LIO-SAM框架:点云预处理前端---畸变矫正
前言
LIO-SAM的全称是:Tightly-coupled Lidar Inertial Odometry via Smoothing and Mapping
从全称上可以看出,该算法是一个紧耦合的雷达惯导里程计(Tightly-coupled Lidar Inertial Odometry),借助的手段就是利用GT-SAM库中的方法。
LIO-SAM 提出了一个利用GT-SAM的紧耦合激光雷达惯导里程计的框架。
实现了高精度、实时的移动机器人的轨迹估计和建图。
其中点云运动畸变矫正的代码在图像投影的节点中
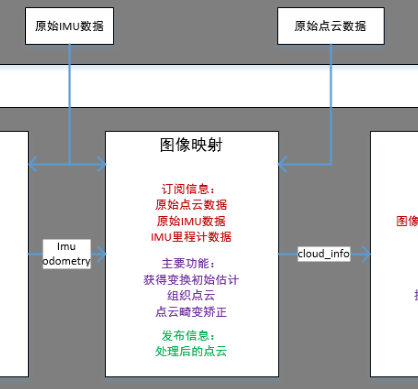
可以看到该节点 订阅 3种消息:
- 原始点云数据
- 原始imu数据
- imu预积分后预测的imu里程计数据
其中完成的一个主要功能就是进行畸变矫正。上一篇博客主要解读其畸变矫正数据预处理部分;本篇博客将解读其畸变矫正处理流程部分。
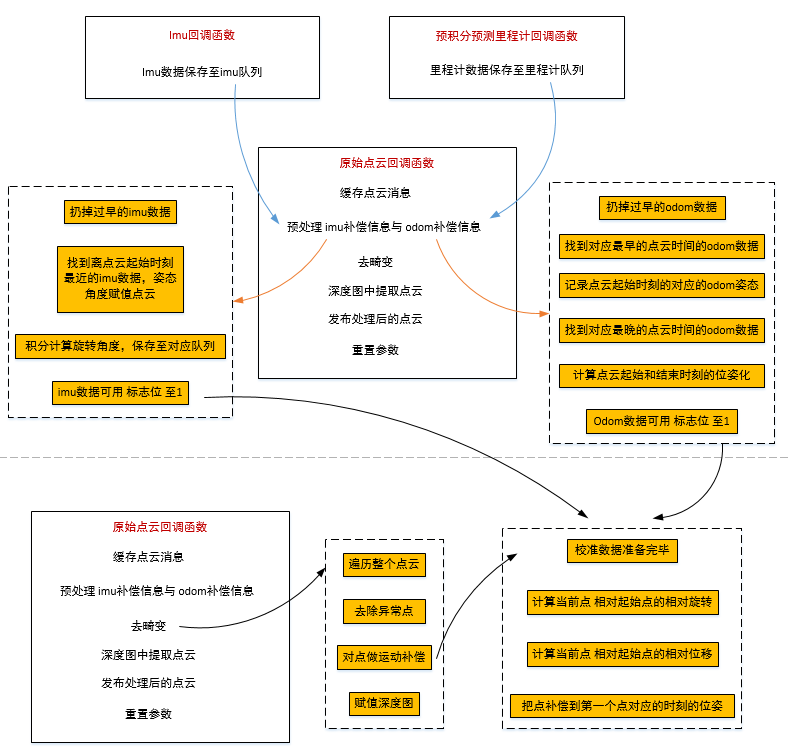
畸变矫正
将点云投影到一个矩阵上,并保存每个点的信息,并在内部进行畸变矫正
void projectPointCloud()
{
int cloudSize = laserCloudIn->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < cloudSize; ++i)
{
遍历整个点云
PointType thisPoint;
thisPoint.x = laserCloudIn->points[i].x;
thisPoint.y = laserCloudIn->points[i].y;
thisPoint.z = laserCloudIn->points[i].z;
thisPoint.intensity = laserCloudIn->points[i].intensity;
取出对应的某个点
float range = pointDistance(thisPoint);
计算这个点距离lidar中心的距离
if (range < lidarMinRange || range > lidarMaxRange)
continue;
距离太小或者太远都认为是异常点
int rowIdn = laserCloudIn->points[i].ring;
if (rowIdn < 0 || rowIdn >= N_SCAN)
continue;
if (rowIdn % downsampleRate != 0)
continue;
取出对应的在第几根scan上
scan id 合理判断
如果需要降采样,就根据scan id 适当跳过
float horizonAngle = atan2(thisPoint.x, thisPoint.y) * 180 / M_PI;
static float ang_res_x = 360.0/float(Horizon_SCAN);
int columnIdn = -round((horizonAngle-90.0)/ang_res_x) + Horizon_SCAN/2;
if (columnIdn >= Horizon_SCAN)
columnIdn -= Horizon_SCAN;
if (columnIdn < 0 || columnIdn >= Horizon_SCAN)
continue;
计算水平角
计算水平分辨率
计算水平线束id ,转换到x负方向为起始,顺时针为正方向,范围[0-H]
对水平角做补偿,因为雷达是顺时针旋转,
对水平id进行检查
if (rangeMat.at<float>(rowIdn, columnIdn) != FLT_MAX)
continue;
如果这个位置有填充了就跳过
点云不是完全的360度,可能会多一些
thisPoint = deskewPoint(&thisPoint, laserCloudIn->points[i].time);
对点做运动补偿
rangeMat.at<float>(rowIdn, columnIdn) = range;
将这个点的距离数据保存进这个range矩阵种
int index = columnIdn + rowIdn * Horizon_SCAN;
算出点的索引
fullCloud->points[index] = thisPoint;
保存这个点的坐标
之后来看下运动补偿得函数deskewPoint
PointType deskewPoint(PointType *point, double relTime)
{
if (deskewFlag == -1 || cloudInfo.imuAvailable == false)
return *point;
判断是否可以进行运动补偿,不能得话则之间返回原点
判断依据:
- deskewFlag 是原始点云 没有 time得标签 则为-1
- cloudInfo.imuAvailable 的原始imu里面的数据判断
double pointTime = timeScanCur + relTime;
relTime 是相对时间,加上起始时间就是绝对时间
float rotXCur, rotYCur, rotZCur;
findRotation(pointTime, &rotXCur, &rotYCur, &rotZCur);
通过findRotation函数 计算当前点 相对起始点的相对旋转
其内部为:
void findRotation(double pointTime, float *rotXCur, float *rotYCur, float *rotZCur)
{
*rotXCur = 0; *rotYCur = 0; *rotZCur = 0;
先将相对旋转至0
int imuPointerFront = 0;
while (imuPointerFront < imuPointerCur)
{
if (pointTime < imuTime[imuPointerFront])
break;
++imuPointerFront;
}
找到距离该点云时间最近的 大于该点云时间的点
if (pointTime > imuTime[imuPointerFront] || imuPointerFront == 0)
{
*rotXCur = imuRotX[imuPointerFront];
*rotYCur = imuRotY[imuPointerFront];
*rotZCur = imuRotZ[imuPointerFront];
}
如果时间戳不在两个imu的旋转之间,就直接赋值了
} else {
int imuPointerBack = imuPointerFront - 1;
double ratioFront = (pointTime - imuTime[imuPointerBack]) / (imuTime[imuPointerFront] - imuTime[imuPointerBack]);
double ratioBack = (imuTime[imuPointerFront] - pointTime) / (imuTime[imuPointerFront] - imuTime[imuPointerBack]);
*rotXCur = imuRotX[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuRotX[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
*rotYCur = imuRotY[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuRotY[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
*rotZCur = imuRotZ[imuPointerFront] * ratioFront + imuRotZ[imuPointerBack] * ratioBack;
}
否则 作一个线性插值,得到相对旋转
算两个权重 进行 插值
float posXCur, posYCur, posZCur;
findPosition(relTime, &posXCur, &posYCur, &posZCur);
这里没有计算平移补偿 如果运动不快的话
if (firstPointFlag == true)
{
transStartInverse = (pcl::getTransformation(posXCur, posYCur, posZCur, rotXCur, rotYCur, rotZCur)).inverse();
firstPointFlag = false;
}
计算第一个点的相对位姿
Eigen::Affine3f transFinal = pcl::getTransformation(posXCur, posYCur, posZCur, rotXCur, rotYCur, rotZCur);
Eigen::Affine3f transBt = transStartInverse * transFinal;
计算当前点和第一点的相对位姿
newPoint.x = transBt(0,0) * point->x + transBt(0,1) * point->y + transBt(0,2) * point->z + transBt(0,3);
newPoint.y = transBt(1,0) * point->x + transBt(1,1) * point->y + transBt(1,2) * point->z + transBt(1,3);
newPoint.z = transBt(2,0) * point->x + transBt(2,1) * point->y + transBt(2,2) * point->z + transBt(2,3);
newPoint.intensity = point->intensity;
return newPoint;
就是R*p+t ,把点补偿到第一个点对应的时刻的位姿
然后看提取出有效的点的信息 函数 cloudExtraction
void cloudExtraction()
{
for (int i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i)
{
遍历每一根scan
cloudInfo.startRingIndex[i] = count - 1 + 5;
这个scan可以计算曲率的起始点(计算曲率需要左右各五个点)
for (int j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j)
{
遍历该 scan上的每 个点
if (rangeMat.at<float>(i,j) != FLT_MAX)//FLT_MAX就是最大的浮点数
{
判断该点 是否 是一个 有效的点
rangeMat的每个点初始化为FLT_MAX ,如果点有效,则会赋值为 range
cloudInfo.pointColInd[count] = j;
点云信息里面 这个点对应着哪一个垂直线
cloudInfo.pointRange[count] = rangeMat.at<float>(i,j);
点云信息里面 保存它的距离信息
extractedCloud->push_back(fullCloud->points[j + i*Horizon_SCAN]);
他的3d坐标信息
cloudInfo.endRingIndex[i] = count -1 - 5;
这个scan可以计算曲率的终端
在上面处理完后
即可发布点云
void publishClouds()
{
cloudInfo.header = cloudHeader;
cloudInfo.cloud_deskewed = publishCloud(&pubExtractedCloud, extractedCloud, cloudHeader.stamp, lidarFrame);
pubLaserCloudInfo.publish(cloudInfo);
}
最后将处理后的点云发布出去
result
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)