华为CANN昇腾算子开发深度解析与实战
华为CANN算子开发深度解析
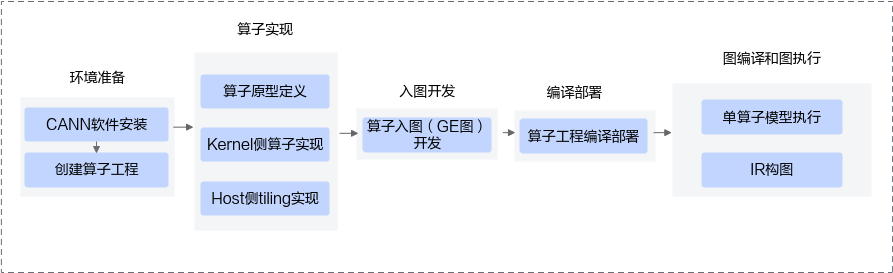
在深度学习模型加速中,算子是最核心的计算单元,而华为CANN框架为昇腾AI处理器提供了完整的算子开发与优化生态。CANN不仅允许开发者实现单个算子的高性能Kernel,还支持算子入图,通过GE(Graph Engine)在图模式下优化模型执行效率,减少内存占用,并支持多流并行和内存复用。
算子开发流程以工程化为基础:首先通过msOpGen创建算子工程,定义算子原型,包括输入、输出及属性信息;随后在Kernel端完成算子核心计算实现,并在Host端提供Tiling策略以适配硬件;最后,算子入图阶段需要额外提供Shape推导、DataType推导、ShapeRange推导以及数据依赖声明,实现算子在GE中的正确注册与执行。
以自定义加法算子为例,可以通过如下方式定义原型并注册算子入图:
namespace ops {
class AddCustom : public OpDef {
public:
AddCustom(const char* name) : OpDef(name)
{
this->Input("x")
.ParamType(REQUIRED)
.DataType({ge::DT_FLOAT16, ge::DT_FLOAT, ge::DT_INT32})
.Format({ge::FORMAT_ND, ge::FORMAT_ND, ge::FORMAT_ND});
this->Input("y")
.ParamType(REQUIRED)
.DataType({ge::DT_FLOAT16, ge::DT_FLOAT, ge::DT_INT32})
.Format({ge::FORMAT_ND, ge::FORMAT_ND, ge::FORMAT_ND});
this->Output("z")
.ParamType(REQUIRED)
.DataType({ge::DT_FLOAT16, ge::DT_FLOAT, ge::DT_INT32})
.Format({ge::FORMAT_ND, ge::FORMAT_ND, ge::FORMAT_ND});
// 图模式下推导函数绑定
this->SetInferShape(ge::InferShape);
this->SetInferShapeRange(ge::InferShapeRange);
this->SetInferDataType(ge::InferDataType);
// Tiling策略绑定
this->AICore()
.SetTiling(optiling::TilingFunc)
.AddConfig("ascendxxx"); // 替换为具体AI处理器型号
}
};
OP_ADD(AddCustom);
} // namespace ops
在图模式下,GE需要提前知道每个Tensor的Shape和DataType,以便进行静态内存分配和计算优化。加法算子输出DataType可直接与输入保持一致,推导函数示例:
namespace ge {
static graphStatus InferDataType(gert::InferDataTypeContext* context)
{
const auto inputDataType = context->GetInputDataType(0);
context->SetOutputDataType(0, inputDataType);
return ge::GRAPH_SUCCESS;
}
} // namespace ge
对于Shape推导,如果输出Shape与输入Shape相同,可使用Follow接口:
this->Output("y1")
.ParamType(REQUIRED)
.DataType({ge::DT_FLOAT, ge::DT_FLOAT})
.Format({ge::FORMAT_ND, ge::FORMAT_ND})
.Follow("x1", FollowType::SHAPE);
但对于依赖输入数据的算子,如Reshape,其输出Shape需要读取第二个输入Tensor的值,实现InferShape如下:
template<typename T>
ge::graphStatus ReshapeInferShapeImpl(
const T *reshape_dims, const gert::Shape &x_shape, gert::Shape &output_shape, int32_t reshape_rank)
{
constexpr T UNKNOWN_DIM = -1;
output_shape.SetDimNum(reshape_rank);
int64_t output_shapesize = 1;
size_t unknown_dim_idx = std::numeric_limits<size_t>::max();
for (int32_t i = 0; i < reshape_rank; i++) {
if (reshape_dims[i] != UNKNOWN_DIM) {
output_shape.SetDim(i, reshape_dims[i]);
output_shapesize *= reshape_dims[i];
} else {
output_shape.SetDim(i, 1);
unknown_dim_idx = i;
}
}
if (unknown_dim_idx == std::numeric_limits<size_t>::max() && output_shapesize == x_shape.GetShapeSize()) {
return ge::GRAPH_SUCCESS;
} else if (unknown_dim_idx != std::numeric_limits<size_t>::max() &&
x_shape.GetShapeSize() % output_shapesize == 0) {
output_shape.SetDim(unknown_dim_idx, x_shape.GetShapeSize() / output_shapesize);
return ge::GRAPH_SUCCESS;
}
return ge::GRAPH_FAILED;
}
ge::graphStatus InferShapeForReshape(InferShapeContext *context) {
const gert::Shape *x_shape = context->GetInputShape(0);
const gert::Tensor *shape_tensor = context->GetInputTensor(1);
gert::Shape *output_shape = context->GetOutputShape(0);
if (!x_shape || !shape_tensor || !output_shape) return ge::GRAPH_FAILED;
auto reshape_size = static_cast<int32_t>(shape_tensor->GetShapeSize());
if (reshape_tensor->GetDataType() == ge::DT_INT32) {
return ReshapeInferShapeImpl<int32_t>(shape_tensor->GetData<int32_t>(), *x_shape, *output_shape, reshape_size);
} else {
return ReshapeInferShapeImpl<int64_t>(shape_tensor->GetData<int64_t>(), *x_shape, *output_shape, reshape_size);
}
}
CANN还支持动态Shape场景,如Unique算子,其输出长度取决于输入去重结果。开发者需实现InferShapeRange来申请最大输出内存:
ge::graphStatus UniqueInferShapeRangeFunc(gert::InferShapeRangeContext *context) {
auto x_shape_range = context->GetInputShapeRange(0U);
auto y_shape_range = context->GetOutputShapeRange(0U);
auto x_max = x_shape_range->GetMax();
auto x_min = x_shape_range->GetMin();
y_shape_range->GetMax()->SetDimNum(1);
y_shape_range->GetMin()->SetDimNum(1);
int64_t x_dim = x_max->GetDim(0);
y_shape_range->GetMax()->SetDim(0, x_dim);
y_shape_range->GetMin()->SetDim(0, x_shape_range->GetMin());
auto idx_shape_range = context->GetOutputShapeRange(1U);
*(idx_shape_range->GetMax()) = *(x_shape_range->GetMax());
*(idx_shape_range->GetMin()) = *(x_shape_range->GetMin());
return ge::GRAPH_SUCCESS;
}
对于Optional或Dynamic类型输入,如DynamicRNNV3算子,实例化后索引可能不固定。开发者可通过以下方式获取对应输入Shape:
auto project_shape = context->GetOptionalInputShape(kProjectInputIndex);
auto dynamic_shape = context->GetDynamicInputShape(ir_index, relative_index);
通过这些机制,CANN能够支持复杂算子在图模式下的正确执行,并充分利用昇腾AI处理器的计算能力。
总结
总结来看,CANN算子开发强调工程化、静态分析和图模式优化。理解Shape/DataType推导、ShapeRange处理、数据依赖声明以及动态输入适配,是实现高性能自定义算子的核心。通过合理利用这些机制,开发者能够在昇腾硬件上实现高效、可扩展的神经网络计算,为AI模型加速提供坚实基础。
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)