Python单例模式
【摘要】
单例模式
概念
"""
单例模式(Singleton Pattern)是一种常用的软件设计模式,该模式的主要目的是确保某一个类只有一个实例存在。
当你希望在整个系统中,某个类只能出现一个实例时,单例对...
单例模式
概念
"""
单例模式(Singleton Pattern)是一种常用的软件设计模式,该模式的主要目的是确保某一个类只有一个实例存在。
当你希望在整个系统中,某个类只能出现一个实例时,单例对象就能派上用场。
比如,某个服务器程序的配置信息存放在一个文件中,客户端通过一个 AppConfig 的类来读取配置文件的信息。
如果在程序运行期间,有很多地方都需要使用配置文件的内容,也就是说,很多地方都需要创建 AppConfig 对象的实例,
这就导致系统中存在多个 AppConfig 的实例对象,而这样会严重浪费内存资源,尤其是在配置文件内容很多的情况下。
事实上,类似 AppConfig 这样的类,我们希望在程序运行期间只存在一个实例对象。
"""
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
优点
当类只有一个实例而且客户可以从一个众所周知的访问点访问它时
比如:数据库链接、Socket创建链接
'''
对唯一实例的受控访问
单利相当于全局变量,但防止了命名空间被污染
与单利模式功能相似的概念:全局变量、静态变量(方法)
那为什么用单例模式,不用全局变量呢?
因为:全局变量可能会有名称空间的干扰,如果有重名的可能会被覆盖
'''
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
单例模式的实现
使用模块 (常用)
# 文件导入的形式
"""
Python 的模块就是天然的单例模式,因为模块在第一次导入时,会生成 .pyc 文件,当第二次导入时,
就会直接加载 .pyc 文件,而不会再次执行模块代码。因此,我们只需把相关的函数和数据定义在一个模块中,
就可以获得一个单例对象了。如果我们真的想要一个单例类,可以考虑这样做:
"""
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
# s1.py 文件中
class Foo(object):
def test(self):
print("123")
v = Foo()
# v是Foo的实例
------
# s2.py 文件中
from s1 import v as v1
print(v1,id(v1)) #<s1.Foo object at 0x0000000002221710> 35788560
from s1 import v as v2
print(v1,id(v2)) #<s1.Foo object at 0x0000000002221710> 35788560
# 两个的内存地址是一样的
# 文件加载的时候,第一次导入后,再次导入时不会再重新加载。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
基于 类 实现
# ======================单例模式:无法支持多线程情况===============
class Singleton(object):
def __init__(self):
import time
time.sleep(1)
@classmethod
def instance(cls, *args, **kwargs):
if not hasattr(Singleton, "_instance"):
Singleton._instance = Singleton(*args, **kwargs)
return Singleton._instance
import threading
def task(arg):
obj = Singleton.instance()
print(obj)
for i in range(10):
t = threading.Thread(target=task,args=[i,])
t.start()
'''
# 打印结果内存地址不一样,没有实现单例
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001FC58CFC5F8>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001FC58B72470>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001FC58CFC6D8>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001FC58D03048>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001FC58D3FDD8>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001FC58D40208>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001FC58D407B8>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001FC58D401D0>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001FC58D4A3C8>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001FC58D4A2E8>
'''
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
# ====================单例模式:支持多线程情况================、
import time
import threading
class Singleton(object):
_instance_lock = threading.Lock()
def __init__(self):
time.sleep(1)
@classmethod
def instance(cls, *args, **kwargs):
if not hasattr(Singleton, "_instance"):
with Singleton._instance_lock: # 为了保证线程安全在内部加锁
if not hasattr(Singleton, "_instance"):
Singleton._instance = Singleton(*args, **kwargs)
return Singleton._instance
# 加锁!未加锁部分并发执行,加锁部分串行执行,速度降低,但是保证了数据安全
def task(arg):
obj = Singleton.instance()
print(obj)
for i in range(10):
t = threading.Thread(target=task,args=[i,])
t.start()
time.sleep(20)
obj = Singleton.instance()
print(obj)
# 使用先说明,以后用单例模式,obj = Singleton.instance()
# 示例:
# obj1 = Singleton.instance()
# obj2 = Singleton.instance()
# print(obj1,obj2)
# 错误示例
# obj1 = Singleton()
# obj2 = Singleton()
# print(obj1,obj2)
'''
打印结果:
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001938A81A320>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001938A81A320>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001938A81A320>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001938A81A320>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001938A81A320>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001938A81A320>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001938A81A320>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001938A81A320>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001938A81A320>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001938A81A320>
'''
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
基于__new__实现的单例模式(最常用)
'''
通过上面例子,当我们实现单例时,为了保证线程安全需要在内部加入锁
当我们实例化一个对象时,是先执行了类的__new__方法(我们没写时,默认调用object.__new__),
实例化对象;然后再执行类的__init__方法,对这个对象进行初始化,
所有我们可以基于这个,实现单例模式
'''
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
# =============单线程下执行===============
import threading
class Singleton(object):
_instance_lock = threading.Lock()
def __init__(self):
pass
def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
if not hasattr(Singleton, "_instance"):
with Singleton._instance_lock:
if not hasattr(Singleton, "_instance"):
# 类加括号就回去执行__new__方法,__new__方法会创建一个类实例:Singleton()
Singleton._instance = object.__new__(cls) # 继承object类的__new__方法,类去调用方法,说明是函数,要手动传cls
return Singleton._instance #obj1
# 类加括号就会先去执行__new__方法,在执行__init__方法
# obj1 = Singleton()
# obj2 = Singleton()
# print(obj1,obj2)
# ===========多线程执行单利============
def task(arg):
obj = Singleton()
print(obj)
for i in range(10):
t = threading.Thread(target=task,args=[i,])
t.start()
# 使用先说明,以后用单例模式,obj = Singleton()
# 示例
# obj1 = Singleton()
# obj2 = Singleton()
# print(obj1,obj2)
'''
打印结果:
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001EBEF5E3E80>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001EBEF5E3E80>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001EBEF5E3E80>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001EBEF5E3E80>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001EBEF5E3E80>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001EBEF5E3E80>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001EBEF5E3E80>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001EBEF5E3E80>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001EBEF5E3E80>
<__main__.Singleton object at 0x000001EBEF5E3E80>
'''
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
基于metaclass(元类)实现的单例模式
"""
1.对象是类创建,创建对象时候类的__init__方法自动执行,
对象()执行类的 __call__ 方法
2.类是type创建,创建类时候type的__init__方法自动执行,
类() 执行type的 __call__方法(类的__new__方法,类的__init__方法)
# 第0步: 执行type的 __init__ 方法【类是type的对象】
class Foo:
def __init__(self):
pass
def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):
pass
# 第1步: 执行type的 __call__ 方法
# 1.1 调用 Foo类(是type的对象)的 __new__方法,用于创建对象。
# 1.2 调用 Foo类(是type的对象)的 __init__方法,用于对对象初始化。
obj = Foo()
# 第2步:执行Foo的 __call__ 方法
obj()
"""
# ===========类的执行流程================
class SingletonType(type):
def __init__(self,*args,**kwargs):
print(self) # 会不会打印? # <class '__main__.Foo'>
super(SingletonType,self).__init__(*args,**kwargs)
def __call__(cls, *args, **kwargs): #cls = Foo
obj = cls.__new__(cls, *args, **kwargs)
obj.__init__(*args, **kwargs)
return obj
class Foo(metaclass=SingletonType):
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
return object.__new__(cls, *args, **kwargs)
'''
1、对象是类创建的,创建对象时类的__init__方法会自动执行,
对象()执行类的__call__方法
2、类是type创建的,创建类时候type类的__init__方法会自动执行,
类()会先执行type的__call__方法(调用类的__new__,__init__方法)
Foo 这个类是由SingletonType这个类创建的
'''
obj = Foo("jaychou")
# ============第三种方式实现单例模式=================
import threading
class SingletonType(type):
_instance_lock = threading.Lock()
def __call__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
if not hasattr(cls, "_instance"):
with SingletonType._instance_lock:
if not hasattr(cls, "_instance"):
cls._instance = super(SingletonType,cls).__call__(*args, **kwargs)
return cls._instance
class Foo(metaclass=SingletonType):
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
obj1 = Foo('name')
obj2 = Foo('name')
print(obj1,obj2)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
metaclass(元类)详解
在Python3中继承type的就是元类
- 1

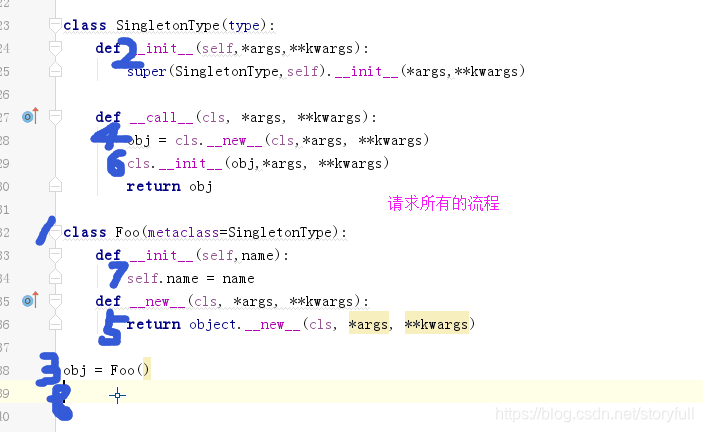
元类的示例:
- 1
# 方式一
class MyType(type):
'''继承type的就是元类'''
def __init__(self,*args,**kwargs):
print("MyType创建的对象",self) #Foo
super(MyType,self).__init__(*args,**kwargs)
def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):
obj = super(MyType,self).__call__(*args,**kwargs)
print("类创建对象",self,obj) #Foo
class Foo(object,metaclass=MyType): # 对象加括号会去执行__call__方法,__call__方法里面继承了type的__call__方法
,type的__call__方法里面会先执行__new__方法,再去执行__init__方法。
所以,Foo就是用type创建出来的
user = "haiyan"
age = 18
obj = Foo()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
# 方式二
class MyType(type):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
print("ssss")
super(MyType, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
def __call__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
v = dir(cls)
obj = super(MyType, cls).__call__(*args, **kwargs)
return obj
# 对象加括号就会去执行__call__方法
class Foo(MyType('Zcc', (object,), {})): # MyType('Zcc', (object,), {})相当于class Zcc(object):pass,也就是创建了一个Zcc的类
user = 'haiyan'
age = 18
obj = Foo()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
# 方式三
class MyType(type):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
print("ssss")
super(MyType, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
def __call__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
v = dir(cls)
obj = super(MyType, cls).__call__(*args, **kwargs)
return obj
# 对象加括号就会去执行__call__方法
def with_metaclass(arg,base):
print("类对象",MyType('Zcc', (base,), {}))
return arg('Zcc', (base,), {}) # 返回一个类对象 <class '__main__.Zcc'>
class Foo(with_metaclass(MyType,object)): # MyType('Zcc', (object,), {})相当于class Zcc(object):pass,也就是创建了一个Zcc的类
user = 'haiyan'
age = 18
obj = Foo()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
class ASD(type):
pass
qqq = ASD("qwe", (object,), {}) #用ASD这个元类创建了一个(qwe,并且继承object类的)类
# class ASD(qwe):
# pass
obj = qqq()
# 能创建类的是元类
# 能创建对象的是类
print(obj) # <__main__.qwe object at 0x00000000024FFBA8>
print(obj.__class__) # <class '__main__.qwe'>
print(obj.__class__.__class__) # <class '__main__.ASD'>
print(obj.__class__.__class__.__class__) # <class 'type'>
print(obj.__class__.__class__.__class__.__class__) # <class 'type'>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
装饰器 实现的单例模式
def Singleton(cls):
_instance = {}
def _singleton(*args, **kargs):
if cls not in _instance:
_instance[cls] = cls(*args, **kargs)
return _instance[cls]
return _singleton
@Singleton
class A(object):
a = 1
def __init__(self, x=0):
self.x = x
a1 = A(2)
a2 = A(3)
------
def wrapper(cls):
instance = {}
def inner(*args,**kwargs):
if cls not in instance:
instance[cls] = cls(*args,**kwargs)
return instance[cls]
return inner
@wrapper
class Singleton(object):
def __init__(self,name,age):
self.name = name
self.age = age
obj1 = Singleton('jaychou',22)
obj2 = Singleton('eason',22)
print(obj1)
print(obj2)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
单例模式的应用
单例模式的应用(在数据库连接池中用到单例模式)
import pymysql
import threading
from DBUtils.PooledDB import PooledDB
class SingletonDBPool(object):
_instance_lock = threading.Lock()
def __init__(self):
self.pool = PooledDB(
creator=pymysql, # 使用链接数据库的模块
maxconnections=6, # 连接池允许的最大连接数,0和None表示不限制连接数
mincached=2, # 初始化时,链接池中至少创建的空闲的链接,0表示不创建
maxcached=5, # 链接池中最多闲置的链接,0和None不限制
maxshared=3,
# 链接池中最多共享的链接数量,0和None表示全部共享。PS: 无用,因为pymysql和MySQLdb等模块的 threadsafety都为1,所有值无论设置为多少,_maxcached永远为0,所以永远是所有链接都共享。
blocking=True, # 连接池中如果没有可用连接后,是否阻塞等待。True,等待;False,不等待然后报错
maxusage=None, # 一个链接最多被重复使用的次数,None表示无限制
setsession=[], # 开始会话前执行的命令列表。如:["set datestyle to ...", "set time zone ..."]
ping=0,
# ping MySQL服务端,检查是否服务可用。# 如:0 = None = never, 1 = default = whenever it is requested, 2 = when a cursor is created, 4 = when a query is executed, 7 = always
host='127.0.0.1',
port=3306,
user='root',
password='123',
database='pooldb',
charset='utf8'
)
def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
if not hasattr(SingletonDBPool, "_instance"):
with SingletonDBPool._instance_lock:
if not hasattr(SingletonDBPool, "_instance"):
SingletonDBPool._instance = object.__new__(cls, *args, **kwargs)
return SingletonDBPool._instance
def connect(self):
return self.pool.connection()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:irrationality,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/weixin_54227557/article/details/122458562
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)