双目视觉标定,矫正,深度图(Vs +OpenCV C++ Python实现)
使用Opencv实现张正友法相机标定之前,有几个问题事先要确认一下,那就是相机为什么需要标定,标定需要的输入和输出分别是哪些?
相机标定的目的:获取摄像机的内参和外参矩阵(同时也会得到每一幅标定图像的选择和平移矩阵),内参和外参系数可以对之后相机拍摄的图像就进行矫正,得到畸变相对很小的图像。
相机标定的输入:标定图像上所有内角点的图像坐标,标定板图像上所有内角点的空间三维坐标(一般情况下假定图像位于Z=0平面上)。
相机标定的输出:摄像机的内参、外参系数。
这三个基础的问题就决定了使用Opencv实现张正友法标定相机的标定流程、标定结果评价以及使用标定结果矫正原始图像的完整流程:
1.准备标定图片
2.对每一张标定图片,提取角点信息
3.对每一张标定图片,进一步提取亚像素角点信息
4.在棋盘标定图上绘制找到的内角点(非必须,仅为了显示)
5.相机标定
6.对标定结果进行评价
7.查看标定效果——利用标定结果对棋盘图进行矫正
8.准备标定图片
1.准备标定图片
标定图片需要使用标定板在不同位置、不同角度、不同姿态下拍摄,最少需要3张,以10~20张为宜。标定板需要是黑白相间的矩形构成的棋盘图,制作精度要求较高,如下图所示:
2.对每一张标定图片,提取角点信息
//! finds checkerboard pattern of the specified size in the image
CV_EXPORTS_W bool findChessboardCorners( InputArray image, Size patternSize, OutputArray corners, int flags=CALIB_CB_ADAPTIVE_THRESH+CALIB_CB_NORMALIZE_IMAGE );
第一个参数Image,传入拍摄的棋盘图Mat图像,必须是8位的灰度或者彩色图像;
第二个参数patternSize,每个棋盘图上内角点的行列数,一般情况下,行列数不要相同,便于后续标定程序识别标定板的方向;
第三个参数corners,用于存储检测到的内角点图像坐标位置,一般用元素是Point2f的向量来表示:vector image_points_buf;
第四个参数flage:用于定义棋盘图上内角点查找的不同处理方式,有默认值。
3.对每一张标定图片,进一步提取亚像素角点信息
为了提高标定精度,需要在初步提取的角点信息上进一步提取亚像素信息,降低相机标定偏差,常用的方法是cornerSubPix,另一个方法是使用find4QuadCornerSubpix函数,这个方法是专门用来获取棋盘图上内角点的精确位置的,或许在相机标定的这个特殊场合下它的检测精度会比cornerSubPix更高?
cornerSubPix函数原型:
//! adjusts the corner locations with sub-pixel accuracy to maximize the certain cornerness criteria CV_EXPORTS_W void cornerSubPix( InputArray image, InputOutputArray corners, Size winSize, Size zeroZone,TermCriteria criteria );
第一个参数image,输入的Mat矩阵,最好是8位灰度图像,检测效率更高;
第二个参数corners,初始的角点坐标向量,同时作为亚像素坐标位置的输出,所以需要是浮点型数据,一般用元素是Pointf2f/Point2d的向量来表示:vector<Point2f/Point2d> iamgePointsBuf;
第三个参数winSize,大小为搜索窗口的一半;
第四个参数zeroZone,死区的一半尺寸,死区为不对搜索区的中央位置做求和运算的区域。它是用来避免自相关矩阵出现某些可能的奇异性。当值为(-1,-1)时表示没有死区;
第五个参数criteria,定义求角点的迭代过程的终止条件,可以为迭代次数和角点精度两者的组合;
find4QuadCornerSubpix函数原型:
//! finds subpixel-accurate positions of the chessboard cornersCV_EXPORTS bool find4QuadCornerSubpix(InputArray img, InputOutputArray corners, Size region_size);
第一个参数img,输入的Mat矩阵,最好是8位灰度图像,检测效率更高;
第二个参数corners,初始的角点坐标向量,同时作为亚像素坐标位置的输出,所以需要是浮点型数据,一般用元素是Pointf2f/Point2d的向量来表示:vector<Point2f/Point2d> iamgePointsBuf;
第三个参数region_size,角点搜索窗口的尺寸;
在其中一个标定的棋盘图上分别运行cornerSubPix和find4QuadCornerSubpix寻找亚像素角点,两者定位到的亚像素角点坐标分别为:
4. 在棋盘标定图上绘制找到的内角点(非必须,仅为了显示)
//! draws the checkerboard pattern (found or partly found) in the imageCV_EXPORTS_W void drawChessboardCorners( InputOutputArray image, Size patternSize, InputArray corners, bool patternWasFound );
第一个参数image,8位灰度或者彩色图像;
第二个参数patternSize,每张标定棋盘上内角点的行列数;
第三个参数corners,初始的角点坐标向量,同时作为亚像素坐标位置的输出,所以需要是浮点型数据,一般用元素是Pointf2f/Point2d的向量来表示:vector<Point2f/Point2d> iamgePointsBuf;
第四个参数patternWasFound,标志位,用来指示定义的棋盘内角点是否被完整的探测到,true表示别完整的探测到,函数会用直线依次连接所有的内角点,作为一个整体,false表示有未被探测到的内角点,这时候函数会以(红色)圆圈标记处检测到的内角点;
以下是drawChessboardCorners函数中第四个参数patternWasFound设置为true和false时内角点的绘制效果:
patternWasFound=ture时,依次连接各个内角点:
5. 相机标定
获取到棋盘标定图的内角点图像坐标之后,就可以使用calibrateCamera函数进行标定,计算相机内参和外参系数,
calibrateCamera函数原型:
//! finds intrinsic and extrinsic camera parameters from several fews of a known calibration pattern.
CV_EXPORTS_W double calibrateCamera( InputArrayOfArrays objectPoints,
InputArrayOfArrays imagePoints,
Size imageSize,
CV_OUT InputOutputArray cameraMatrix,
CV_OUT InputOutputArray distCoeffs,
OutputArrayOfArrays rvecs, OutputArrayOfArrays tvecs,
int flags=0, TermCriteria criteria = TermCriteria(
TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS, 30, DBL_EPSILON) );
第一个参数objectPoints,为世界坐标系中的三维点。在使用时,应该输入一个三维坐标点的向量的向量,即vector<vector> object_points。需要依据棋盘上单个黑白矩阵的大小,计算出(初始化)每一个内角点的世界坐标。
第二个参数imagePoints,为每一个内角点对应的图像坐标点。和objectPoints一样,应该输入vector<vector> image_points_seq形式的变量;
第三个参数imageSize,为图像的像素尺寸大小,在计算相机的内参和畸变矩阵时需要使用到该参数;
第四个参数cameraMatrix为相机的内参矩阵。输入一个Mat cameraMatrix即可,如Mat cameraMatrix=Mat(3,3,CV_32FC1,Scalar::all(0));
第五个参数distCoeffs为畸变矩阵。输入一个Mat distCoeffs=Mat(1,5,CV_32FC1,Scalar::all(0))即可;
第六个参数rvecs为旋转向量;应该输入一个Mat类型的vector,即vectorrvecs;
第七个参数tvecs为位移向量,和rvecs一样,应该为vector tvecs;
第八个参数flags为标定时所采用的算法。有如下几个参数:
CV_CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS:使用该参数时,在cameraMatrix矩阵中应该有fx,fy,u0,v0的估计值。否则的话,将初始化(u0,v0)图像的中心点,使用最小二乘估算出fx,fy。
CV_CALIB_FIX_PRINCIPAL_POINT:在进行优化时会固定光轴点。当CV_CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS参数被设置,光轴点将保持在中心或者某个输入的值。
CV_CALIB_FIX_ASPECT_RATIO:固定fx/fy的比值,只将fy作为可变量,进行优化计算。当CV_CALIB_USE_INTRINSIC_GUESS没有被设置,fx和fy将会被忽略。只有fx/fy的比值在计算中会被用到。
CV_CALIB_ZERO_TANGENT_DIST:设定切向畸变参数(p1,p2)为零。
CV_CALIB_FIX_K1,…,CV_CALIB_FIX_K6:对应的径向畸变在优化中保持不变。
CV_CALIB_RATIONAL_MODEL:计算k4,k5,k6三个畸变参数。如果没有设置,则只计算其它5个畸变参数。
第九个参数criteria是最优迭代终止条件设定。
在使用该函数进行标定运算之前,需要对棋盘上每一个内角点的空间坐标系的位置坐标进行初始化,标定的结果是生成相机的内参矩阵cameraMatrix、相机的5个畸变系数distCoeffs,另外每张图像都会生成属于自己的平移向量和旋转向量。
6. 对标定结果进行评价
对标定结果进行评价的方法是通过得到的摄像机内外参数,对空间的三维点进行重新投影计算,得到空间三维点在图像上新的投影点的坐标,计算投影坐标和亚像素角点坐标之间的偏差,偏差越小,标定结果越好。
对空间三维坐标点进行反向投影的函数是projectPoints,函数原型是:
//! projects points from the model coordinate space to the image coordinates. Also computes derivatives of the image coordinates w.r.t the intrinsic and extrinsic camera parameters
CV_EXPORTS_W void projectPoints( InputArray objectPoints,
InputArray rvec, InputArray tvec,
InputArray cameraMatrix, InputArray distCoeffs,
OutputArray imagePoints,
OutputArray jacobian=noArray(),
double aspectRatio=0 );
第一个参数objectPoints,为相机坐标系中的三维点坐标;
第二个参数rvec为旋转向量,每一张图像都有自己的选择向量;
第三个参数tvec为位移向量,每一张图像都有自己的平移向量;
第四个参数cameraMatrix为求得的相机的内参数矩阵;
第五个参数distCoeffs为相机的畸变矩阵;
第六个参数iamgePoints为每一个内角点对应的图像上的坐标点;
第七个参数jacobian是雅可比行列式;
第八个参数aspectRatio是跟相机传感器的感光单元有关的可选参数,如果设置为非0,则函数默认感光单元的dx/dy是固定的,会依此对雅可比矩阵进行调整;
下边显示了某一张标定图片上的亚像素角点坐标和根据标定结果把空间三维坐标点映射回图像坐标点的对比:
7. 查看标定效果——利用标定结果对棋盘图进行矫正
利用求得的相机的内参和外参数据,可以对图像进行畸变的矫正,这里有两种方法可以达到矫正的目的,分别说明一下。
方法一:使用initUndistortRectifyMap和remap两个函数配合实现。
initUndistortRectifyMap用来计算畸变映射,remap把求得的映射应用到图像上。
initUndistortRectifyMap的函数原型:
//! initializes maps for cv::remap() to correct lens distortion and optionally rectify the image
CV_EXPORTS_W void initUndistortRectifyMap( InputArray cameraMatrix, InputArray distCoeffs,
InputArray R, InputArray newCameraMatrix,
Size size, int m1type, OutputArray map1, OutputArray map2 );
第一个参数cameraMatrix为之前求得的相机的内参矩阵;
第二个参数distCoeffs为之前求得的相机畸变矩阵;
第三个参数R,可选的输入,是第一和第二相机坐标之间的旋转矩阵;
第四个参数newCameraMatrix,输入的校正后的3X3摄像机矩阵;
第五个参数size,摄像机采集的无失真的图像尺寸;
第六个参数m1type,定义map1的数据类型,可以是CV_32FC1或者CV_16SC2;
第七个参数map1和第八个参数map2,输出的X/Y坐标重映射参数;
remap函数原型:
//! warps the image using the precomputed maps. The maps are stored in either floating-point or integer fixed-point format
CV_EXPORTS_W void remap( InputArray src, OutputArray dst,
InputArray map1, InputArray map2,
int interpolation, int borderMode=BORDER_CONSTANT,
const Scalar& borderValue=Scalar());
第一个参数src,输入参数,代表畸变的原始图像;
第二个参数dst,矫正后的输出图像,跟输入图像具有相同的类型和大小;
第三个参数map1和第四个参数map2,X坐标和Y坐标的映射;
第五个参数interpolation,定义图像的插值方式;
第六个参数borderMode,定义边界填充方式;
方法二:使用undistort函数实现
undistort函数原型:
//! corrects lens distortion for the given camera matrix and distortion coefficients
CV_EXPORTS_W void undistort( InputArray src, OutputArray dst,
InputArray cameraMatrix,
InputArray distCoeffs,
InputArray newCameraMatrix=noArray() );
第一个参数src,输入参数,代表畸变的原始图像;
第二个参数dst,矫正后的输出图像,跟输入图像具有相同的类型和大小;
第三个参数cameraMatrix为之前求得的相机的内参矩阵;
第四个参数distCoeffs为之前求得的相机畸变矩阵;
第五个参数newCameraMatrix,默认跟cameraMatrix保持一致;
方法一相比方法二执行效率更高一些,推荐使用。
标定之前我们先写个拍照程序,python代码
import cv2
import time
AUTO = True # 自动拍照,或手动按s键拍照
INTERVAL = 2 # 自动拍照间隔
cv2.namedWindow("left")
cv2.namedWindow("right")
cv2.moveWindow("left", 0, 0)
cv2.moveWindow("right", 400, 0)
left_camera = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
right_camera = cv2.VideoCapture(1)
counter = 0
utc = time.time()
pattern = (12, 8) # 棋盘格尺寸
folder = "./snapshot/" # 拍照文件目录
def shot(pos, frame):
global counter
path = folder + pos + "_" + str(counter) + ".jpg"
cv2.imwrite(path, frame)
print("snapshot saved into: " + path)
while True:
ret, left_frame = left_camera.read()
ret, right_frame = right_camera.read()
cv2.imshow("left", left_frame)
cv2.imshow("right", right_frame)
now = time.time()
if AUTO and now - utc >= INTERVAL:
shot("left", left_frame)
shot("right", right_frame)
counter += 1
utc = now
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
if key == ord("q"):
break
elif key == ord("s"):
shot("left", left_frame)
shot("right", right_frame)
counter += 1
left_camera.release()
right_camera.release()
cv2.destroyWindow("left")
cv2.destroyWindow("right")
弄了半天解释,下面我们正式开始上完整代码 (c++标定):
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
void main()
{
ifstream fin("calibdata.txt"); /* 标定所用图像文件的路径 */
ofstream fout("caliberation_result.txt"); /* 保存标定结果的文件 */
//读取每一幅图像,从中提取出角点,然后对角点进行亚像素精确化
Mat img;
//img = imread("left01.jpg");
//cout << "hello";
//imshow("XIAORUN", img);
cout << "开始提取角点………………";
int image_count = 0; /* 图像数量 */
Size image_size; /* 图像的尺寸 */
Size board_size = Size(6, 9); /* 标定板上每行、列的角点数 */
vector<Point2f> image_points_buf; /* 缓存每幅图像上检测到的角点 */
vector<vector<Point2f>> image_points_seq; /* 保存检测到的所有角点 */
string filename;
int count = -1;//用于存储角点个数。
while (getline(fin, filename))
{
image_count++;
// 用于观察检验输出
cout << "image_count = " << image_count << endl;
/* 输出检验*/
cout << "-->count = " << count;
Mat imageInput = imread(filename);
//imshow("xiaorun", filename);
if (image_count == 1) //读入第一张图片时获取图像宽高信息
{
printf("hello");
image_size.width = imageInput.cols;
image_size.height = imageInput.rows;
cout << "image_size.width = " << image_size.width << endl;
cout << "image_size.height = " << image_size.height << endl;
}
/* 提取角点 */
if (0 == findChessboardCorners(imageInput, board_size, image_points_buf))
{
cout << "can not find chessboard corners!\n"; //找不到角点
printf("hello");
exit(1);
}
else
{
Mat view_gray;
cvtColor(imageInput, view_gray, CV_RGB2GRAY);
/* 亚像素精确化 */
find4QuadCornerSubpix(view_gray, image_points_buf, Size(11, 11)); //对粗提取的角点进行精确化
image_points_seq.push_back(image_points_buf); //保存亚像素角点
/* 在图像上显示角点位置 */
drawChessboardCorners(view_gray, board_size, image_points_buf, true); //用于在图片中标记角点
imshow("Camera Calibration", view_gray);//显示图片
//printf("world");
waitKey(500);//暂停0.5S
}
}
int total = image_points_seq.size();
cout << "total = " << total << endl;
int CornerNum = board_size.width*board_size.height; //每张图片上总的角点数
for (int ii = 0; ii<total; ii++)
{
if (0 == ii%CornerNum)// 24 是每幅图片的角点个数。此判断语句是为了输出 图片号,便于控制台观看
{
int i = -1;
i = ii / CornerNum;
int j = i + 1;
cout << "--> 第 " << j << "图片的数据 --> : " << endl;
}
if (0 == ii % 3) // 此判断语句,格式化输出,便于控制台查看
{
cout << endl;
}
else
{
cout.width(10);
}
//输出所有的角点
cout << " -->" << image_points_seq[ii][0].x;
cout << " -->" << image_points_seq[ii][0].y;
}
cout << "角点提取完成!\n";
//以下是摄像机标定
cout << "开始标定………………";
/*棋盘三维信息*/
Size square_size = Size(10, 10); /* 实际测量得到的标定板上每个棋盘格的大小 */
vector<vector<Point3f> > object_points; /* 保存标定板上角点的三维坐标 */
/*内外参数*/
//Mat cameraMatrix = Mat(3, 3, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0)); /* 摄像机内参数矩阵 */
Mat cameraMatrix = Mat(3, 3, CV_64F, Scalar::all(0)); /* 摄像机内参数矩阵 */
vector<int> point_counts; // 每幅图像中角点的数量
Mat distCoeffs = Mat(1, 5, CV_64F, Scalar::all(0)); /* 摄像机的5个畸变系数:k1,k2,p1,p2,k3 */
vector<Mat> tvecsMat; /* 每幅图像的旋转向量 */
vector<Mat> rvecsMat; /* 每幅图像的平移向量 */
/* 初始化标定板上角点的三维坐标 */
int i, j, t;
for (t = 0; t<image_count; t++)
{
vector<Point3f> tempPointSet;
for (i = 0; i<board_size.height; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j<board_size.width; j++)
{
Point3f realPoint;
/* 假设标定板放在世界坐标系中z=0的平面上 */
realPoint.x = i*square_size.width;
realPoint.y = j*square_size.height;
realPoint.z = 0;
tempPointSet.push_back(realPoint);
}
}
object_points.push_back(tempPointSet);
}
/* 初始化每幅图像中的角点数量,假定每幅图像中都可以看到完整的标定板 */
for (i = 0; i<image_count; i++)
{
point_counts.push_back(board_size.width*board_size.height);
}
/* 开始标定 */
calibrateCamera(object_points, image_points_seq, image_size, cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, rvecsMat, tvecsMat, 0);
cout << "标定完成!\n";
//对标定结果进行评价
cout << "开始评价标定结果………………\n";
double total_err = 0.0; /* 所有图像的平均误差的总和 */
double err = 0.0; /* 每幅图像的平均误差 */
vector<Point2f> image_points2; /* 保存重新计算得到的投影点 */
cout << "\t每幅图像的标定误差:\n";
fout << "每幅图像的标定误差:\n";
for (i = 0; i<image_count; i++)
{
vector<Point3f> tempPointSet = object_points[i];
/* 通过得到的摄像机内外参数,对空间的三维点进行重新投影计算,得到新的投影点 */
projectPoints(tempPointSet, rvecsMat[i], tvecsMat[i], cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, image_points2);
/* 计算新的投影点和旧的投影点之间的误差*/
vector<Point2f> tempImagePoint = image_points_seq[i];
Mat tempImagePointMat = Mat(1, tempImagePoint.size(), CV_32FC2);
Mat image_points2Mat = Mat(1, image_points2.size(), CV_32FC2);
for (int j = 0; j < tempImagePoint.size(); j++)
{
image_points2Mat.at<Vec2f>(0, j) = Vec2f(image_points2[j].x, image_points2[j].y);
tempImagePointMat.at<Vec2f>(0, j) = Vec2f(tempImagePoint[j].x, tempImagePoint[j].y);
}
err = norm(image_points2Mat, tempImagePointMat, NORM_L2);
total_err += err /= point_counts[i];
std::cout << "第" << i + 1 << "幅图像的平均误差:" << err << "像素" << endl;
fout << "第" << i + 1 << "幅图像的平均误差:" << err << "像素" << endl;
}
std::cout << "总体平均误差:" << total_err / image_count << "像素" << endl;
fout << "总体平均误差:" << total_err / image_count << "像素" << endl << endl;
std::cout << "评价完成!" << endl;
//保存定标结果
std::cout << "开始保存定标结果………………" << endl;
Mat rotation_matrix = Mat(3, 3, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0)); /* 保存每幅图像的旋转矩阵 */
fout << "相机内参数矩阵:" << endl;
fout << cameraMatrix << endl << endl;
fout << "畸变系数:\n";
fout << distCoeffs << endl << endl << endl;
for (int i = 0; i<image_count; i++)
{
fout << "第" << i + 1 << "幅图像的旋转向量:" << endl;
fout << tvecsMat[i] << endl;
/* 将旋转向量转换为相对应的旋转矩阵 */
Rodrigues(tvecsMat[i], rotation_matrix);
fout << "第" << i + 1 << "幅图像的旋转矩阵:" << endl;
fout << rotation_matrix << endl;
fout << "第" << i + 1 << "幅图像的平移向量:" << endl;
fout << rvecsMat[i] << endl << endl;
}
std::cout << "完成保存" << endl;
fout << endl;
system("pause");
return;
}
以下是我的工程目录图,我用的VS
在进行完立体标定后,我们将得到如下的数据:
每幅图像的标定误差:
第1幅图像的平均误差:0.0645257像素
第2幅图像的平均误差:0.0556487像素
第3幅图像的平均误差:0.0668032像素
第4幅图像的平均误差:0.0669439像素
第5幅图像的平均误差:0.0699647像素
第6幅图像的平均误差:0.0570037像素
第7幅图像的平均误差:0.0579455像素
第8幅图像的平均误差:0.0736451像素
第9幅图像的平均误差:0.0551833像素
第10幅图像的平均误差:0.0538387像素
第11幅图像的平均误差:0.0715703像素
第12幅图像的平均误差:0.0566535像素
第13幅图像的平均误差:0.0547182像素
总体平均误差:0.0618804像素
相机内参数矩阵:
[531.4017560022933, 0, 340.5121891820963;
0, 531.3698083055915, 232.0990886525732;
0, 0, 1]
畸变系数:
[-0.257272028772218, -0.1302531787363336, 0.0008829663197048428, -0.0006837432466250165, 0.5184868514845824]
第1幅图像的旋转向量:
[-28.89378134491334;
6.940661936528073;
167.1204988426566]
第1幅图像的旋转矩阵:
[0.9955462542172515, -0.09422195396417896, 0.003143104384498384;
0.09415810515313683, 0.9954210224680247, 0.01646934311632131;
-0.00468048586906741, -0.01610004409572948, 0.9998594309362416]
第1幅图像的平移向量:
[-2.948281786953482;
-0.01894177912098307;
0.4152828312972277]
第2幅图像的旋转向量:
[26.03544643046547;
43.91450787470743;
136.0862657817351]
第2幅图像的旋转矩阵:
[0.6825105514846874, -0.6756261709260313, 0.2787626665676329;
0.7111305927667627, 0.7019288669448416, -0.03986409136959795;
-0.1687383392808543, 0.2254443233025845, 0.9595322975009123]
第2幅图像的平移向量:
[-2.015742838932253;
1.703940309126829;
0.8331268576092087]
第3幅图像的旋转向量:
[-33.77454120034904;
5.743476206332025;
114.6452900299365]
第3幅图像的旋转矩阵:
[0.965621241947457, -0.2599369928735916, 0.002894276366398319;
0.2589247530787128, 0.9627310687215274, 0.07814641105919914;
-0.02309955287398991, -0.07471043470720912, 0.9969376919361017]
第3幅图像的平移向量:
[2.802519696251568;
0.5076535731226879;
-0.2745520274610763]
第4幅图像的旋转向量:
[-39.39511332708067;
23.70843751957927;
125.784028616703]
第4幅图像的旋转矩阵:
[-0.2746493468889726, -0.9353480887148267, -0.2229163277801369;
0.7900186121940573, -0.3516621879557613, 0.502199460323428;
-0.5481225489253625, -0.03817929412243534, 0.8355261892124484]
第4幅图像的平移向量:
[3.002234256141708;
-0.00400244227416397;
-0.3671838709588458]
第5幅图像的旋转向量:
[-24.66419344573827;
-33.35496576817189;
127.9981045127136]
第5幅图像的旋转矩阵:
[-0.7973055508582415, -0.4012524790882016, -0.4508883526952193;
0.5702727751718082, -0.7455077586910236, -0.3449741202312586;
-0.1977190442736369, -0.5321791331469685, 0.8232208390064367]
第5幅图像的平移向量:
[2.202107819324158;
1.745118658236513;
-0.5795807069710756]
第6幅图像的旋转向量:
[22.65481087785099;
-30.94432086018879;
154.5260983737024]
第6幅图像的旋转矩阵:
[-0.5031681185939065, -0.8628775660656608, 0.04758308955153689;
0.7780182281326339, -0.47627662896687, -0.4096928232143093;
0.376177459617167, -0.1691238560362068, 0.9109816903733131]
第6幅图像的平移向量:
[-1.842008361814392;
-2.052208601005723;
0.3800526676603065]
第7幅图像的旋转向量:
[-36.53410155359971;
-41.84414929889709;
171.0877268216408]
第7幅图像的旋转矩阵:
[-0.6205995951224508, 0.7679973189172715, -0.1582285077656138;
-0.6082734212882752, -0.5988575334947455, -0.5209348323263152;
-0.4948328884462981, -0.2270457502629647, 0.8388030995408999]
第7幅图像的平移向量:
[-1.733916815779325;
-2.391789747062651;
0.4528209495941528]
第8幅图像的旋转向量:
[-15.28243311989739;
-42.186329743771;
139.3718472606405]
第8幅图像的旋转矩阵:
[-0.3117727744769933, -0.8599284356641205, -0.4041297101565;
0.9396968574994601, -0.2161230350739815, -0.265067255080763;
0.1405971304847916, -0.4624001721957611, 0.8754533269414044]
第8幅图像的平移向量:
[1.878123485371093;
2.329063127619266;
-0.6472659033171607]
第9幅图像的旋转向量:
[-34.5076812436337;
17.05488837745683;
118.7499736578379]
第9幅图像的旋转矩阵:
[0.6990407940968939, 0.6903065696339664, -0.1865979852746805;
-0.7149197819557983, 0.6802228085739861, -0.1618228539607185;
0.01522082641178847, 0.2465233672816922, 0.9690173145137491]
第9幅图像的平移向量:
[-2.876120276333252;
-0.1957040007389426;
-0.6124122530079469]
第10幅图像的旋转向量:
[-21.20487737172965;
-34.20312037796457;
106.5638091288479]
第10幅图像的旋转矩阵:
[0.6988312675615038, -0.6614562825141631, -0.2722323379044556;
0.696333305265863, 0.7161479631838994, 0.04745548234999518;
0.1635689073629226, -0.2227278185366526, 0.9610606283653512]
第10幅图像的平移向量:
[2.066933913261819;
1.710771982627043;
0.6288999130379216]
第11幅图像的旋转向量:
[-29.04641580853675;
-38.50059779271402;
131.5069985192775]
第11幅图像的旋转矩阵:
[-0.2130220048767629, -0.8323873050727694, -0.5116180213713907;
0.9768802614895983, -0.171766038065828, -0.1272846529601369;
0.01807152872056927, -0.5269039784636864, 0.8497326740386298]
第11幅图像的平移向量:
[2.06198453711422;
2.022378057987192;
-0.469262913272761]
第12幅图像的旋转向量:
[-33.50658838699139;
-23.14254577539127;
124.8553718957804]
第12幅图像的旋转矩阵:
[0.8267797779285817, 0.5596059438392754, 0.05723972770828568;
-0.5429455504181263, 0.8204725811420597, -0.1789828843080928;
-0.1471235130409919, 0.1169013738749031, 0.9821856956281929]
第12幅图像的平移向量:
[-2.165238130223722;
-1.589828213544792;
-0.3561883069589877]
第13幅图像的旋转向量:
[-26.29312469675964;
-31.1157322108203;
105.1063346599477]
第13幅图像的旋转矩阵:
[0.935106092368815, 0.3438815383948325, 0.08556917415710266;
-0.3350443685383915, 0.9366013698695151, -0.1025823818657877;
-0.1154203930223587, 0.06725594033058423, 0.9910372199694687]
第13幅图像的平移向量:
[2.252597215040192;
1.846655046640037;
0.6334501170964321]
应用标定数据
我们使用如下的代码来将其配置到python中,上面的参数都是手动填写至下面的内容中的,这样免去保存成文件再去读取,在托运填写的时候要注意数据的对应位置。
# filename: camera_configs.py
import cv2
import numpy as np
left_camera_matrix = np.array([[824.93564, 0., 251.64723],
[0., 825.93598, 286.58058],
[0., 0., 1.]])
left_distortion = np.array([[0.23233, -0.99375, 0.00160, 0.00145, 0.00000]])
right_camera_matrix = np.array([[853.66485, 0., 217.00856],
[0., 852.95574, 269.37140],
[0., 0., 1.]])
right_distortion = np.array([[0.30829, -1.61541, 0.01495, -0.00758, 0.00000]])
om = np.array([0.01911, 0.03125, -0.00960]) # 旋转关系向量
R = cv2.Rodrigues(om)[0] # 使用Rodrigues变换将om变换为R
T = np.array([-70.59612, -2.60704, 18.87635]) # 平移关系向量
size = (640, 480) # 图像尺寸
# 进行立体更正
R1, R2, P1, P2, Q, validPixROI1, validPixROI2 = cv2.stereoRectify(left_camera_matrix, left_distortion,
right_camera_matrix, right_distortion, size, R,
T)
# 计算更正map
left_map1, left_map2 = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(left_camera_matrix, left_distortion, R1, P1, size, cv2.CV_16SC2)
right_map1, right_map2 = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(right_camera_matrix, right_distortion, R2, P2, size, cv2.CV_16SC2)
这样,我们得到了左右摄像头的两个map,并得到了立体的Q,这些参数都将应用于下面的转换成深度图中
转换成深度图
import numpy as np
import cv2
import camera_configs
cv2.namedWindow("left")
cv2.namedWindow("right")
cv2.namedWindow("depth")
cv2.moveWindow("left", 0, 0)
cv2.moveWindow("right", 600, 0)
cv2.createTrackbar("num", "depth", 0, 10, lambda x: None)
cv2.createTrackbar("blockSize", "depth", 5, 255, lambda x: None)
camera1 = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
camera2 = cv2.VideoCapture(1)
# 添加点击事件,打印当前点的距离
def callbackFunc(e, x, y, f, p):
if e == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:
print threeD[y][x]
cv2.setMouseCallback("depth", callbackFunc, None)
while True:
ret1, frame1 = camera1.read()
ret2, frame2 = camera2.read()
if not ret1 or not ret2:
break
# 根据更正map对图片进行重构
img1_rectified = cv2.remap(frame1, camera_configs.left_map1, camera_configs.left_map2, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
img2_rectified = cv2.remap(frame2, camera_configs.right_map1, camera_configs.right_map2, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
# 将图片置为灰度图,为StereoBM作准备
imgL = cv2.cvtColor(img1_rectified, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
imgR = cv2.cvtColor(img2_rectified, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 两个trackbar用来调节不同的参数查看效果
num = cv2.getTrackbarPos("num", "depth")
blockSize = cv2.getTrackbarPos("blockSize", "depth")
if blockSize % 2 == 0:
blockSize += 1
if blockSize < 5:
blockSize = 5
# 根据Block Maching方法生成差异图(opencv里也提供了SGBM/Semi-Global Block Matching算法,有兴趣可以试试)
stereo = cv2.StereoBM_create(numDisparities=16*num, blockSize=blockSize)
disparity = stereo.compute(imgL, imgR)
disp = cv2.normalize(disparity, disparity, alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U)
# 将图片扩展至3d空间中,其z方向的值则为当前的距离
threeD = cv2.reprojectImageTo3D(disparity.astype(np.float32)/16., camera_configs.Q)
cv2.imshow("left", img1_rectified)
cv2.imshow("right", img2_rectified)
cv2.imshow("depth", disp)
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
if key == ord("q"):
break
elif key == ord("s"):
cv2.imwrite("./snapshot/BM_left.jpg", imgL)
cv2.imwrite("./snapshot/BM_right.jpg", imgR)
cv2.imwrite("./snapshot/BM_depth.jpg", disp)
camera1.release()
camera2.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
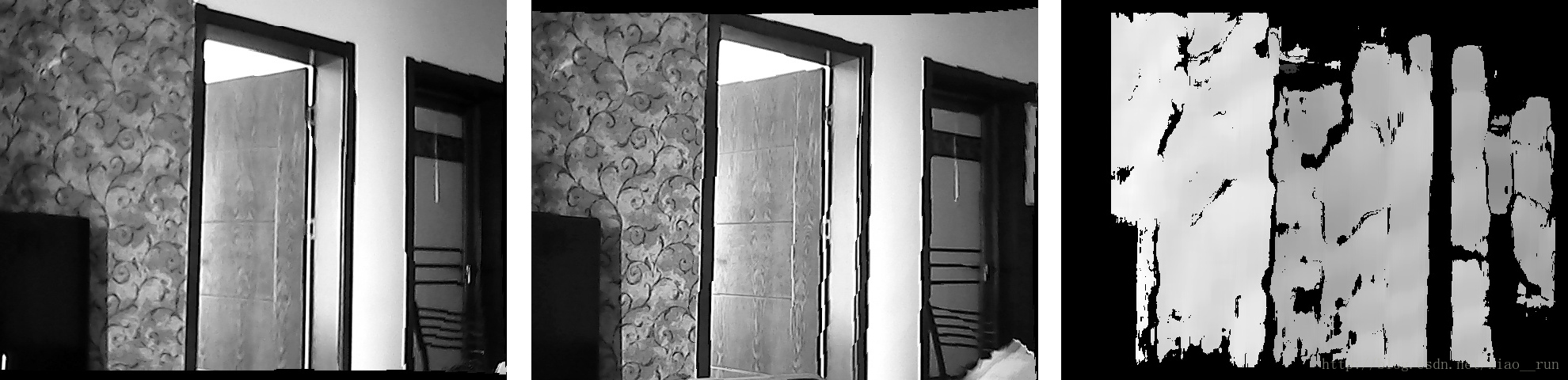
下面则是一附成像图,最右侧的为生成的disparity图,按照上面的代码,在图上点击则可以读取到该点的距离

- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)