平衡车gazebo仿真
0. 简介
gazebo作为ros当中常用的模块,可以做很多有趣的工作,正值双旦,最近想着以平衡车为基础开一个系列来向大家展示如何搭建一个仿真机器人平台。
1. 模型的创建
首先现在solid works 里面将模型文件建立出来,注意各个坐标系以及他们之间的关系。然后根据自己创建的节点命名一个urdf文件。
在这个模型文件里,由于我还可能去添加很多其他的传感器或者是摄像头,所以我在写文件的时候才用了模块化设计,显示设计一个基本的底座文件。由于是直接从solidworks里面直接导出的文件,所以我在这里为了简化步骤,没有采用xacro的宏定义。在solidworks导出的时候,我将文件命名成XXX description的格式,计划在这个模型文件里面专门去放模型的参数。
首先第一步,复制solidworks提供的urdf文件并保存成格式xacro的格式。在launch文件里面xacro格式的文件可以通过下面的方法进行加载:
<!-- 加载机器人模型描述参数 -->
<param name="robot_description" command="$(find xacro)/xacro --inorder '$(find balance_car_description)/urdf/basic_balance_car.xacro'" />
<!-- 在gazebo中加载机器人模型-->
<node name="urdf_spawner" pkg="gazebo_ros" type="spawn_model" respawn="false" output="screen"
args="-urdf -model mrobot -param robot_description"/>
除此以外,还可以通过加载节点joint_state_publisher 以及robot_state_publisher来对模型的关节转角进行监视。(后续如果做倒立摆的话这个参数十分重要)
下面是对模型文件的调整,为了降低模型的耦合性,我把最基本的模型放在了一个文件夹中。内容是
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<robot name="balance_car" xmlns:xacro="http://www.ros.org/wiki/xacro">
<xacro:include filename="$(find balance_car_description)/urdf/balance_car.xacro" />
</robot>
然后中间的内容回通过xacro这段函数自动补齐,成目标balance_car.xacro 文件,文件里面的内容是
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!-- This URDF was automatically created by SolidWorks to URDF Exporter! Originally created by Stephen Brawner (brawner@gmail.com)
Commit Version: 1.6.0-4-g7f85cfe Build Version: 1.6.7995.38578
For more information, please see http://wiki.ros.org/sw_urdf_exporter -->
<robot name="balance_car" xmlns:xacro="http://www.ros.org/wiki/xacro">
<link
name="base_link">
<inertial>
<origin
xyz="-0.0001013 -4.6079E-18 0.048988"
rpy="0 0 0" />
<mass
value="2.0238" />
<inertia
ixx="0.0086841"
ixy="7.4918E-20"
ixz="9.9913E-06"
iyy="0.0034402"
iyz="6.8377E-19"
izz="0.0085679" />
</inertial>
<visual>
<origin
xyz="0 0 0"
rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<mesh
filename="package://balance_car_description/meshes/base_link.STL" />
</geometry>
<material
name="">
<color
rgba="0.79216 0.81961 0.93333 1" />
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<origin
xyz="0 0 0"
rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<mesh
filename="package://balance_car_description/meshes/base_link.STL" />
</geometry>
</collision>
</link>
<link
name="right_wheel_link">
<inertial>
<origin
xyz="-5.5511E-17 -0.029793 -3.1225E-17"
rpy="0 0 0" />
<mass
value="0.34165" />
<inertia
ixx="0.00033311"
ixy="4.7339E-21"
ixz="4.447E-20"
iyy="0.00061076"
iyz="1.8805E-20"
izz="0.00033311" />
</inertial>
<visual>
<origin
xyz="0 0 0"
rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<mesh
filename="package://balance_car_description/meshes/right_wheel_link.STL" />
</geometry>
<material
name="">
<color
rgba="0.79216 0.81961 0.93333 1" />
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<origin
xyz="0 0 0"
rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<mesh
filename="package://balance_car_description/meshes/right_wheel_link.STL" />
</geometry>
</collision>
</link>
<joint
name="right_wheel_joint"
type="continuous">
<origin
xyz="0 -0.09 -0.01"
rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent
link="base_link" />
<child
link="right_wheel_link" />
<axis
xyz="0 1 0" />
</joint>
<link
name="left_wheel_link">
<inertial>
<origin
xyz="-0.0001013 -4.6079E-18 0.048988"
rpy="0 0 0" />
<mass
value="2.0238" />
<inertia
ixx="0.0086841"
ixy="7.4918E-20"
ixz="9.9913E-06"
iyy="0.0034402"
iyz="6.8377E-19"
izz="0.0085679" />
</inertial>
<visual>
<origin
xyz="0 0 0"
rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<mesh
filename="package://balance_car_description/meshes/left_wheel_link.STL" />
</geometry>
<material
name="">
<color
rgba="0.79216 0.81961 0.93333 1" />
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<origin
xyz="0 0 0"
rpy="0 0 0" />
<geometry>
<mesh
filename="package://balance_car_description/meshes/left_wheel_link.STL" />
</geometry>
</collision>
</link>
<joint
name="left_wheel_joint"
type="continuous">
<origin
xyz="0 0.09 -0.01"
rpy="0 0 0" />
<parent
link="base_link" />
<child
link="left_wheel_link" />
<axis
xyz="0 1 0" />
</joint>
<!--====================这段话下面是我自己添加的部分了========================-->
<gazebo reference="left_wheel_link">
<material>Gazebo/Gray</material>
</gazebo>
<gazebo reference="right_wheel_link">
<material>Gazebo/Gray</material>
</gazebo>
<gazebo reference="base_link">
<material>Gazebo/Blue</material>
</gazebo>
<transmission name="right_wheel_joint_trans">
<type>transmission_interface/SimpleTransmission</type>
<joint name="right_wheel_joint" >
<hardwareInterface>hardware_interface/VelocityJointInterface</hardwareInterface>
</joint>
<actuator name="right_wheel_joint_motor">
<hardwareInterface>hardware_interface/VelocityJointInterface</hardwareInterface>
<mechanicalReduction>1</mechanicalReduction>
</actuator>
</transmission>
<transmission name="left_wheel_joint_trans">
<type>transmission_interface/SimpleTransmission</type>
<joint name="left_wheel_joint" >
<hardwareInterface>hardware_interface/VelocityJointInterface</hardwareInterface>
</joint>
<actuator name="left_wheel_joint_motor">
<hardwareInterface>hardware_interface/VelocityJointInterface</hardwareInterface>
<mechanicalReduction>1</mechanicalReduction>
</actuator>
</transmission>
<gazebo>
<plugin name="differential_drive_controller"
filename="libgazebo_ros_diff_drive.so">
<rosDebugLevel>Debug</rosDebugLevel>
<publishWheelTF>true</publishWheelTF>
<robotNamespace>/</robotNamespace>
<publishTf>1</publishTf>
<publishWheelJointState>true</publishWheelJointState>
<alwaysOn>true</alwaysOn>
<updateRate>100.0</updateRate>
<legacyMode>true</legacyMode>
<leftJoint>left_wheel_joint</leftJoint>
<rightJoint>right_wheel_joint</rightJoint>
<wheelSeparation>0.2</wheelSeparation>
<wheelDiameter>0.6</wheelDiameter>
<broadcastTF>1</broadcastTF>
<wheelTorque>30</wheelTorque>
<wheelAcceleration>1.8</wheelAcceleration>
<commandTopic>cmd_vel</commandTopic>
<odometryFrame>odom</odometryFrame>
<odometryTopic>odom</odometryTopic>
<robotBaseFrame>base_footprint</robotBaseFrame>
</plugin>
</gazebo>
</robot>
其中我标记出了我自己在solidworks导出urdf文件新添加的内容。首先是对各个部分模型的颜色加以区分,然后为各个关节(主动关节)添加了相应的传动装置。
launch文件里面,除了添加了运行机器人的模型以外,还添加了发布各个关节的节点状态,还添加了gazebo的启动文件以及参数。
2. gazebo启动以及其参数
<!-- 设置launch文件的参数 -->
<arg name="paused" default="false"/>
<arg name="use_sim_time" default="true"/>
<arg name="gui" default="true"/>
<arg name="headless" default="false"/>
<arg name="debug" default="false"/>
<!-- 运行gazebo仿真环境 -->
<include file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch">
<arg name="debug" value="$(arg debug)" />
<arg name="gui" value="$(arg gui)" />
<arg name="paused" value="$(arg paused)"/>
<arg name="use_sim_time" value="$(arg use_sim_time)"/>
<arg name="headless" value="$(arg headless)"/>
</include>
加载机器人节点状态发布节点
<!-- 运行joint_state_publisher节点,发布机器人的关节状态 -->
<node name="joint_state_publisher" pkg="joint_state_publisher" type="joint_state_publisher" ></node>
加载机器人状态发布的节点
<!-- 运行robot_state_publisher节点,发布tf -->
<node name="robot_state_publisher" pkg="robot_state_publisher" type="robot_state_publisher" output="screen" >
<param name="publish_frequency" type="double" value="50.0" />
</node>
3. 通过差速轮进行简单控制
由于在配置ros_control 的时候出了一点点问题而且没有解决,所以我现在先打算将差速轮的插件先用上,等我问题解决了以后我再尝试用ros control来控制。
在控制的部分,我重新创建了一个功能包,所有关于控制的算法都放在这里。
写一个简单的速度发布程序,如下所示:
#!/usr/bin/python3
import rospy
from geometry_msgs.msg import Twist
def talker():
rospy.init_node('controller',anonymous=True)
vel_publisher=rospy.Publisher('cmd_vel',Twist,queue_size=1)
vel_cmd=Twist()
vel_cmd.linear.x=1
vel_cmd.angular.z=2
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
vel_publisher.publish(vel_cmd)
if __name__=='__main__':
try:
talker()
except rospy.ROSInterruptException:
pass
在发布的程序里面,知道的需要发布节点是vel_cmd,其是一个Twist类型的函数。在建立gazebo以后。注意这里发布者的书写方法。
4. 设置IMU
在urdf文件里面重新宏定义一个IMU文件,这里可以放关于IMU的xacro文件。但是IMU数据需要四元数解算。
在urdf/sensor的文件夹下面,定义这样一个文件:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<robot xmlns:xacro="http://www.ros.org/wiki/xacro" name="imu">
<xacro:macro name="imu_sensor" params="fix_link">
<!-- IMU plugin for 'body_link' -->
<gazebo reference="${fix_link}">
<gravity>true</gravity>
<sensor name="${fix_link}_imu_sensor" type="imu">
<always_on>true</always_on>
<update_rate>100</update_rate>
<visualize>true</visualize>
<topic>__default_topic__</topic>
<plugin filename="libgazebo_ros_imu_sensor.so" name="imu_plugin">
<topicName>imu</topicName>
<bodyName>${fix_link}</bodyName>
<updateRateHZ>100.0</updateRateHZ>
<gaussianNoise>0.0</gaussianNoise>
<xyzOffset>0 0 0</xyzOffset>
<rpyOffset>0 0 0</rpyOffset>
<frameName>imu_link</frameName>
</plugin>
<pose>0 0 0 0 0 0</pose>
</sensor>
</gazebo>
</xacro:macro>
</robot>
当我们需要用传感器的时候,可以直接include传感器的文件,然后照着宏定义创建一个工程实例
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<robot name="balance_car" xmlns:xacro="http://www.ros.org/wiki/xacro">
<xacro:include filename="$(find balance_car_description)/urdf/balance_car.xacro" />
<xacro:include filename="$(find balance_car_description)/urdf/sensor/imu.xacro" />
<xacro:imu_sensor fix_link="base_link"/>
</robot>
然后在control.py里面这样写
#!/usr/bin/python3
import rospy
from sensor_msgs.msg import Imu
import math
def imu_cb(imu_data):
x = imu_data.orientation.x
y = imu_data.orientation.y
z = imu_data.orientation.z
w = imu_data.orientation.w
roll=math.atan2(2*(w*x+y*z),1-2*(x**2+y**2))
pitch=math.asin(2*(w*y-z*x))
yaw=math.atan2(2*(w*z+x*y),1-2*(y**2+z**2))
print(pitch)
if __name__=='__main__':
try:
rospy.init_node('control_node',anonymous=True)
rospy.Subscriber("/imu",Imu,imu_cb)
rospy.spin()
except rospy.ROSInterruptException:
pass
5. 姿态稳定控制
roll,pitch,yaw需要在获得base_link以后进行四元数解算才能获得真实值。
这个是控制的效果:
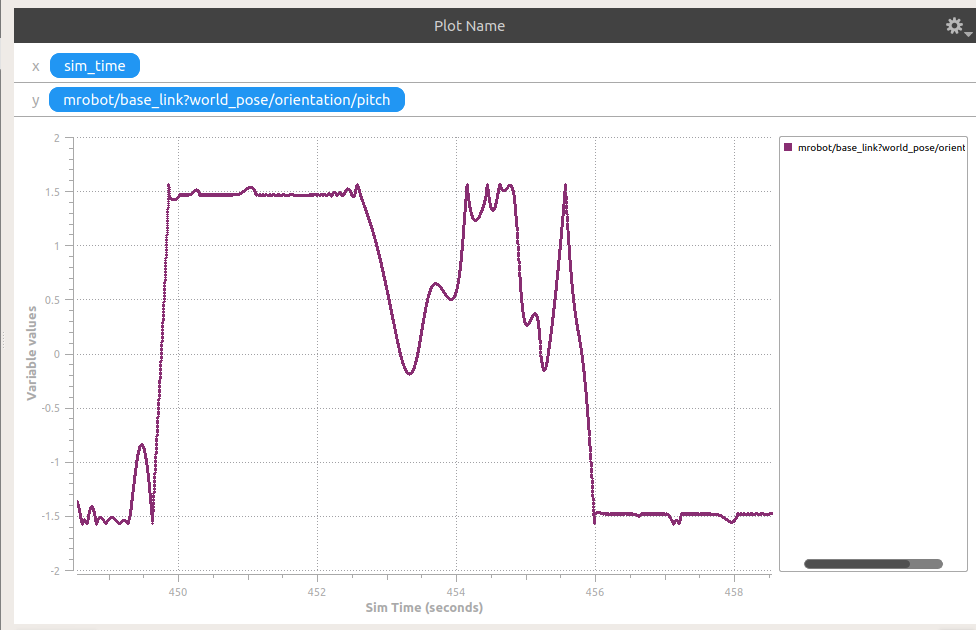
(期望是0)挺发散的,可以说并不怎么样。加大了kp的值,但是控制效果依然不佳。
…详情请参照古月居
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)