 方法被调用了"); } public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher) { System.out.println("SubBookClass.setApplicationEventPublisher() 方法被调用了"); } public void setEmbeddedValueResolver(StringValueResolver resolver) { System.out.println("SubBookClass.setEmbeddedValueResolver() 方法被调用了"); } public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) { System.out.println("SubBookClass.setEnvironment() 方法被调用了"); } public void setMessageSource(MessageSource messageSource) { System.out.println("SubBookClass.setMessageSource() 方法被调用了"); } public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) { System.out.println("SubBookClass.setResourceLoader() 方法被调用了"); }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
上述SubBookClass类与Book是
互补关系。
- 新建一个SubBean-Lifecycle.xml,注入SubBookClass
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <bean id="bookClass" class="com.bean.lifecycle.SubBookClass" init-method="myPostConstruct" destroy-method="myPreDestory"> <property name="bookSystem" value="Java System" /> </bean> <bean class="com.bean.lifecycle.MyBeanPostProcessor"/>
</beans>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 完整的SpringBeanLifecycleApplication 如下:
public class SpringBeanLifecycleApplication { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 为面试而准备的Bean生命周期加载过程 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Bean-Lifecycle.xml"); Book book = (Book)context.getBean("book"); System.out.println("Book name = " + book.getBookName()); ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) context).destroy(); // 完整的加载过程,当然了解的越多越好 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("SubBean-Lifecycle.xml"); SubBookClass subBookClass = (SubBookClass) applicationContext.getBean("bookClass"); System.out.println("BookSystemName = " + subBookClass.getBookSystem()); ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) applicationContext).registerShutdownHook(); }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
输出完整的结果:
Book Initializing
setBookName: Book name has set.
Book.setBeanName invoke
Book.setBeanFactory invoke
Book.setApplicationContext invoke
MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization
@PostConstruct
Book.afterPropertiesSet invoke
Book.myPostConstruct invoke
MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization
Book name = thingking in java
@PreDestory
Book.destory invoke
Book.myPreDestory invoke
---------------destroy-----------------
Book Initializing
设置BookSystem 的属性值
Book.setBeanName invoke
SubBookClass.setBeanClassLoader() 方法被调用了
Book.setBeanFactory invoke
SubBookClass.setEnvironment() 方法被调用了
SubBookClass.setEmbeddedValueResolver() 方法被调用了
SubBookClass.setResourceLoader() 方法被调用了
SubBookClass.setApplicationEventPublisher() 方法被调用了
SubBookClass.setMessageSource() 方法被调用了
Book.setApplicationContext invoke
MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization
Book.afterPropertiesSet invoke
Book.myPostConstruct invoke
MyBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization
BookSystemName = Java System
Book.destory invoke
Book.myPreDestory invoke
---------------destroy-----------------
后记:这篇文章是我翻阅各种书籍和从网上查找资料,包括国外一些网站从而得到的结论,记录下来,但是我没有发现Spring Bean的生命周期(非常详细) 这篇文章中InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter 这个类和工厂后置处理器接口方法,知道的大佬欢迎指教谢谢。
另外,添加我的微信 becomecxuan,加入每日一题群,每天一道面试题分享,更多内容请参见我的 Github,成为最好的 bestJavaer
我自己肝了六本 PDF,微信搜索「程序员cxuan」关注公众号后,在后台回复 cxuan ,领取全部 PDF,这些 PDF 如下
文章来源: cxuan.blog.csdn.net,作者:程序员cxuan,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:cxuan.blog.csdn.net/article/details/112598804
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者

评论(0)