大数据ClickHouse进阶(十八):数据字典类型
数据字典类型
在创建字典表语句中使用“layout”来指定字典的类型,目前扩展字典支持7种类型,分别为flat、hashed、range_hashed、cache、complex_key_hashed、complex_key_cache、ip_trie,不同的字典类型决定了数据在内存中以何种结构组织和存储。
扩展字典根据使用时传入的条件不同,可以划分为两类:
- 支持单个数值型条件(条件类型必须是UInt64)
flat、hashed、range_hashed、cache
- 支持复合条件
complex_key_hashed、complex_key_cache、ip_trie
下面分别介绍以上不同字典类型配置使用。

一、flat
flat字典是所有类型中性能最高的字典类型,只能使用UInt64数值型key。flat字典在内存中使用数组结构保存,默认最多保存50万行数据,如果在创建字典时数据量超出上限,则创建失败。
flat数据字典使用如下:
#创建flat数据字典
CREATE DICTIONARY flat_dic_test(
local_id UInt64,
local_name String
)
primary key local_id
SOURCE(ClickHouse(
HOST 'node1'
PORT 9000
USER 'default'
TABLE 'loc_info'
PASSWORD ''
DB 'dic_test_db'
))
LIFETIME (MIN 1 MAX 10)
LAYOUT(FLAT());
#使用flat字典表
select dictGet('dic_test_db.flat_dic_test','local_name',toUInt64(100)) as local_name;
┌─local_name─┐
│ 北京 │
└────────────┘二、hashed
hashed字典同样只能够使用UInt64数值型key,与flat不同的是hashed字典在内存中通过散列结构保存,没有存储上限。
三、range_hashed
range_hashed字典可以看做hashed字典的变种,在原有功能的基础上增加了指定时间区间的特性,数据会以散列结构存储并按照时间排序。时间区间通过range_min和range_max元素指定,创建range_hashed字典表时必须指定Range时间范围且起始结束字段必须是Date或者DateTime类型。
range_hashed字典表使用案例如下:
#创建普通表 rate表,表中四列代表:用户、开始时间、结束时间、优惠金额
create table rate(id UInt64, start Date, end Date, discount Float32) ENGINE=MergeTree() order by id;
#向表rate中插入如下数据
insert into rate values (111, '2021-11-01', '2021-11-03', 100),(111, '2021-11-04', '2021-11-20', 200),(222, '2021-11-10', '2021-11-12',300);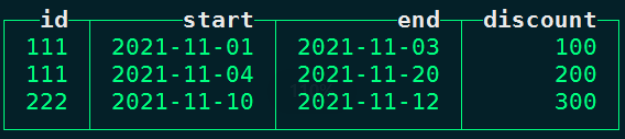
#创建range_hashed字典表
CREATE DICTIONARY hash_range_dic_test (
id UInt64,
start Date,
end Date,
discount Float32
)
PRIMARY KEY id
SOURCE(ClickHouse(
host 'node1'
port 9000
user 'default'
db 'dic_test_db'
password ''
table 'rate'
))
LAYOUT(RANGE_HASHED())
RANGE(MIN start MAX end)
LIFETIME(30);
#使用range_dic查询数据
select dictGetFloat32('dic_test_db.hash_range_dic_test', 'discount', toUInt64(111), toDate('2021-11-02')) as discount;
┌─discount─┐
│ 100 │
└──────────┘
select dictGetFloat32('dic_test_db.hash_range_dic_test', 'discount', toUInt64(111), toDate('2021-11-19')) as discount;
┌─discount─┐
│ 200 │
└──────────┘
select dictGetFloat32('dic_test_db.hash_range_dic_test', 'discount', toUInt64(222), toDate('2021-11-20')) AS discount;
┌─discount─┐
│ 0 │
└──────────┘注意:以上我们查询对应数据时,需要多传入一个时间参数,dictGet函数会根据数据找到传入条件所属范围,找到对应的值返回。
四、cache
cache字典只能够使用UInt64数值类型的key,该字典数据在内存中通过固定长度的向量数组保存,定长的向量数组又称cells,在创建cache字典表时需要指定向量数组长度,长度必须是2的整数倍,若不是,会自动向上取2的整数倍的整数。
cache字典用于一些数据不适合长期存放在内存,但是频繁访问的数据需要放在内存的场景。cache字典的取数并不是一次性将所有数据加载到内存中,当从cache字典中获取数据时,首先在cells中查询有没有该数据缓存,没有就会从源头加载数据并缓存到cells中,所以cache性能最不稳定,性能好坏完全取决于缓存的命中率,建议少使用此类型字典。
cache字典表使用案例如下:
#创建cache数据字典
CREATE DICTIONARY cache_dic_test(
local_id UInt64,
local_name String
)
primary key local_id
SOURCE(ClickHouse(
HOST 'node1'
PORT 9000
USER 'default'
TABLE 'loc_info'
PASSWORD ''
DB 'dic_test_db'
))
LIFETIME (MIN 1 MAX 10)
LAYOUT(CACHE(SIZE_IN_CELLS 100000));
#使用cache字典表
select dictGet('dic_test_db.cache_dic_test','local_name',toUInt64(100)) as local_name;
┌─local_name─┐
│ 北京 │
└────────────┘五、complex_key_hashed
complex_key_hashed字典在功能方面与hashed字典完全相同,只是将当个数值型key替换成了复合型。
complex_key_hashed使用案例如下:
#创建普通表 student_info
create table student_info(
id UInt64,
code String,
name String,
age UInt8
)engine=MergeTree()
order by id;
#向表student_info中插入数据
insert into student_info values (1,'001','张三',18),(2,'002','李四',19),(3,'003','王五',20);
#创建complex_key_hashed 字典表
CREATE DICTIONARY complex_key_hashed_dic_test
(
id UInt64,
code String,
name String,
age UInt8
)
PRIMARY KEY id,code
SOURCE(ClickHouse(
host 'node1'
port 9000
user 'default'
db 'dic_test_db'
password ''
table 'student_info'
))
LAYOUT(COMPLEX_KEY_HASHED())
LIFETIME(30);
#使用complex_key_hashed字典表查询数据
SELECT dictGet('dic_test_db.complex_key_hashed_dic_test', 'name', tuple(toUInt64(2), '002')) AS name;
┌─name─┐
│ 李四 │
└──────┘注意:使用complex_key_hashed字典表时传入条件key时,格式为tuple,tuple中到底传入几个参数,需要与创建该字典时指定的primary key顺序一样。
六、complex_key_cache
complex_key_cache字典同样与cache字典的特性完全相同,只是将单个数值型key替换成了复合型。
complex_key_cache使用案例如下:
#创建complex_key_cache字典表
CREATE DICTIONARY complex_key_cache_dic_test
(
id UInt64,
code String,
name String,
age UInt8
)
PRIMARY KEY id,age
SOURCE(ClickHouse(
host 'node1'
port 9000
user 'default'
db 'dic_test_db'
password ''
table 'student_info'
))
LAYOUT(COMPLEX_KEY_CACHE(SIZE_IN_CELLS 100000))
LIFETIME(30);
#使用complex_key_cache字典表查询
SELECT dictGet('dic_test_db.complex_key_cache_dic_test', 'name', tuple(toUInt64(3), 20)) AS name;
┌─name─┐
│ 王五 │
└──────┘七、ip_trie
ip_trie为复合型key的字典,但是比较特殊,因为在查询时只能在tuple中指定单个字段,用于指代IP前缀,ip_trie字典的数据在内存中使用trie树结构保存,此字典专门用于IP前缀查询的场景,例如通过IP前缀查询对应的ASN信息。
扩展:ASN(Autonomous System Number)是为每个大型网络分配的编号,该编号全球唯一。通过查询IP地址隶属的ASN编号,可以了解该IP地址隶属的网络运营商,以及大致的地址位置。
ip_trie字典表使用案例如下:
创建IP信息表
create table ip_info(prefix String, asn UInt32, ccode String) ENGINE=TinyLog;
#向表ip_info中插入数据
insert into ip_info values
('192.168.179.1',11223,'NP')
('192.168.179.2',11224,'US')
('192.168.179.3',11225,'RU')
('192.168.179.4',11226,'CN')
;
#创建ip_tire字典表
CREATE DICTIONARY ip_tire_dict_test (
prefix String,
asn UInt32,
ccode String
)
PRIMARY KEY prefix
SOURCE(ClickHouse(
host 'node1'
port 9000
user 'default'
db 'dic_test_db'
password ''
table 'ip_info'
))
LAYOUT(IP_TRIE())
LIFETIME(30);
#使用ip_tire字典表查询数据
select dictGetUInt32('dic_test_db.ip_tire_dict_test', 'asn', tuple(IPv4StringToNum('192.168.179.3'))) as asn,dictGet('dic_test_db.ip_tire_dict_test', 'ccode', tuple(IPv4StringToNum('192.168.179.3'))) as ccode;
┌───asn─┬─ccode─┐
│ 11225 │ RU │
└───────┴───────┘- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)