MixNet解析以及pytorch源码
@[toc]
摘要
MixConv 的主要思想是在单个深度卷积操作中混合多个不同大小的内核,以便它可以轻松地从输入图像中捕获不同类型的模式。 大核来捕获高分辨率的特征(我理解是全局的特征),又需要小核来捕获低分辨率的特征(我理解是图片的纹理特征),以提高模型的准确性和效率。网络结构如图:
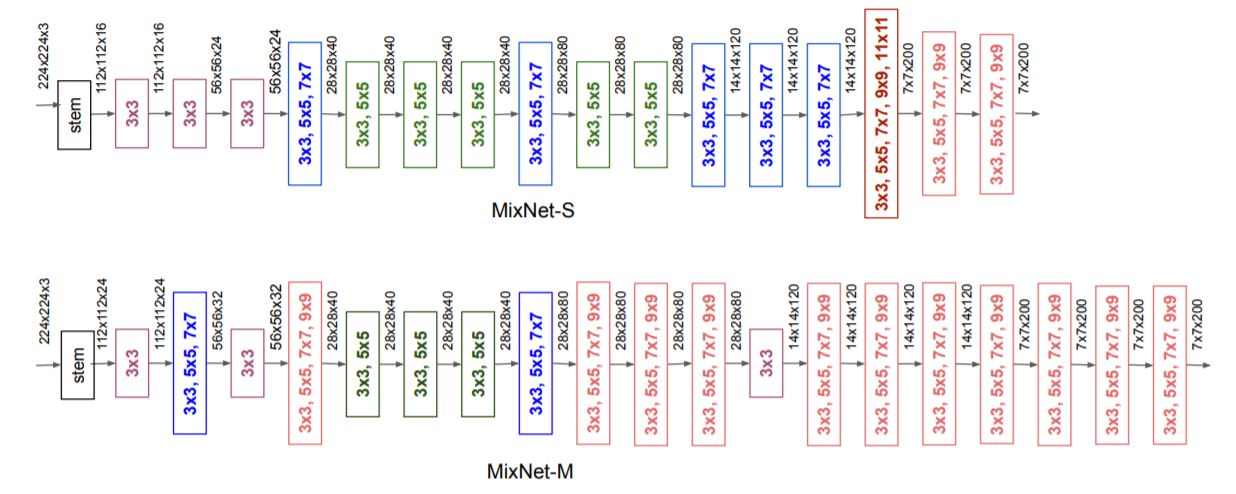
这种特征拼接和Inceptions 有很多相似的地方,但是卷积采用分组卷积的方式,所以参数的计算量比较小。想要理解MixNet,首先要理解大小卷积核的优缺点,然后,理解分组卷积。

大卷积核与小卷积核
究竟是大卷积核好,还是小的卷积核好,这个大家一直在争论。CNN的鼻祖LeNet和惊艳到大家的AlexNet都使用了大卷积核。后来,到VGG开始使用3×3的卷积核,再发展到YOLOV4、5里面使用了大量的1×1的卷积核。
卷积核越大,receptive field(感受野)越大,看到的图片信息越多,因此获得的特征越好。但是大的卷积核会导致计算量的暴增,不利于模型深度的增加,计算性能也会降低。
于是在VGG、Inception网络中,利用2个3×3卷积核的组合来代替1个5×5卷积核,感受野不变,计算量还得到降低。多个 3x3 的卷积层比一个大尺寸 filter卷积层有更多的非线性(更多层的非线性函数),使得判决函数更加具有判决性。
正因为这些因素,导致了人们越来越喜欢小卷积核。
最近,人们又开始重新审视大卷积核,比如MixNet使用了3×3、5×5、7×7和9×9等,还有更猛的RepLKNet,直接使用31×31大小的卷积核。但是都不再是普通的卷积了,比如MixNet使用的是分组卷积,这样大大降低模型的计算量。
分组卷积
分组卷积则是对输入feature map进行分组,然后每组分别卷积。如下图:
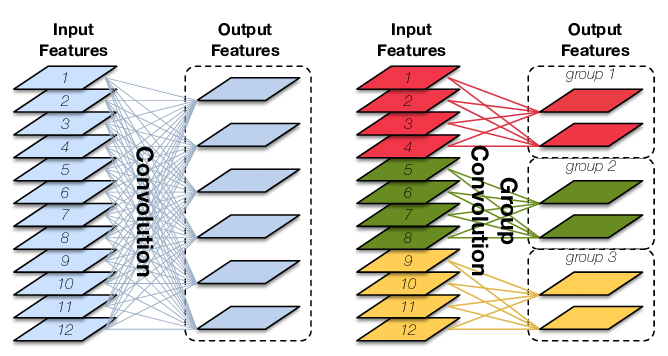
分组卷积则是对输入feature map进行分组,然后每组分别卷积。
假设输入feature map的尺寸仍为 ,输出feature map的数量为 个,如果设定要分成G个groups,则每组的输入feature map数量为 ,每组的输出feature map数量为 ,每个卷积核的尺寸为 ,卷积核的总数仍为 个,每组的卷积核数量为 ,卷积核只与其同组的输入map进行卷积,卷积核的总参数量为 ,总参数量减少为原来的 。
计算量公式:
分组卷积的参数量为:
举例:
输入的尺寸是227×227×3,卷积核大小是11×11,输出是6,输出维度是55×55,group为3
我们带入公式可以计算出
参数量:
=726
运算量:
=2205225
MinNet核心代码
mixnet_s参数列表:
mixnet_s = [(16, 16, [3], [1], [1], 1, 1, 'ReLU', 0.0),
(16, 24, [3], [1, 1], [1, 1], 2, 6, 'ReLU', 0.0),
(24, 24, [3], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 3, 'ReLU', 0.0),
(24, 40, [3, 5, 7], [1], [1], 2, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(40, 40, [3, 5], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(40, 40, [3, 5], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(40, 40, [3, 5], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(40, 80, [3, 5, 7], [1], [1, 1], 2, 6, 'Swish', 0.25),
(80, 80, [3, 5], [1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.25),
(80, 80, [3, 5], [1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.25),
(80, 120, [3, 5, 7], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(120, 120, [3, 5, 7, 9], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 3, 'Swish', 0.5),
(120, 120, [3, 5, 7, 9], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 3, 'Swish', 0.5),
(120, 200, [3, 5, 7, 9, 11], [1], [1], 2, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(200, 200, [3, 5, 7, 9], [1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(200, 200, [3, 5, 7, 9], [1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.5)]
列的含义
第一列:in_channels,输入的通道。
第二列:out_channels,输出的通道。
第三列:卷积核的大小。
第四列:信道扩张,应用在MixNetBlock的扩展阶段。
第五列:信道映射,应用在MixNetBlock的末尾,映射输出通道。
第六列:stride,特征图缩放的倍数。
第七列:信道扩张的倍数。
第八列:激活函数
第九列:SE注意力机制放大的倍率。0代表没有SE。
行代表每个MixNetBlock的配置,MixNetBlock的代码如下:
class MixNetBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size=[3],
expand_ksize=[1],
project_ksize=[1],
stride=1,
expand_ratio=1,
non_linear='ReLU',
se_ratio=0.0
):
super(MixNetBlock, self).__init__()
expand = (expand_ratio != 1)
expand_channels = in_channels * expand_ratio
se = (se_ratio != 0.0)
self.residual_connection = (stride == 1 and in_channels == out_channels)
conv = []
if expand:
# 扩展阶段
pw_expansion = nn.Sequential(
GroupedConv2d(in_channels, expand_channels, expand_ksize),
nn.BatchNorm2d(expand_channels),
NON_LINEARITY[non_linear]
)
conv.append(pw_expansion)
# depthwise convolution phase
dw = nn.Sequential(
MDConv(expand_channels, kernel_size, stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(expand_channels),
NON_LINEARITY[non_linear]
)
conv.append(dw)
if se:
# squeeze and excite
squeeze_excite = SqueezeAndExcite(expand_channels, in_channels, se_ratio)
conv.append(squeeze_excite)
# projection phase
pw_projection = nn.Sequential(
GroupedConv2d(expand_channels, out_channels, project_ksize),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
)
conv.append(pw_projection)
self.conv = nn.Sequential(*conv)
def forward(self, x):
if self.residual_connection:
return x + self.conv(x)
else:
return self.conv(x)
我们将网络打印出来,选择“(80, 120, [3, 5, 7], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 6, ‘Swish’, 0.5),”这组配置,结合MixNetBlock的代码来学习。
(10): MixNetBlock(
(conv): Sequential(
(0): Sequential(
(0): GroupedConv2d(
(grouped_conv): ModuleList(
(0): Conv2d(40, 240, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(1): Conv2d(40, 240, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
)
)
(1): BatchNorm2d(480, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): Swish(
(sigmoid): Sigmoid()
)
)
(1): Sequential(
(0): MDConv(
(mixed_depthwise_conv): ModuleList(
(0): Conv2d(160, 160, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=160, bias=False)
(1): Conv2d(160, 160, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2), groups=160, bias=False)
(2): Conv2d(160, 160, kernel_size=(7, 7), stride=(1, 1), padding=(3, 3), groups=160, bias=False)
)
)
(1): BatchNorm2d(480, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): Swish(
(sigmoid): Sigmoid()
)
)
(2): SqueezeAndExcite(
(se_reduce): Conv2d(480, 40, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(non_linear1): Swish(
(sigmoid): Sigmoid()
)
(se_expand): Conv2d(40, 480, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(non_linear2): Sigmoid()
)
(3): Sequential(
(0): GroupedConv2d(
(grouped_conv): ModuleList(
(0): Conv2d(240, 60, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(1): Conv2d(240, 60, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
)
)
(1): BatchNorm2d(120, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
)
)
pw_expansion:通道扩展,将80个通道拆为两个40的channel作为卷积的输出,输入的channel×expand_ratio作为扩张的输出,然后拼接位480channel的特征图。
将480的channel拆解位3个160的channel,分别输入到混合卷积中,混合卷积由3×3、5×5和7×7构成的分组卷积中,分组为160,计算完成后拼接成480channel的特征图。
将特征图数据SE注意力中,计算完成后得到480channel的特征图。
最后,将480channel的特征图拆为两个240的特征图,分别输入到1×1的卷积中,得到60channel的特征图,然后,做拼接,得到120channel的特征图。
完整代码:
import math
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.autograd import Variable
class Swish(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Swish, self).__init__()
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
return x * self.sigmoid(x)
NON_LINEARITY = {
'ReLU': nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
'Swish': Swish(),
}
def _RoundChannels(c, divisor=8, min_value=None):
if min_value is None:
min_value = divisor
new_c = max(min_value, int(c + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor)
if new_c < 0.9 * c:
new_c += divisor
return new_c
def _SplitChannels(channels, num_groups):
split_channels = [channels // num_groups for _ in range(num_groups)]
split_channels[0] += channels - sum(split_channels)
return split_channels
def Conv3x3Bn(in_channels, out_channels, stride, non_linear='ReLU'):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 3, stride, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
NON_LINEARITY[non_linear]
)
def Conv1x1Bn(in_channels, out_channels, non_linear='ReLU'):
return nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
NON_LINEARITY[non_linear]
)
class SqueezeAndExcite(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels, squeeze_channels, se_ratio):
super(SqueezeAndExcite, self).__init__()
squeeze_channels = squeeze_channels * se_ratio
if not squeeze_channels.is_integer():
raise ValueError('channels must be divisible by 1/ratio')
squeeze_channels = int(squeeze_channels)
self.se_reduce = nn.Conv2d(channels, squeeze_channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=True)
self.non_linear1 = NON_LINEARITY['Swish']
self.se_expand = nn.Conv2d(squeeze_channels, channels, 1, 1, 0, bias=True)
self.non_linear2 = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
y = torch.mean(x, (2, 3), keepdim=True)
y = self.non_linear1(self.se_reduce(y))
y = self.non_linear2(self.se_expand(y))
y = x * y
return y
class GroupedConv2d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0):
super(GroupedConv2d, self).__init__()
self.num_groups = len(kernel_size)
self.split_in_channels = _SplitChannels(in_channels, self.num_groups)
self.split_out_channels = _SplitChannels(out_channels, self.num_groups)
print(self.split_in_channels)
self.grouped_conv = nn.ModuleList()
for i in range(self.num_groups):
self.grouped_conv.append(nn.Conv2d(
self.split_in_channels[i],
self.split_out_channels[i],
kernel_size[i],
stride=stride,
padding=padding,
bias=False
))
def forward(self, x):
if self.num_groups == 1:
return self.grouped_conv[0](x)
x_split = torch.split(x, self.split_in_channels, dim=1)
x = [conv(t) for conv, t in zip(self.grouped_conv, x_split)]
x = torch.cat(x, dim=1)
return x
class MDConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels, kernel_size, stride):
super(MDConv, self).__init__()
self.num_groups = len(kernel_size)
self.split_channels = _SplitChannels(channels, self.num_groups)
self.mixed_depthwise_conv = nn.ModuleList()
for i in range(self.num_groups):
self.mixed_depthwise_conv.append(nn.Conv2d(
self.split_channels[i],
self.split_channels[i],
kernel_size[i],
stride=stride,
padding=kernel_size[i] // 2,
groups=self.split_channels[i],
bias=False
))
def forward(self, x):
if self.num_groups == 1:
return self.mixed_depthwise_conv[0](x)
x_split = torch.split(x, self.split_channels, dim=1)
x = [conv(t) for conv, t in zip(self.mixed_depthwise_conv, x_split)]
x = torch.cat(x, dim=1)
return x
class MixNetBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size=[3],
expand_ksize=[1],
project_ksize=[1],
stride=1,
expand_ratio=1,
non_linear='ReLU',
se_ratio=0.0
):
super(MixNetBlock, self).__init__()
expand = (expand_ratio != 1)
expand_channels = in_channels * expand_ratio
se = (se_ratio != 0.0)
self.residual_connection = (stride == 1 and in_channels == out_channels)
conv = []
if expand:
# expansion phase
pw_expansion = nn.Sequential(
GroupedConv2d(in_channels, expand_channels, expand_ksize),
nn.BatchNorm2d(expand_channels),
NON_LINEARITY[non_linear]
)
conv.append(pw_expansion)
# depthwise convolution phase
dw = nn.Sequential(
MDConv(expand_channels, kernel_size, stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(expand_channels),
NON_LINEARITY[non_linear]
)
conv.append(dw)
if se:
# squeeze and excite
squeeze_excite = SqueezeAndExcite(expand_channels, in_channels, se_ratio)
conv.append(squeeze_excite)
# projection phase
pw_projection = nn.Sequential(
GroupedConv2d(expand_channels, out_channels, project_ksize),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
)
conv.append(pw_projection)
self.conv = nn.Sequential(*conv)
def forward(self, x):
if self.residual_connection:
return x + self.conv(x)
else:
return self.conv(x)
class MixNet(nn.Module):
# [in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, expand_ksize, project_ksize, stride, expand_ratio, non_linear, se_ratio]
mixnet_s = [(16, 16, [3], [1], [1], 1, 1, 'ReLU', 0.0),
(16, 24, [3], [1, 1], [1, 1], 2, 6, 'ReLU', 0.0),
(24, 24, [3], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 3, 'ReLU', 0.0),
(24, 40, [3, 5, 7], [1], [1], 2, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(40, 40, [3, 5], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(40, 40, [3, 5], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(40, 40, [3, 5], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(40, 80, [3, 5, 7], [1], [1, 1], 2, 6, 'Swish', 0.25),
(80, 80, [3, 5], [1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.25),
(80, 80, [3, 5], [1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.25),
(80, 120, [3, 5, 7], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(120, 120, [3, 5, 7, 9], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 3, 'Swish', 0.5),
(120, 120, [3, 5, 7, 9], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 3, 'Swish', 0.5),
(120, 200, [3, 5, 7, 9, 11], [1], [1], 2, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(200, 200, [3, 5, 7, 9], [1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(200, 200, [3, 5, 7, 9], [1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.5)]
mixnet_m = [(24, 24, [3], [1], [1], 1, 1, 'ReLU', 0.0),
(24, 32, [3, 5, 7], [1, 1], [1, 1], 2, 6, 'ReLU', 0.0),
(32, 32, [3], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 3, 'ReLU', 0.0),
(32, 40, [3, 5, 7, 9], [1], [1], 2, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(40, 40, [3, 5], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(40, 40, [3, 5], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(40, 40, [3, 5], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(40, 80, [3, 5, 7], [1], [1], 2, 6, 'Swish', 0.25),
(80, 80, [3, 5, 7, 9], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.25),
(80, 80, [3, 5, 7, 9], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.25),
(80, 80, [3, 5, 7, 9], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.25),
(80, 120, [3], [1], [1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(120, 120, [3, 5, 7, 9], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 3, 'Swish', 0.5),
(120, 120, [3, 5, 7, 9], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 3, 'Swish', 0.5),
(120, 120, [3, 5, 7, 9], [1, 1], [1, 1], 1, 3, 'Swish', 0.5),
(120, 200, [3, 5, 7, 9], [1], [1], 2, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(200, 200, [3, 5, 7, 9], [1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(200, 200, [3, 5, 7, 9], [1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.5),
(200, 200, [3, 5, 7, 9], [1], [1, 1], 1, 6, 'Swish', 0.5)]
def __init__(self, net_type='mixnet_s', input_size=224, num_classes=1000, stem_channels=16, feature_size=1536,
depth_multiplier=1.0):
super(MixNet, self).__init__()
if net_type == 'mixnet_s':
config = self.mixnet_s
stem_channels = 16
dropout_rate = 0.2
elif net_type == 'mixnet_m':
config = self.mixnet_m
stem_channels = 24
dropout_rate = 0.25
elif net_type == 'mixnet_l':
config = self.mixnet_m
stem_channels = 24
depth_multiplier *= 1.3
dropout_rate = 0.25
else:
raise TypeError('Unsupported MixNet type')
assert input_size % 32 == 0
# depth multiplier
if depth_multiplier != 1.0:
stem_channels = _RoundChannels(stem_channels * depth_multiplier)
for i, conf in enumerate(config):
conf_ls = list(conf)
conf_ls[0] = _RoundChannels(conf_ls[0] * depth_multiplier)
conf_ls[1] = _RoundChannels(conf_ls[1] * depth_multiplier)
config[i] = tuple(conf_ls)
# stem convolution
self.stem_conv = Conv3x3Bn(3, stem_channels, 2)
# building MixNet blocks
layers = []
for in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, expand_ksize, project_ksize, stride, expand_ratio, non_linear, se_ratio in config:
layers.append(MixNetBlock(
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
expand_ksize=expand_ksize,
project_ksize=project_ksize,
stride=stride,
expand_ratio=expand_ratio,
non_linear=non_linear,
se_ratio=se_ratio
))
self.layers = nn.Sequential(*layers)
# last several layers
self.head_conv = Conv1x1Bn(config[-1][1], feature_size)
self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(input_size // 32, stride=1)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout_rate)
self.classifier = nn.Linear(feature_size, num_classes)
self._initialize_weights()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.stem_conv(x)
x = self.layers(x)
x = self.head_conv(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.dropout(x)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
def _initialize_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2.0 / n))
if m.bias is not None:
m.bias.data.zero_()
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
m.weight.data.fill_(1)
m.bias.data.zero_()
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
n = m.weight.size(1)
m.weight.data.normal_(0, 0.01)
m.bias.data.zero_()
if __name__ == '__main__':
net = MixNet()
x_image = Variable(torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224))
y = net(x_image)
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)