ROS1云课→25机器人控制配置
移动机器人控制和运动学动力学模型密切相关。
差动驱动轮系统控制器。控制采用速度命令的形式,将其拆分然后发送到差动驱动轴距的两个车轮上。里程计是从硬件的反馈中计算出来的,并发布。如果仿真就简单了很多。
参考如下(机器翻译):

带转向机构的车轮系统控制器。控制采用速度命令的形式,该命令被拆分然后发送到转向驱动轮座的单个后轮和单个前转向。里程计是从硬件的反馈中计算出来的,并发布。
创建基础控制器
对于导航功能包集来说,一个基础控制器是非常重要的,因为这是唯一能够有效地控制机器人的方法。它能够直接和机器人的电子设备通信。
ROS并不提供任何标准的基础控制器,因此必须自己编写针对移动平台的基础控制器。
机器人通过geometry_msgs/Twist类型的消息进行控制。这个类型正是之前看到的Odometry消息所使用的。
所以基础控制器必须订阅名称为cmd_vel的主题,必须生成正确的线速度和角速度命令来驱动平台。
现在先复习一下消息的结构。在命令行窗口内输入以下命令查看消息的具体结构:
$ rosmsg show geometry_msgs/Twist
这个命令的输出结果如下所示:

二维环境控制:
geometry_msgs/Vector3 linear
float64 x
float64 y
float64 z
geometry_msgs/Vector3 angular
float64 x
float64 y
float64 z
三维环境控制:
geometry_msgs/Vector3 linear
float64 x
float64 y
float64 z
geometry_msgs/Vector3 angular
float64 x
float64 y
float64 z
其中,线速度向量linear包含了x、y和z轴的线速度。角速度向量angular包含了各个轴向的角速度。
两轮差速结构(diff):
diff-drive-controller
对于两轮机器人,只需要使用线速度x和角速度z。这是因为机器人基于差动轮驱动平台,驱动它的两个电动机只能够让机器人前进、后退或者转向。
车式转向结构(ackermann):
-
rosmsg show ackermann_msgs/AckermannDrive [21:27:00]
-
float32 steering_angle
-
float32 steering_angle_velocity
-
float32 speed
-
float32 acceleration
-
float32 jerk
-
mobile_base_controller:
-
type : "ackermann_steering_controller/AckermannSteeringController"
-
rear_wheel: 'rear_wheel_joint'
-
front_steer: 'front_steer_joint'
-
publish_rate: 50.0 # default: 50
-
pose_covariance_diagonal : [0.001, 0.001, 1000000.0, 1000000.0, 1000000.0, 1000.0]
-
twist_covariance_diagonal: [0.001, 0.001, 1000000.0, 1000000.0, 1000000.0, 1000.0]
-
-
# Wheel separation between the rear and the front, and diameter of the rear.
-
# These are both optional.
-
# ackermann_steering_controller will attempt to read either one or both from the
-
# URDF if not specified as a parameter.
-
wheel_separation_h : 1.0
-
wheel_radius : 0.3
-
-
# Wheel separation and radius multipliers for odometry calibration.
-
wheel_separation_h_multiplier: 1.0 # default: 1.0
-
wheel_radius_multiplier : 1.0 # default: 1.0
-
-
# Steer position angle multipliers for fine tuning.
-
steer_pos_multiplier : 1.0
-
-
# Velocity commands timeout [s], default 0.5
-
cmd_vel_timeout: 0.25
-
-
# Base frame_id
-
base_frame_id: base_footprint #default: base_link
-
-
# Odom frame_id
-
odom_frame_id: odom
-
-
# Velocity and acceleration limits
-
# Whenever a min_* is unspecified, default to -max_*
-
linear:
-
x:
-
has_velocity_limits : true
-
max_velocity : 1.0 # m/s
-
min_velocity : -0.5 # m/s
-
has_acceleration_limits: true
-
max_acceleration : 0.8 # m/s^2
-
min_acceleration : -0.4 # m/s^2
-
has_jerk_limits : true
-
max_jerk : 5.0 # m/s^3
-
-
angular:
-
z:
-
has_velocity_limits : true
-
max_velocity : 1.7 # rad/s
-
has_acceleration_limits: true
-
max_acceleration : 1.5 # rad/s^2
-
has_jerk_limits : true
-
max_jerk : 2.5 # rad/s^3
如何在地图中移动机器人呢?
两轮差动cmd_vel。

使用rqt
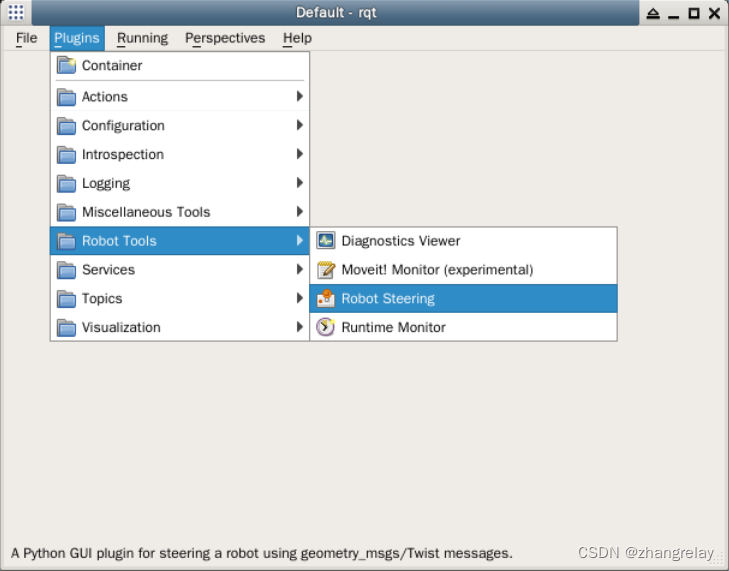
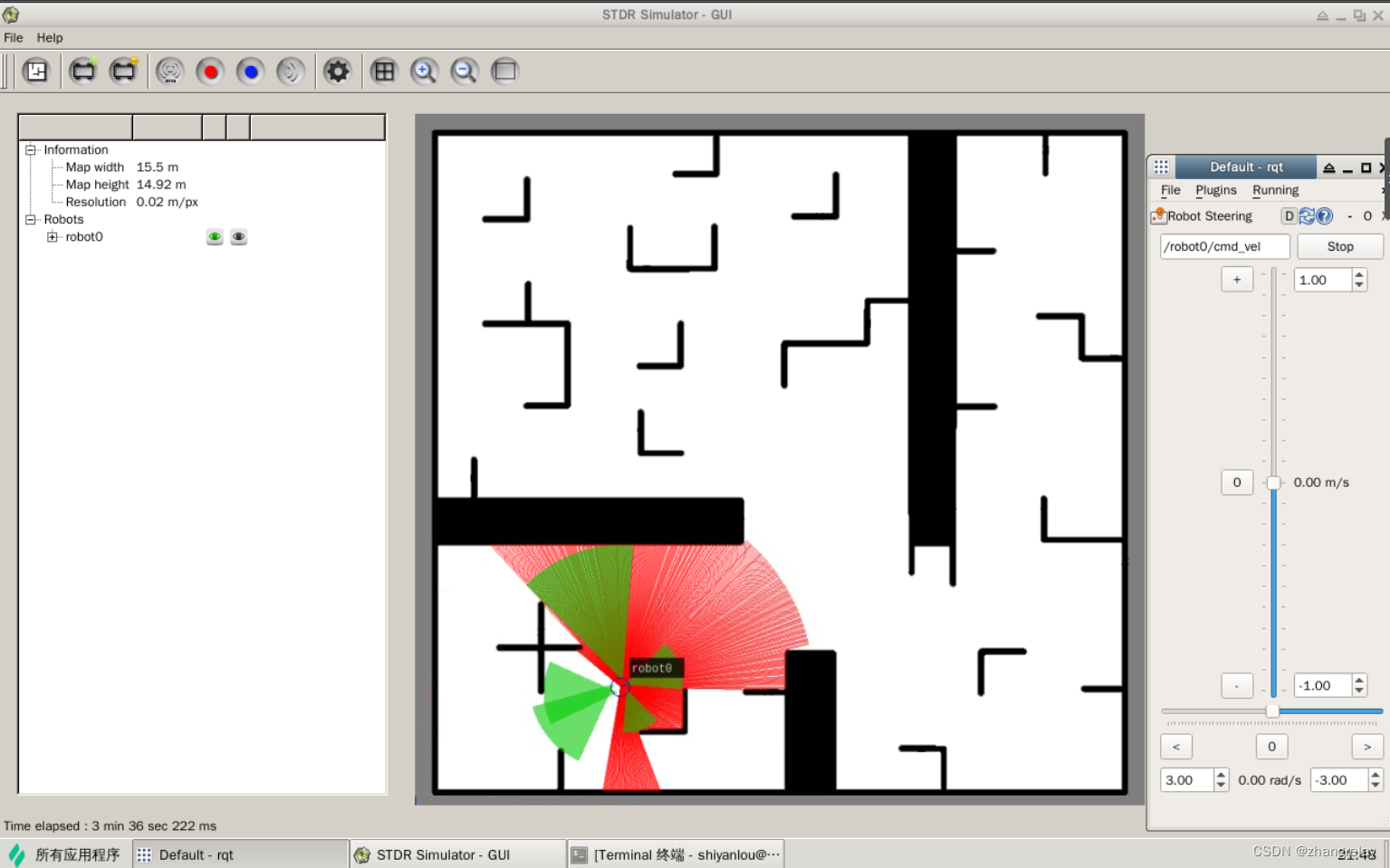
如果需要自动避障参考:
-
/******************************************************************************
-
STDR Simulator - Simple Two DImensional Robot Simulator
-
Copyright (C) 2013 STDR Simulator
-
This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
-
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
-
the Free Software Foundation; either version 3 of the License, or
-
(at your option) any later version.
-
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
-
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
-
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
-
GNU General Public License for more details.
-
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
-
along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation,
-
Inc., 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
-
-
Authors :
-
* Manos Tsardoulias, etsardou@gmail.com
-
* Aris Thallas, aris.thallas@gmail.com
-
* Chris Zalidis, zalidis@gmail.com
-
******************************************************************************/
-
# include "stdr_samples/obstacle_avoidance/obstacle_avoidance.h"
-
-
/**
-
@namespace stdr_samples
-
@brief The main namespace for STDR Samples
-
**/
-
namespace stdr_samples
-
{
-
/**
-
@brief Default contructor
-
@param argc [int] Number of input arguments
-
@param argv [char **] Input arguments
-
@return void
-
**/
-
ObstacleAvoidance::ObstacleAvoidance(int argc,char **argv)
-
{
-
if(argc != 3)
-
{
-
ROS_ERROR(
-
"Usage : stdr_obstacle avoidance <robot_frame_id> <laser_frame_id>");
-
exit(0);
-
}
-
laser_topic_ = std::string("/") +
-
std::string(argv[1]) + std::string("/") + std::string(argv[2]);
-
speeds_topic_ = std::string("/") +
-
std::string(argv[1]) + std::string("/cmd_vel");
-
-
subscriber_ = n_.subscribe(
-
laser_topic_.c_str(),
-
1,
-
&ObstacleAvoidance::callback,
-
this);
-
-
cmd_vel_pub_ = n_.advertise<geometry_msgs::Twist>(speeds_topic_.c_str(), 1);
-
}
-
-
/**
-
@brief Default destructor
-
@return void
-
**/
-
ObstacleAvoidance::~ObstacleAvoidance(void)
-
{
-
-
}
-
-
/**
-
@brief Callback for the ros laser message
-
@param msg [const sensor_msgs::LaserScan&] The new laser scan message
-
@return void
-
**/
-
void ObstacleAvoidance::callback(const sensor_msgs::LaserScan& msg)
-
{
-
scan_ = msg;
-
float linear = 0, rotational = 0;
-
for(unsigned int i = 0 ; i < scan_.ranges.size() ; i++)
-
{
-
float real_dist = scan_.ranges[i];
-
linear -= cos(scan_.angle_min + i * scan_.angle_increment)
-
/ (1.0 + real_dist * real_dist);
-
rotational -= sin(scan_.angle_min + i * scan_.angle_increment)
-
/ (1.0 + real_dist * real_dist);
-
}
-
geometry_msgs::Twist cmd;
-
-
linear /= scan_.ranges.size();
-
rotational /= scan_.ranges.size();
-
-
//~ ROS_ERROR("%f %f",linear,rotational);
-
-
if(linear > 0.3)
-
{
-
linear = 0.3;
-
}
-
else if(linear < -0.3)
-
{
-
linear = -0.3;
-
}
-
-
cmd.linear.x = 0.3 + linear;
-
cmd.angular.z = rotational;
-
cmd_vel_pub_.publish(cmd);
-
}
-
}
文章来源: zhangrelay.blog.csdn.net,作者:zhangrelay,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:zhangrelay.blog.csdn.net/article/details/126809483
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者



评论(0)