C#排序算法(二)
【摘要】 👉一、计数排序 👉1-1 介绍找出待排序的数组中最大和最小的元素统计数组中每个值为i的元素出现的次数,存入数组C的第i项对所有的计数累加(从C中的第一个元素开始,每一项和前一项相加)向填充目标数组:将每个元素i放在新数组的第C(i)项,每放一个元素就将C(i)减去1 👉1-2 动态展示效果 👉1-3 算法代码如下using System.Collections;using Syst...
👉一、计数排序
👉1-1 介绍
找出待排序的数组中最大和最小的元素
统计数组中每个值为i的元素出现的次数,存入数组C的第i项
对所有的计数累加(从C中的第一个元素开始,每一项和前一项相加)
向填充目标数组:将每个元素i放在新数组的第C(i)项,每放一个元素就将C(i)减去1
👉1-2 动态展示效果

👉1-3 算法代码如下
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Counting_Sort : MonoBehaviour
{
public int[] test = { 3, 44, 38, 5, 47, 15, 36, 26, 27, 2, 46, 4, 19, 50, 48 };
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
SortRealize(test);
}
public void SortRealize(int[] nums)
{
// 长度小于等于0直接return
if (nums.Length <= 0)
return;
int min = nums[0];
int max = min;
// 找出数组最大元素和最小元素
foreach (int item in nums)
{
if (item > max)
{
max = item;
}
else if (item < min)
{
min = item;
}
}
// 把所有元素存入counting数组
int[] counting = new int[max - min + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++)
{
counting[nums[i] - min] += 1;
}
int index = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < counting.Length; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < counting[i]; j++)
{
index++;
nums[index] = i + min;
}
}
}
}
👉1-4 运行结果如下

👉二、基数排序
👉2-1 介绍
基数排序是一种非比较型排序和利用桶的算法,直接利用每个位数作为下标放入桶中,无需与其他元素比较大小
将待比较的数字从较低位到较高位依次放入桶中, 再按照桶的顺序取出
直到最长位数的数字被完全比较,即可得到已排序的数组
👉2-2 动态展示效果

👉2-3 算法代码如下
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using UnityEngine;
public class Radix_Sort : MonoBehaviour
{
public int[] test = { 3, 44, 38, 5, 47, 15, 36, 26, 27, 2, 46, 4, 19, 50, 48 };
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
SortRealize(test);
}
public void SortRealize(int[] nums,int bucketNum=10)
{
int maxLength = MaxLength(nums);
//创建bucket时,在二维中增加一组标识位,
//其中bucket[x, 0]表示这一维所包含的数字的个数
//通过这样的技巧可以少写很多代码
int[,] bucket = new int[bucketNum, nums.Length + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < maxLength; i++)
{
foreach (var num in nums)
{
int bit = (int)(num / Math.Pow(10, i) % 10);
bucket[bit, ++bucket[bit, 0]] = num;
}
for (int count = 0, j = 0; j < bucketNum; j++)
{
for (int k = 1; k <= bucket[j, 0]; k++)
{
nums[count++] = bucket[j, k];
}
}
//最后要重置这个标识
for (int j = 0; j < bucketNum; j++)
{
bucket[j, 0] = 0;
}
}
}
private static int MaxLength(int[] array)
{
if (array.Length <= 0)
return 0;
int max = array.Max(); // 取出数组的最大值
return (int)Math.Log10(max) + 1; // 取出位数
}
}
👉运行效果如下

👉三、桶排序
👉3-1 介绍
桶排序是计数排序的升级版
根据数组的最大值与最小值申请一些桶(生成对应的序列)
将数组的元素放入桶中,并保证桶里是有序的
合并每个桶,得到的就是一个有序的序列
👉3-2 动态展示效果
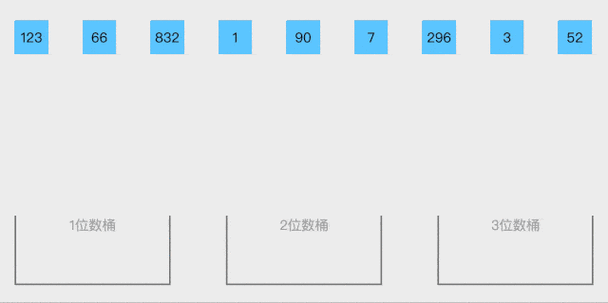
👉3-3 算法代码如下
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using UnityEngine;
public class Bucket_Sort : MonoBehaviour
{
public int[] test = { 3, 44, 38, 5, 47, 15, 36, 26, 27, 2, 46, 4, 19, 50, 48 };
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
SortRealize(test);
}
public void SortRealize(int[] nums, int bucketsize = 5)
{
int max = nums.Max(), min = nums.Min(); // 最大值与最小值
int bucketnums = (max - min) / bucketsize + 1; // 分配的桶数量
List<List<int>> buckets = new List<List<int>>();
// 生成桶
for (int i = 0; i < bucketnums; i++)
{
buckets.Add(new List<int>());
}
//将数组的元素放入桶中,并保证桶里是有序的
for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++)
{
int bucketIndex = (nums[i] - min) / bucketsize;
buckets[bucketIndex].Add(nums[i]);
}
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < buckets.Count; i++)
{
buckets[i].Sort(); // 对生成的每个桶排序
for (int j = 0; j < buckets[i].Count; j++)
{
nums[index++] = buckets[i][j];
}
}
}
}
👉3-4 运行效果如下

👉四、希尔排序
👉4-1 介绍
希尔排序是插入排序的优化版本
设定一个增量gap,将数组按照gap分组
依次对每一组进行插入排序
缩小增量gap,重复前两个步骤,直到gap缩小到一,那么最后一次排序就是
插入排序
👉4-2 动态展示效果
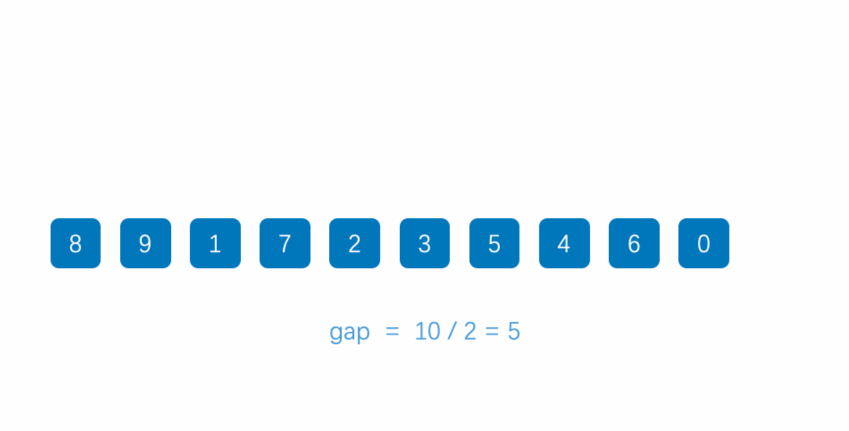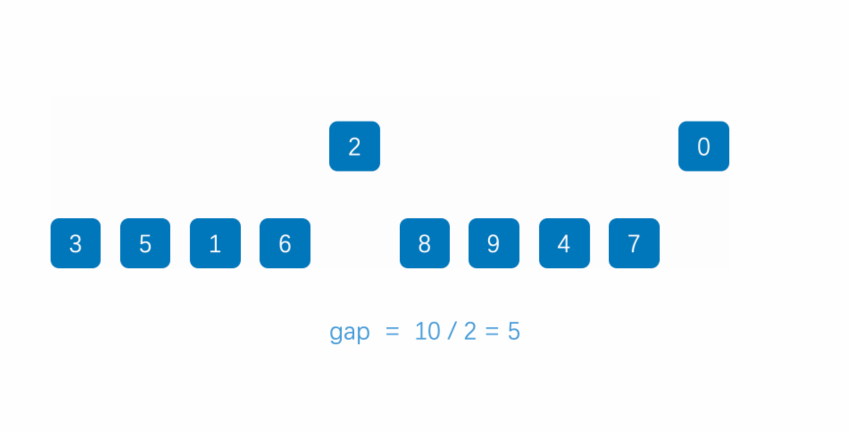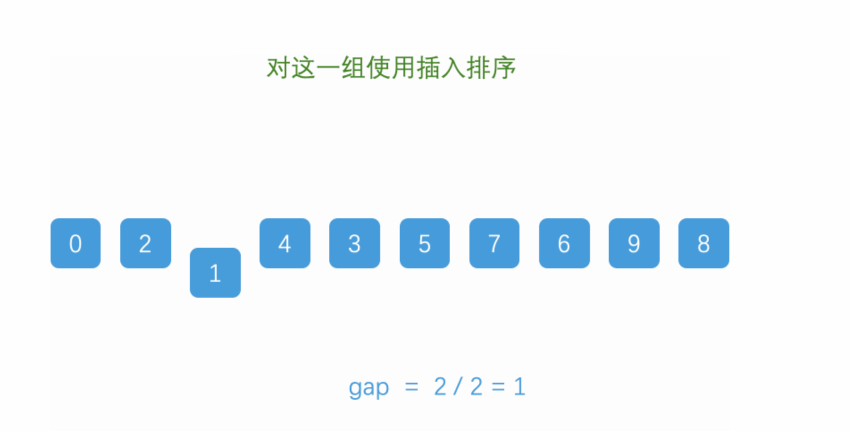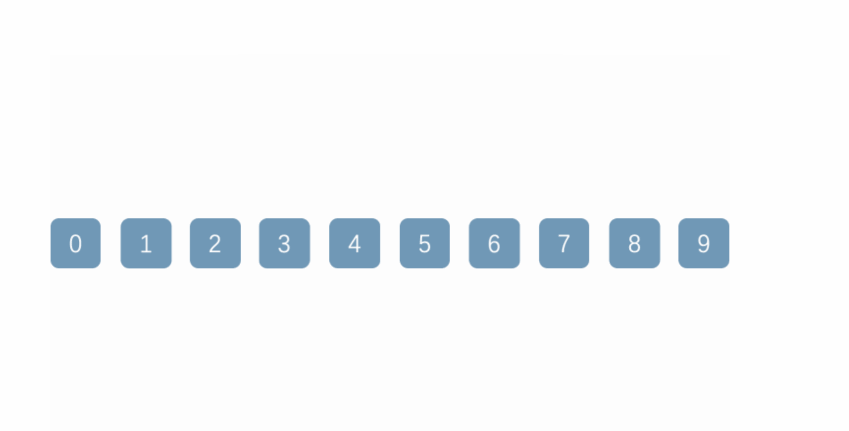
👉4-3 算法代码如下
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Hill_Sort : MonoBehaviour
{
public int[] test = { 3, 44, 38, 5, 47, 15, 36, 26, 27, 2, 46, 4, 19, 50, 48 };
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
SortRealize(test);
}
public void SortRealize(int[] nums)
{
int n = nums.Length; // 数组的长度
int gap = n / 2; // 设定一个增量gap
while (gap >= 1)
{
// 分组
for (int i = gap; i < n; i++)
{
int curNum = nums[i]; // 当前要插入的无序区的元素的值
int idx = i - gap; // 当前元素所在小组的有序区的最后一个元素的索引
while (idx >= 0 && curNum < nums[idx]) // 插入排序
{
nums[idx + gap] = nums[idx];
idx -= gap;
}
nums[idx + gap] = curNum;
}
gap /= 2; // 缩小增量
}
}
}
👉4-4 运行结果如下

【声明】本内容来自华为云开发者社区博主,不代表华为云及华为云开发者社区的观点和立场。转载时必须标注文章的来源(华为云社区)、文章链接、文章作者等基本信息,否则作者和本社区有权追究责任。如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)