虫子 栈 内核必备,基本算法,linux二次发育,项目远见
【摘要】 栈 栈的概念及结构 栈的实现 栈节点 栈初始化函数StackInit 入栈函数StackPush 栈销毁函数StackDestroy 出栈函数StackPop 判断栈是否为空 函数StackEmpty 取栈顶元素函数StackTop 栈大小函数StackSize 遍历栈 代码 Stack.h Stack.c test.c 练习 例1有效的括号 栈 栈的概念及结构栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允...
栈
栈的概念及结构
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在==固定的一端==进行插入和删除元素操作。==进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。==栈中的数据元素遵守==后进先出==LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,==入数据在栈顶==

出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。==出数据也在栈顶==

栈的实现
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,==相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的代价比较小。==
栈节点
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top; //栈顶
int capacity; //容量
}ST;
栈初始化函数StackInit

//栈初始化函数
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
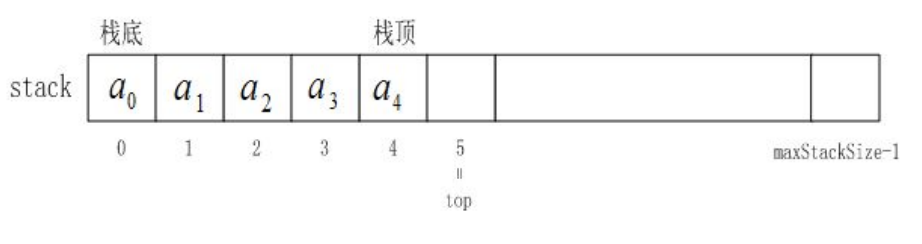
入栈函数StackPush
//入栈函数
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)//判断是否扩容
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a,newcapacity*sizeof(STDataType));
if (!tmp)
{
printf("relloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
//扩容扩好以后把数据给过去
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
==提前把栈销毁函数写好==
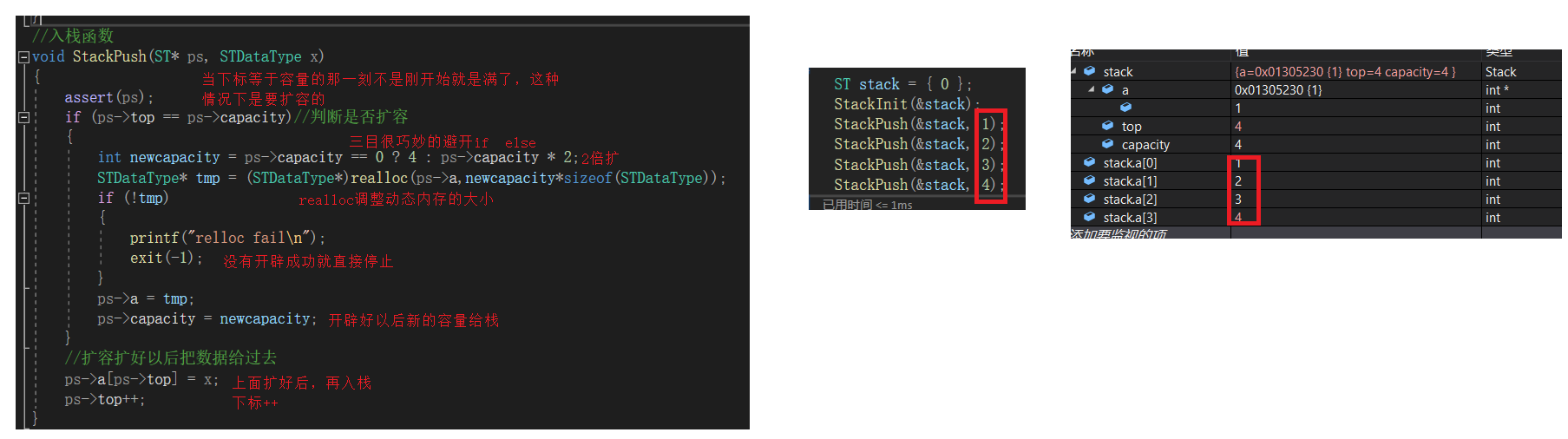
栈销毁函数StackDestroy
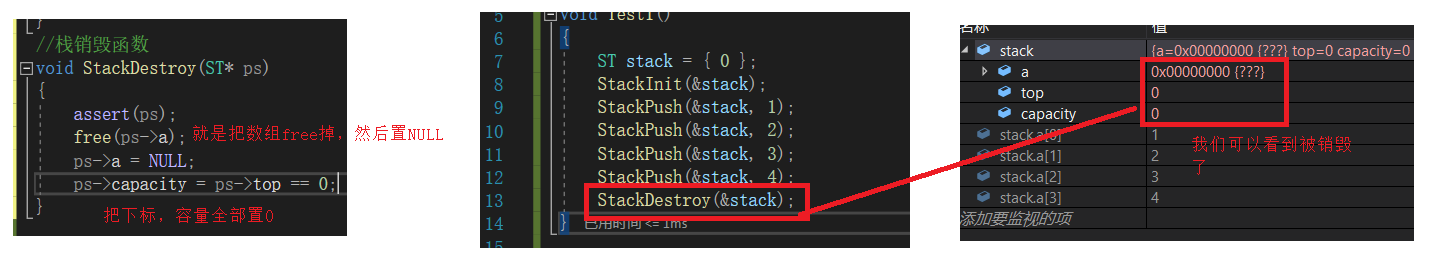
//栈销毁函数
void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
出栈函数StackPop
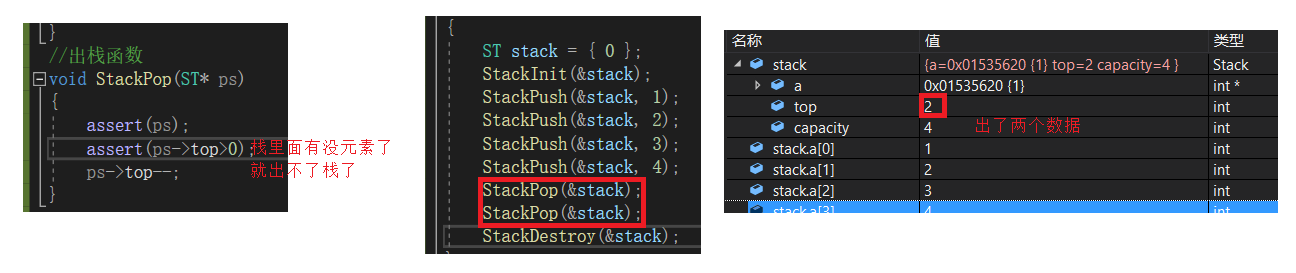
//出栈函数
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top>0);
ps->top--;
}
判断栈是否为空 函数StackEmpty
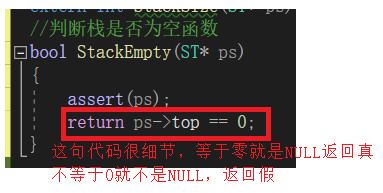
//判断栈是否为空函数
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
取栈顶元素函数StackTop
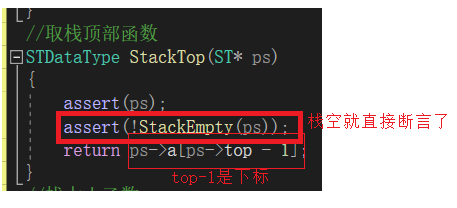
//取栈顶部函数
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
栈大小函数StackSize

//栈大小函数
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
遍历栈
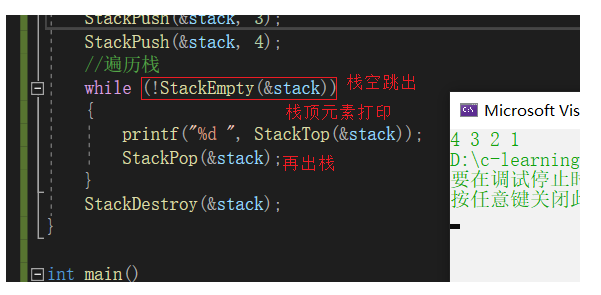
while (!StackEmpty(&stack))
{
printf("%d ", StackTop(&stack));
StackPop(&stack);
}
代码
Stack.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top; //栈顶
int capacity; //容量
}ST;
//栈初始化函数
extern void StackInit(ST* ps);
//栈销毁函数
extern void StackDestroy(ST* ps);
//入栈函数
extern void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
//出栈函数
extern void StackPop(ST* ps);
//取栈顶部函数
extern STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);
//栈大小函数
extern int StackSize(ST* ps);
//判断栈是否为空函数
extern bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);
Stack.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Stack.h"
//栈初始化函数
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
//入栈函数
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)//判断是否扩容
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a,newcapacity*sizeof(STDataType));
if (!tmp)
{
printf("relloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
//扩容扩好以后把数据给过去
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
//栈销毁函数
void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
//出栈函数
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top>0);
ps->top--;
}
//取栈顶部函数
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
//栈大小函数
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
//判断栈是否为空函数
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"Stack.h"
void Test1()
{
ST stack = { 0 };
StackInit(&stack);
StackPush(&stack, 1);
StackPush(&stack, 2);
StackPush(&stack, 3);
StackPush(&stack, 4);
//遍历栈
while (!StackEmpty(&stack))
{
printf("%d ", StackTop(&stack));
StackPop(&stack);
}
printf("\n");
StackDestroy(&stack);
}
int main()
{
Test1();
return 0;
}
练习
例1有效的括号
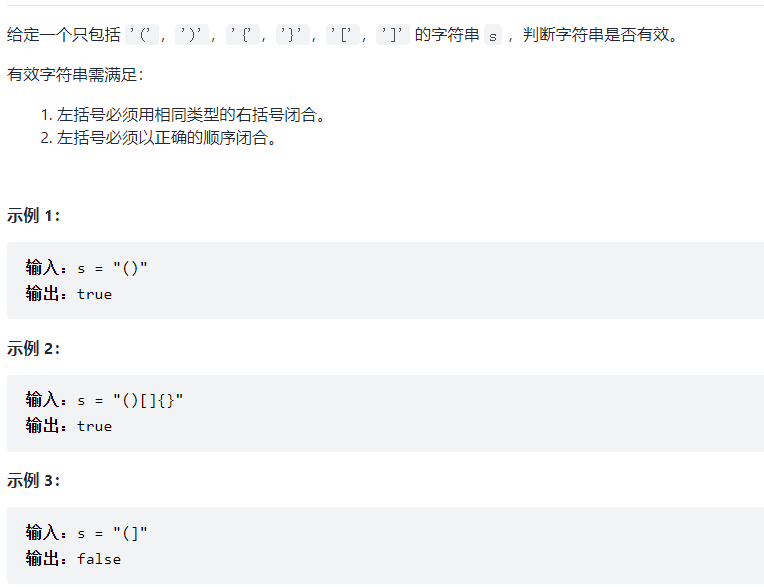

typedef char STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top; //栈顶
int capacity; //容量
}ST;
//栈初始化函数
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
//栈销毁函数
void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
//入栈函数
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)//判断是否扩容
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a,newcapacity*sizeof(STDataType));
if (!tmp)
{
printf("relloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
//扩容扩好以后把数据给过去
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
//判断栈是否为空函数
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
//取栈顶部函数
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
//出栈函数
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top>0);
ps->top--;
}
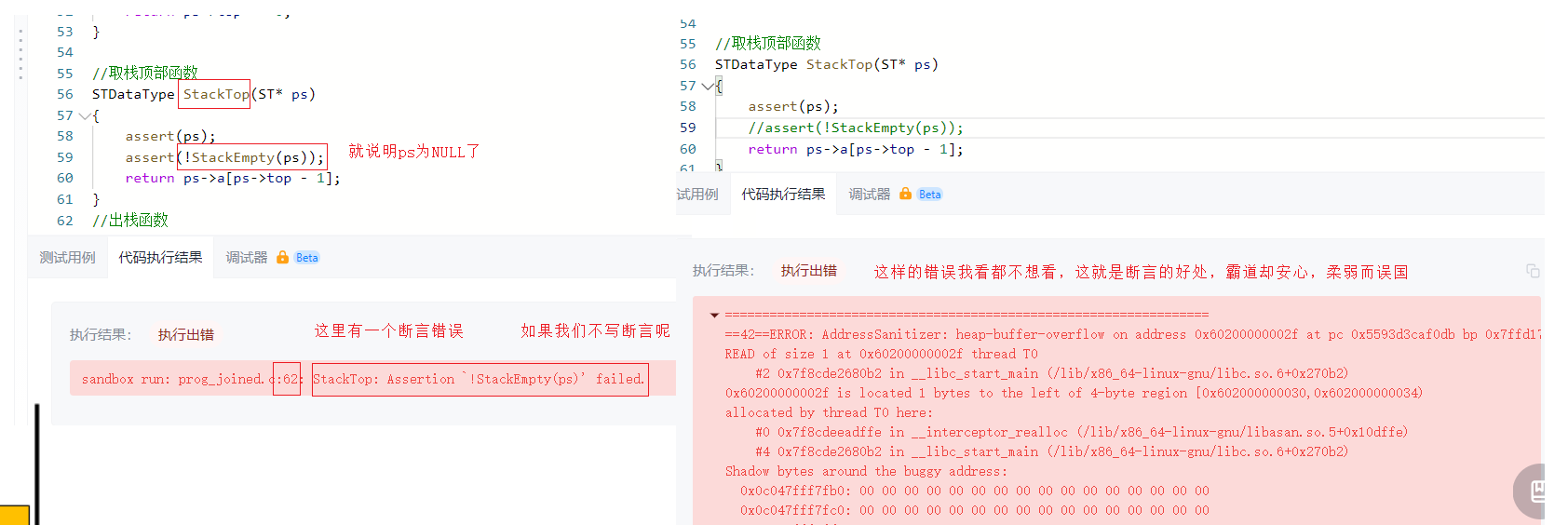
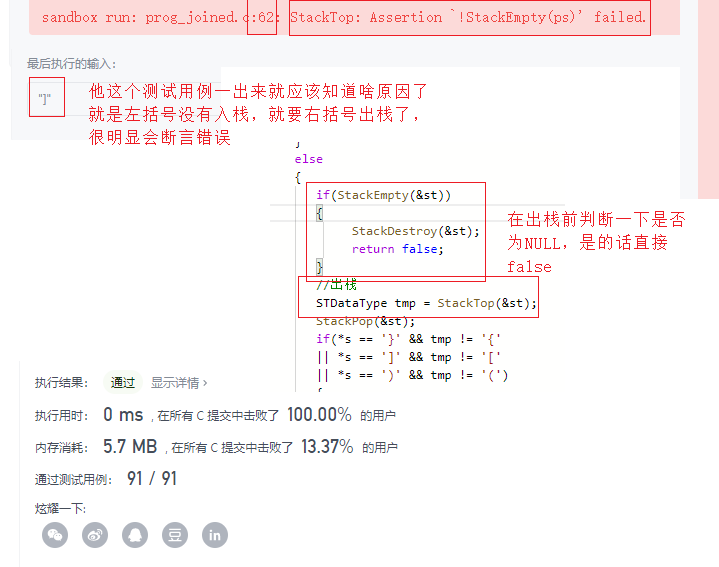
bool isValid(char * s){
ST st = {0};
StackInit(&st);
while(*s)
{
//如果是左括号就入栈
if(*s == '('
|| *s == '{'
|| *s == '[')
{
//入栈
StackPush(&st,*s);
s++;
}
else
{
if(StackEmpty(&st))
{
StackDestroy(&st);
return false;
}
//出栈
STDataType tmp = StackTop(&st);
StackPop(&st);
if(*s == '}' && tmp != '{'
|| *s == ']' && tmp != '['
|| *s == ')' && tmp != '(')
{
StackDestroy(&st);
return false;
}
else
{
s++;
}
}
}
//如果栈不是空说明还有左括号
bool ret = StackEmpty(&st);
StackDestroy(&st);
return ret;
}
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户原创内容,未经允许不得转载,如需转载请自行联系原作者进行授权。如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)