FreeRTOS记录(三、RTOS任务调度原理解析_Systick、PendSV、SVC)(上)
RTOS的任务调度原理和所使用的内核中断、寄存器息息相关
文中截图大多是《Cortex-M3与Cortex-M4权威指南》翻译版本里面的内容
需要对内核有一定的了解,本文尽量用简单的描述表达清楚
虽然是FreeRTOS的记录,但是原理上来说对于其他RTOS也是一样的!
说明:FreeRTOS 专栏与我的 RT-Thread 专栏不同,我的 RT-Thread 专栏是从理论学习一步一步循序渐进,从 0 起步的 完整教学,而 FreeRTOS 更偏向于 我直接拿来使用,需要用到什么,然后引出知识点,在使用中发现问题,解然后再解决问题。
本 FreeRTOS 专栏记录的开发环境:
FreeRTOS记录(一、熟悉开发环境以及CubeMX下FreeRTOS配置)
FreeRTOS 记录(二、FreeRTOS 任务 API 认识和源码简析)
总结写在前面:
在Cortex-M内核上,FreeRTOS使用Systick定时器作为心跳时钟,一般默认心跳时钟为1ms,进入Systick中断后,内核会进入处理模式进行处理,在Systick中断处理中,系统会在 ReadList 就绪链表从高优先级到低优先找需要执行的任务,进行调度,如果有任务的状态发生了变化,改变了状态链表,就会产生一个pendSV异常,进入pendSV异常,通过改变进程栈指针(PSP)切换到不同的任务。
对于相同优先级的任务,每隔一个Systick,运行过的任务被自动排放至该优先级链表的尾部(时间片调度)
用户也可以在线程模式下主动触发PendSV,进行任务切换。
在FreeRTOS中SVC只使用了一次(M0中没有使用),就是第一次。
FreeRTOS进入临界区是通过配置BASEPRI寄存器来进行的。
Systick
我们已经知道,在Cortex-M系列中 systick是作为FreeRTOS 的心跳时钟,是调度器的核心。
系统是在Systick中进行上下文切换。
那么他是如何进行上下文切换的呢,那就得来说说内核的中断管理了,记住一句话
操作系统的入口是中断(好像是废话,嵌入式所有程序的入口都是中断= =!)
Systick 源码解析
Systick 初始化
systick的初始化在port.c中, vPortSetupTimerInterrupt函数:
/*
* Setup the systick timer to generate the tick interrupts at the required
* frequency.
*/
__attribute__(( weak )) void vPortSetupTimerInterrupt( void )
{
/* Calculate the constants required to configure the tick interrupt. */
#if( configUSE_TICKLESS_IDLE == 1 )
{
ulTimerCountsForOneTick = ( configSYSTICK_CLOCK_HZ / configTICK_RATE_HZ );
xMaximumPossibleSuppressedTicks = portMAX_24_BIT_NUMBER / ulTimerCountsForOneTick;
ulStoppedTimerCompensation = portMISSED_COUNTS_FACTOR / ( configCPU_CLOCK_HZ / configSYSTICK_CLOCK_HZ );
}
#endif /* configUSE_TICKLESS_IDLE */
/*
Stop and clear the SysTick.
清0,保证上电后的准确性
*/
portNVIC_SYSTICK_CTRL_REG = 0UL;
portNVIC_SYSTICK_CURRENT_VALUE_REG = 0UL;
/*
Configure SysTick to interrupt at the requested rate.
portNVIC_SYSTICK_LOAD_REG systick装载值
portNVIC_SYSTICK_CTRL_REG systick控制寄存器 配置系统时钟源,开启中断,使能
*/
portNVIC_SYSTICK_LOAD_REG = ( configSYSTICK_CLOCK_HZ / configTICK_RATE_HZ ) - 1UL;
portNVIC_SYSTICK_CTRL_REG = ( portNVIC_SYSTICK_CLK_BIT | portNVIC_SYSTICK_INT_BIT | portNVIC_SYSTICK_ENABLE_BIT );
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------*/
Systick 中断服务函数
每一节拍进入一次Systick 中断,因为Systick 如果调度器返回true,触发pendSV异常:
/*-----------------------------------------------------------*/
void xPortSysTickHandler( void )
{
/* The SysTick runs at the lowest interrupt priority, so when this interrupt
executes all interrupts must be unmasked. There is therefore no need to
save and then restore the interrupt mask value as its value is already
known.
进入临界区,在上面一篇文章讲过,通过配置BASEPRI寄存器,关闭的中断等级在CubeMX中设置
*/
portDISABLE_INTERRUPTS();
{
/*
Increment the RTOS tick.
操作系统调度接口
如果调度器返回true,触发pendSV异常
*/
if( xTaskIncrementTick() != pdFALSE )
{
/*
A context switch is required. Context switching is performed in
the PendSV interrupt. Pend the PendSV interrupt.
往中断控制及状态寄存器ICSR(地址:0xE000_ED04)的bit28写1挂起一次PendSV中断
触发pendSV
*/
portNVIC_INT_CTRL_REG = portNVIC_PENDSVSET_BIT;
}
}
/*
开中断,执行pendSV
*/
portENABLE_INTERRUPTS();
}
Systick 任务调度
Systick中断中调用xTaskIncrementTick任务调度如下,源码注释:
/*----------------------------------------------------------*/
BaseType_t xTaskIncrementTick( void )
{
TCB_t * pxTCB;
TickType_t xItemValue;
BaseType_t xSwitchRequired = pdFALSE;// 返回值,表示是否进行上下文切换
/* Called by the portable layer each time a tick interrupt occurs.
Increments the tick then checks to see if the new tick value will cause any
tasks to be unblocked. */
traceTASK_INCREMENT_TICK( xTickCount );
/*
uxSchedulerSuspended 表示内核调度器是否挂起
pdFALSE 表示内核没有挂起
*/
if( uxSchedulerSuspended == ( UBaseType_t ) pdFALSE )
{
/*
Minor optimisation. The tick count cannot change in this
block.
tick计数增加1
*/
const TickType_t xConstTickCount = xTickCount + ( TickType_t ) 1;
/* Increment the RTOS tick, switching the delayed and overflowed
delayed lists if it wraps to 0. */
xTickCount = xConstTickCount;
/*
判断tick是否溢出越界
*/
if( xConstTickCount == ( TickType_t ) 0U ) /*lint !e774 'if' does not always evaluate to false as it is looking for an overflow. */
{
taskSWITCH_DELAYED_LISTS();//如果溢出,要更新延时列表
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
/* See if this tick has made a timeout expire. Tasks are stored in
the queue in the order of their wake time - meaning once one task
has been found whose block time has not expired there is no need to
look any further down the list.
当前节拍大于时间片的锁定时间
说明有任务需要进行调度了,时间片用完了
*/
if( xConstTickCount >= xNextTaskUnblockTime )
{
/*
会一直遍历整个任务延时列表,
找到时间片最短的任务,进行切换
*/
for( ;; )
{
/*
判断任务延时列表中,是否为空,
也就是说,有没有任务在等待调度
*/
if( listLIST_IS_EMPTY( pxDelayedTaskList ) != pdFALSE )
{
/* The delayed list is empty. Set xNextTaskUnblockTime
to the maximum possible value so it is extremely
unlikely that the
if( xTickCount >= xNextTaskUnblockTime ) test will pass
next time through.
如果没有任务等待,把时间片赋值为最大值,不再调度
*/
xNextTaskUnblockTime = portMAX_DELAY; /*lint !e961 MISRA exception as the casts are only redundant for some ports. */
break;
}
else
{
/* The delayed list is not empty, get the value of the
item at the head of the delayed list. This is the time
at which the task at the head of the delayed list must
be removed from the Blocked state.
1、从任务延时列表中,获取第一个任务控制块
2、延时列表,插入永远是把时间片最短的任务,放在第一个
3、获取任务控制块的延时时间
*/
pxTCB = listGET_OWNER_OF_HEAD_ENTRY( pxDelayedTaskList ); /*lint !e9079 void * is used as this macro is used with timers and co-routines too. Alignment is known to be fine as the type of the pointer stored and retrieved is the same. */
xItemValue = listGET_LIST_ITEM_VALUE( &( pxTCB->xStateListItem ) );
/*
再次判断,这个任务的时间片是否到达
*/
if( xConstTickCount < xItemValue )
{
/* It is not time to unblock this item yet, but the
item value is the time at which the task at the head
of the blocked list must be removed from the Blocked
state - so record the item value in
xNextTaskUnblockTime.
没有到达,把此任务的时间片更新为当前系统的时间片
*/
xNextTaskUnblockTime = xItemValue;
/*
直接退出,不用调度
*/
break; /*lint !e9011 Code structure here is deedmed easier to understand with multiple breaks. */
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
/*
It is time to remove the item from the Blocked state.
把任务从延时列表中移除
*/
( void ) uxListRemove( &( pxTCB->xStateListItem ) );
/*
Is the task waiting on an event also? If so remove
it from the event list.
把任务从事件列表中移除
*/
if( listLIST_ITEM_CONTAINER( &( pxTCB->xEventListItem ) ) != NULL )
{
( void ) uxListRemove( &( pxTCB->xEventListItem ) );
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
/*
Place the unblocked task into the appropriate ready
list.
把任务添加到就绪列表中
*/
prvAddTaskToReadyList( pxTCB );
/* A task being unblocked cannot cause an immediate
context switch if preemption is turned off.
抢占式处理
*/
#if ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 1 )
{
/* Preemption is on, but a context switch should
only be performed if the unblocked task has a
priority that is equal to or higher than the
currently executing task.
判断优先级是否大于当前任务
大于则进行调度
*/
if( pxTCB->uxPriority >= pxCurrentTCB->uxPriority )
{
xSwitchRequired = pdTRUE;
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
#endif /* configUSE_PREEMPTION */
}
}
}
/* Tasks of equal priority to the currently running task will share
processing time (time slice) if preemption is on, and the application
writer has not explicitly turned time slicing off.
时间片处理机制
1、获取就绪列表长度
2、就绪列表指的是,当前任务优先级的列表
3、如果有其他任务在就绪列表中,就开始调度
*/
#if ( ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 1 ) && ( configUSE_TIME_SLICING == 1 ) )
{
if( listCURRENT_LIST_LENGTH( &( pxReadyTasksLists[ pxCurrentTCB->uxPriority ] ) ) > ( UBaseType_t ) 1 )
{
xSwitchRequired = pdTRUE;
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
#endif /* ( ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 1 ) && ( configUSE_TIME_SLICING == 1 ) ) */
#if ( configUSE_TICK_HOOK == 1 )
{
/* Guard against the tick hook being called when the pended tick
count is being unwound (when the scheduler is being unlocked). */
if( uxPendedTicks == ( UBaseType_t ) 0U )
{
vApplicationTickHook();
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
#endif /* configUSE_TICK_HOOK */
}
else //内核调度器挂起了
{
++uxPendedTicks;//挂起的tick+1
/* The tick hook gets called at regular intervals, even if the
scheduler is locked. */
#if ( configUSE_TICK_HOOK == 1 )
{
vApplicationTickHook();
}
#endif
}
/*
如果是抢占模式,要开启调度
*/
#if ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 1 )
{
if( xYieldPending != pdFALSE )
{
xSwitchRequired = pdTRUE;
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
#endif /* configUSE_PREEMPTION */
return xSwitchRequired;//返回调度器状态
}
Systick优先级分析
结合后面的中断管理和任务调度相关的内容,需要说明一下Systick优先级的问题。先来看一下简单的任务调度模型。
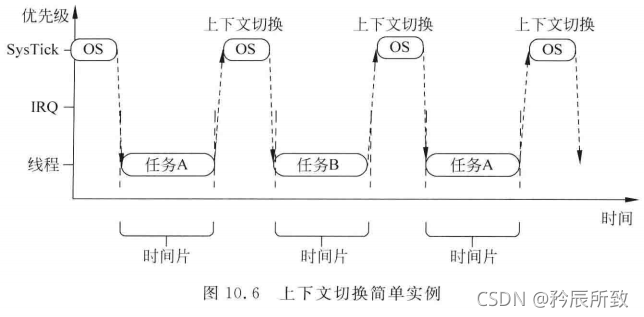
在上面图示中,可以看到优先级SysTick优先级最高!那么这和我们常听到的SysTick优先级需要设置为最低优先级怎么相互冲突呢?初学者往往在这个问题上感到困惑。
首先要明白:SysTick是中断,中断优先级和任务优先级没有任何关系,不管中断优先级是多少,中断的优先级永远高于任何线程任务的优先级
那么在上图中的线程,不管什么线程,SysTick中断来了肯定是需要去执行SysTick中断事件的。
上图中还有一个IRQ,比SysTick优先级低,这也是可能的,但是实际上我们应用过程中,一般都把SysTick优先级设置为最低,因为不想让SysTick中断打断用户的IRQ中断。
那么SysTick中断优先级和外设中断优先级是怎么确定的?
1、SysTick属于内核异常,用SHPRx(x=1.2.3)来设置其优先级;外设中断属于 ISR,用NVIC_IPRx来设置优先级。
SPRH1-SPRH3是一个32位的寄存器,只能通过字节访问,每8个字段控制着一个内核外设的中断优先级的配置。位7:4这高四位有效,所以可编程为0 ~ 15。如果软件优先级配置相同,那就根据他们在中断向量表里面的位置编号来决定优先级大小,编号越小,优先级越高。
对于SysTick的配置,系统默认配置为15,(1UL << __NVIC_PRIO_BITS) - 1UL) 在m3、m4中__NVIC_PRIO_BITS为4:
/*
core_cm0/3/4.h中关于SysTick_Config
m3 m4 中是 4 ,4位就是0~15
#define __NVIC_PRIO_BITS 4U
m0 中是2, 2位就是 0 ~ 3
#endif
*/
__STATIC_INLINE uint32_t SysTick_Config(uint32_t ticks)
{
if ((ticks - 1UL) > SysTick_LOAD_RELOAD_Msk)
{
return (1UL); /* Reload value impossible */
}
SysTick->LOAD = (uint32_t)(ticks - 1UL); /* set reload register */
NVIC_SetPriority (SysTick_IRQn, (1UL << __NVIC_PRIO_BITS) - 1UL); /* set Priority for Systick Interrupt */
SysTick->VAL = 0UL; /* Load the SysTick Counter Value */
SysTick->CTRL = SysTick_CTRL_CLKSOURCE_Msk |
SysTick_CTRL_TICKINT_Msk |
SysTick_CTRL_ENABLE_Msk; /* Enable SysTick IRQ and SysTick Timer */
return (0UL); /* Function successful */
}
/*
NVIC_SetPriority对中断分了类,分内核中断和外设中断,
内核外设中断枚举值小于0,普通外设>=0。其中,SysTick_IRQn = -1。
*/
__STATIC_INLINE void NVIC_SetPriority(IRQn_Type IRQn, uint32_t priority)
{
if ((int32_t)(IRQn) < 0)
{
SCB->SHP[(((uint32_t)(int32_t)IRQn) & 0xFUL)-4UL] = (uint8_t)((priority << (8U - __NVIC_PRIO_BITS)) & (uint32_t)0xFFUL);
}
else
{
NVIC->IP[((uint32_t)(int32_t)IRQn)] = (uint8_t)((priority << (8U - __NVIC_PRIO_BITS)) & (uint32_t)0xFFUL);
}
}
2、NVIC的中断优先级分组不仅对片上外设有效,同样对内核的外设也有效。
systick的优先级15转换成二进制值就是1111,又因为NVIC的优先级分组2,那么前两位的11就是3,3抢占,后两位的11也是3,3子优先级。这样就可以和外设的优先级进行对比。
如果外设中断的优先级也分成了15,无论怎么分组,SYSTICK优先级高于同优先级的外设(毕竟内核异常优先级高于外设中断,因为中断向量表里面的位置编号内核的靠前更小)。
3、设置systick优先级的方法NVIC_SetPriority (SysTick_IRQn, (1<<__NVIC_PRIO_BITS) - 15); 即SCB->SHP[11] = 0x00;设置最高的话可以得到精准延时,但是会频繁打断用户使用的中断程序,不建议。
内核中断管理
中断是微处理器外部发送的,通过中断通道送入处理器内部,一般是硬件引起的;
而异常通常是微处理器内部发生的,大多是软件引起的,比如除法出错异常,特权调用异常。
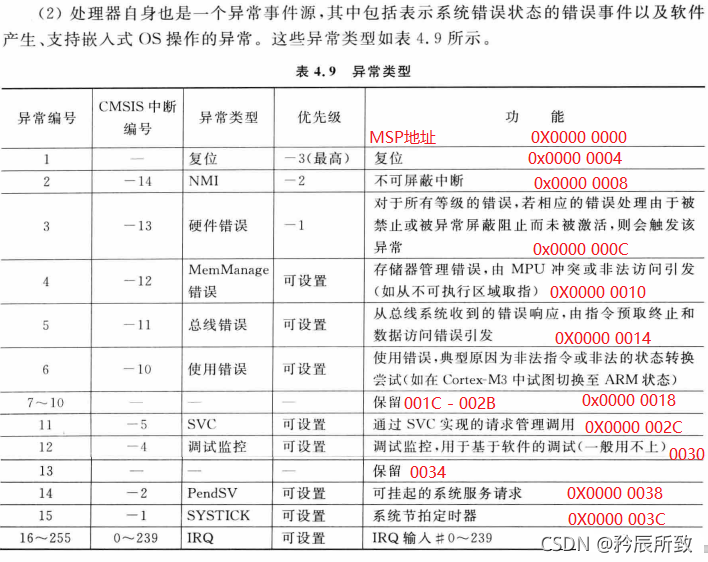
Cortex-M的异常类型
如下图:
Cortex-M的寄存器
如下图:
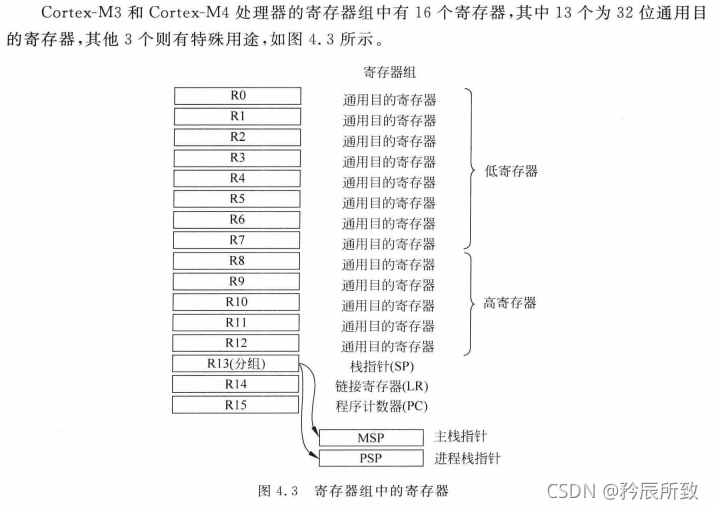
这个图主要记住 R13 寄存器,有两个指针:MSP: 主栈指针 和 PSP: 进程栈指针,相关说明如下:

Cortex-M的特殊寄存器
如下图:
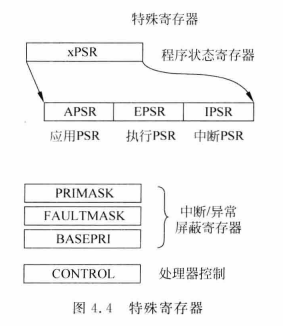
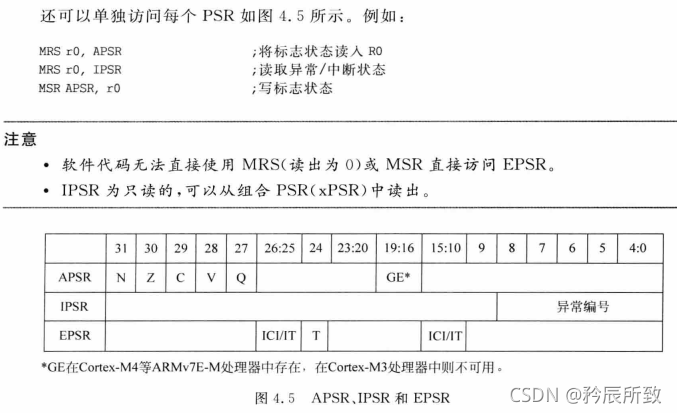
xPSR
组合程序状态寄存器,该寄存器由三个程序状态寄存器组成
应用PSR(APSR) : 包含前一条指令执行后的条件标志
中断PSR(IPSR) : 包含当前ISR的异常编号
执行PSR(EPSR) : 包含Thumb状态位
PRIMSK
PRIMSK:中断屏蔽特殊寄存器。
利用PRIMSK,可以禁止除HardFault 和 NMI外的所有异常。


BASEPRI
利用BASEPRI寄存器来选择屏蔽低于特定优先级的异常或中断。(在上一篇博文中的进入临界区所使用的寄存器就是这个寄存器)

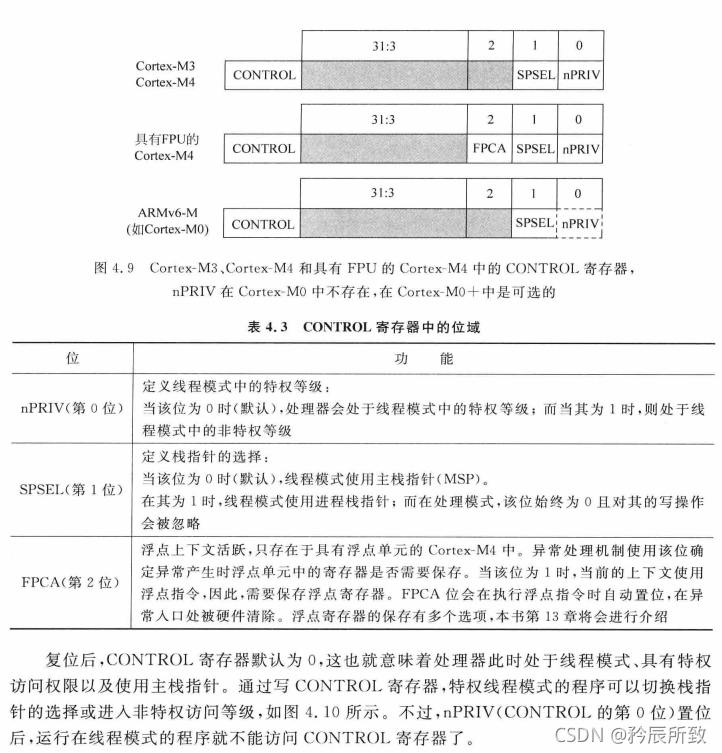
CONTROL
CONTROL:控制寄存器,部分介绍如下:
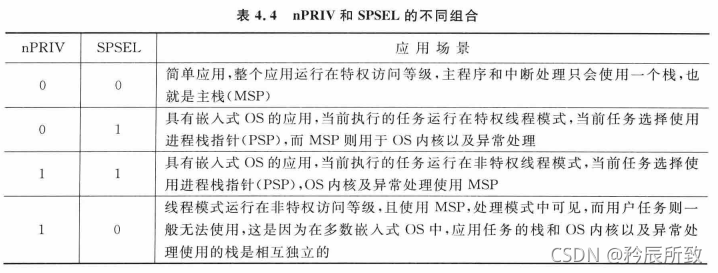
Cortex-M的工作模式
Cortex-M有两种工作模式和两种工作状态:
线程模式(Thread Mode):芯片复位后,进入线程模式,执行用户程序;
处理模式(Handler Mode):当处理器发生了异常或者中断,则进入处理模式,处理完后返回线程模式。
Thumb状态: 正常运行时处理器的状态
调试状态:调试程序时处理器的状态
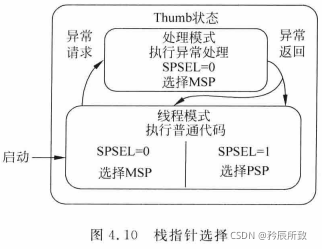
进入Systick后,发生异常,则进入处理模式进行处理:
如果是裸机编程,从哪里进去就返回哪里
但是用了操作系统,该返回哪里呢?
所以这里就有必要单独讲解下MSP和PSP
影子栈指针
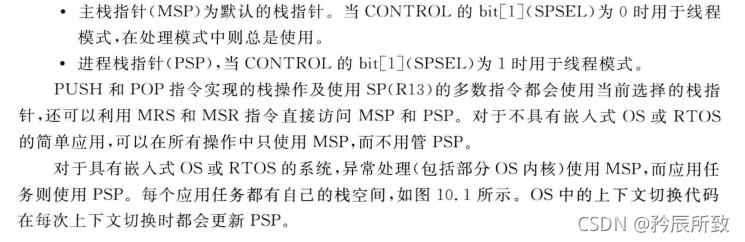
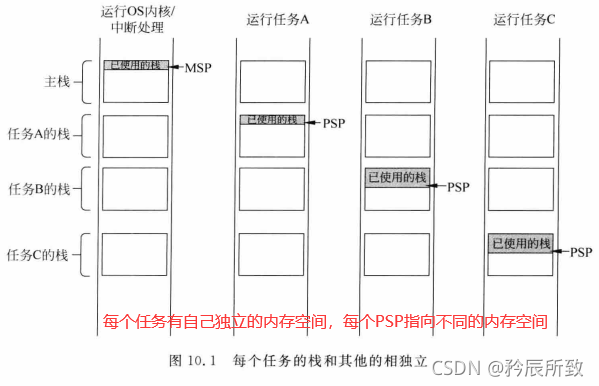
在上面的Cortex-M的寄存器图中我们标注过R13寄存器:
堆栈指针SP。
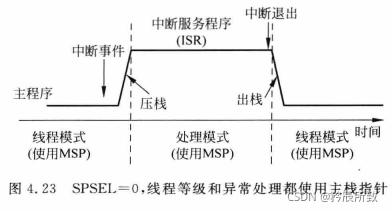
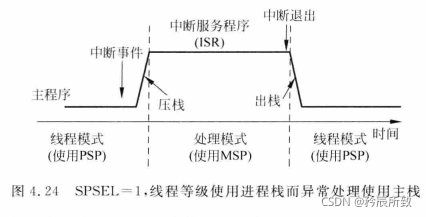
在处理模式下,只能使用主堆栈(MSP)。
在线程模式下,可以使用主堆栈也可以使用进程栈。
由 CONTROL 寄存器控制,如下:
(由于文章字数限制,分为上下两篇)
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)