支持多智能体协同的 LLM-MCP 调用架构与调度优化
支持多智能体协同的 LLM-MCP 调用架构与调度优化
随着大型语言模型(LLM, Large Language Model)的推理能力不断增强,它们在服务调度、函数调用甚至多智能体协同中的角色愈发重要。而微服务通信协议 MCP(Microservice Communication Protocol)作为服务注册与管理的核心机制,也在逐步向智能化调度过渡。本文将探讨 MCP 与 LLM 函数调用结合的架构设计思路,重点研究并行协作机制与负载调度策略,并提供示例代码说明。
1. 背景与动机
1.1 LLM 的函数调用能力兴起
现代 LLM(如 GPT-4、Claude、Gemini)已具备理解任务并自主调用函数的能力,支持:
- 工具函数自动匹配调用
- 参数结构化解析与响应生成
- 多步任务自动规划
这为 LLM 提供了一种“调用外部服务”的桥梁能力,逐步从文本生成向任务执行转变。
1.2 MCP 在微服务智能调度中的优势
MCP 强调服务元数据注册与心跳管理,能够:
- 动态发现/注销服务实例
- 通过注册中心调度请求
- 支持负载均衡与优雅降级
MCP 作为函数调用代理中间层,可有效管理 LLM 的“服务调用需求”。
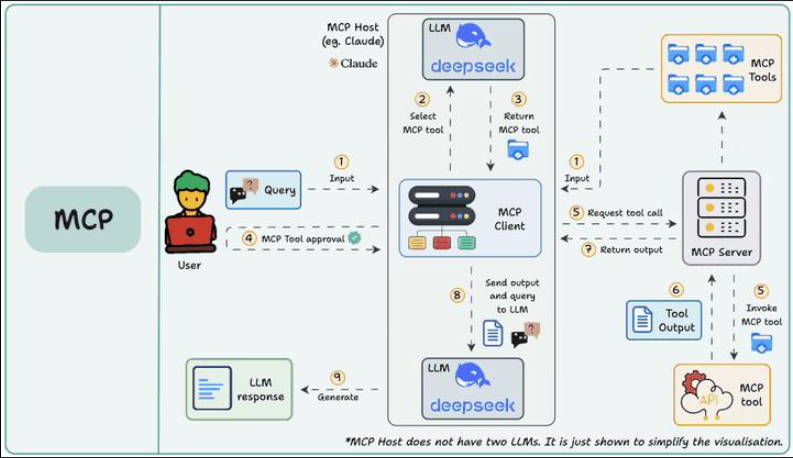
2. 架构设计:LLM + MCP 并行协作模型
2.1 模型框架
+---------+ +--------------+ +-------------+ +-------------+
| 用户 | <---> | LLM Core | ---> | MCP 服务注册 | ---> | 后端微服务 |
+---------+ +--------------+ +-------------+ +-------------+
| ↑
| |
+-----------------+ +--------------+
| Function Router | <-------- | 负载调度模块 |
+-----------------+ +--------------+
- LLM Core:通过自然语言识别任务意图与参数。
- MCP 服务注册:维护所有可调用函数的注册信息。
- Function Router:根据调用意图与参数路由最优服务。
- 负载调度模块:支持并发策略(RoundRobin、LeastLoad、Cost-aware等)。
2.2 并行调用示例
支持多个服务接口的并行协同,LLM 可同时请求不同处理单元(如图像识别、推荐服务)并在响应中融合结果。
3. 并行任务调度机制分析
3.1 常见策略
| 策略 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Round Robin | 顺序循环分发请求 |
| Least Load | 将任务分配至当前负载最小节点 |
| Cost-aware | 综合考虑响应时间、历史性能等权重 |
| Latency-aware | 以延迟反馈为主要调度依据 |
3.2 自定义调度器示例代码(Python)
以下示例展示一个支持 LLM 函数调用的服务注册与调度实现:
import random
from typing import List, Dict
class MCPRegistry:
def __init__(self):
self.services = {} # key: function_name, value: list of service instances
def register(self, function_name: str, instance: Dict):
self.services.setdefault(function_name, []).append(instance)
def discover(self, function_name: str) -> List[Dict]:
return self.services.get(function_name, [])
class LoadBalancer:
def __init__(self, strategy="round_robin"):
self.strategy = strategy
self.counter = {}
def select_instance(self, instances: List[Dict], function_name: str) -> Dict:
if not instances:
raise ValueError("No instances available")
if self.strategy == "round_robin":
idx = self.counter.get(function_name, 0) % len(instances)
self.counter[function_name] = idx + 1
return instances[idx]
elif self.strategy == "least_load":
return min(instances, key=lambda x: x.get("load", 0))
else:
return random.choice(instances)
注册服务:
registry = MCPRegistry()
registry.register("get_weather", {"url": "http://api.weather.com", "load": 0.3})
registry.register("get_weather", {"url": "http://api.weather2.com", "load": 0.6})
分配请求:
lb = LoadBalancer(strategy="least_load")
instances = registry.discover("get_weather")
selected = lb.select_instance(instances, "get_weather")
print("调用地址:", selected["url"])
4. LLM 与 MCP 函数调用集成实践
4.1 OpenAI Function Calling 示例
functions = [
{
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Get the current weather for a location",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {"type": "string"},
},
"required": ["location"]
}
}
]
# 使用函数提示词进行对话
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "What's the weather in Shanghai?"}],
functions=functions,
function_call="auto"
)
然后 LLM 自动调用 MCP 注册的“get_weather”服务。
4.2 并发请求(异步调用)
import asyncio
import aiohttp
async def call_service(instance):
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.get(instance["url"]) as resp:
return await resp.text()
async def main():
tasks = [call_service(i) for i in registry.discover("get_weather")]
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
print("结果融合:", results)
asyncio.run(main())
5. 多模态函数协作与 Agent 扩展
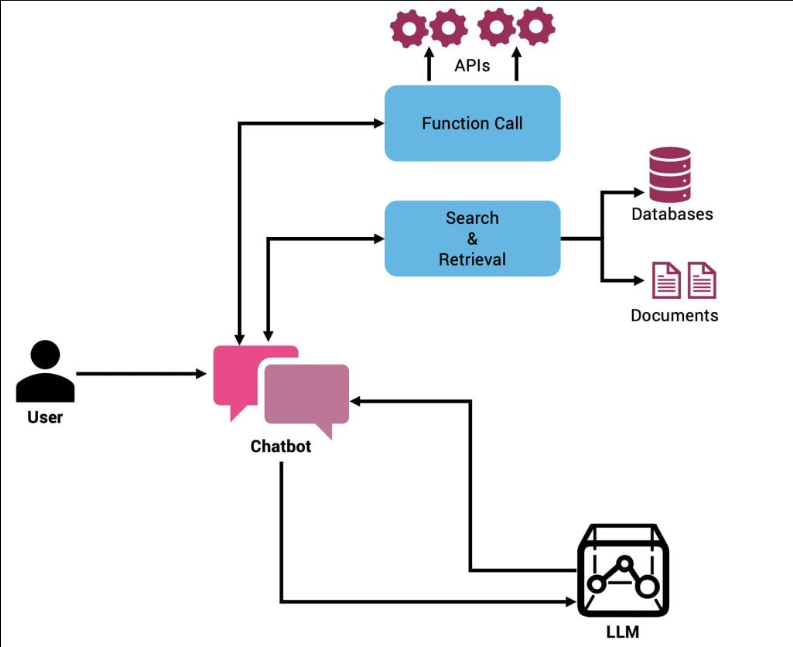
5.1 多模态协同架构
LLM 可同时调用:
get_image_analysis()图像分析函数get_weather()天气接口get_translation()翻译函数
通过 MCP 统一注册与调度,构建“智能函数网”。
5.2 与多 Agent 系统集成
每个 Agent 可注册自身函数接口至 MCP,实现:
- 专家型 Agent 接入
- 动态服务发布与卸载
- LLM 自主调度执行路径
6. 安全性与资源保护机制
6.1 并发限制与熔断策略
MCP 可集成如下机制:
- 最大调用阈值控制(Rate Limit)
- 重试/熔断机制(Circuit Breaker)
- 权重降级策略(基于优先级动态降级)
6.2 权限管理
函数调用前进行 token 鉴权,或将服务暴露给特定角色的 Agent 子系统,防止滥用。
7. 总结与展望
MCP 与 LLM 函数调用的结合,标志着智能系统从“被动响应”向“主动协同”的重大跃迁。通过引入服务注册中心、负载调度机制与并行调用能力,LLM 能够不再局限于文本生成,而是具备真实的任务执行与智能推理能力。
本文从体系架构出发,系统性地分析了:
- LLM 如何通过 MCP 实现函数自动发现与选择;
- 多策略调度器(如 Round Robin、Least Load)如何提升调用效率;
- 并发任务执行与异步请求的代码实现;
- 多模态函数协作与多 Agent 系统的扩展方式;
- 安全性保障与服务限流的必要机制。
未来,随着 LLM 越来越多地参与业务逻辑的执行决策,MCP 将不再只是“服务目录”,而将成为 AI 原生系统中的 动态智能调用中枢。真正意义上的“机器调用机器”、“智能调度智能”正逐步走向落地。此方向值得深入研究与工程实践。
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)