分别使用 TensorRT 和 CUDA 加速 MTCNN
Github 现有的 TensorRT 加速的 MTCNN 【PKUZHOU/MTCNN_FaceDetection_TensorRT】不是基于插件的,而是走了使用 scale 和 ReLU 、eltwise-sum 层 “曲线救国”的路线——

PKUZHOU 认为 PReLU 会破坏 TensorRT 的 CBR 优化,但实际上实现 PReLU 插件以后耗时更少,如图

左侧是“曲线救国”版,右侧是实现了 PReLU 插件,一张 1920x1080 的图像,能有200多 ms 的提升(原谅我笔记本的显卡是 GTX 970m,古老的 Maxwell 架构,连半精度都不支持,更别提 Int8 了,抹泪)。
插件的实现代码
prelu_plugn.h
-
#ifndef PRELU_PLUGIN_H
-
#define PRELU_PLUGIN_H
-
-
#include "kernels.h"
-
-
#include <cstring>
-
#include <assert.h>
-
-
#include <cuda.h>
-
#include <cuda_runtime_api.h>
-
#include <cuda_fp16.h> // __half
-
-
#include <NvInfer.h>
-
#include <NvCaffeParser.h>
-
-
using namespace nvinfer1;
-
using namespace nvcaffeparser1;
-
-
/*
-
Prelu layer
-
*/
-
class PreluPlugin : public IPlugin
-
{
-
public:
-
PreluPlugin(const Weights* weights, int nbWeights);
-
PreluPlugin(const void* buffer, size_t size);
-
~PreluPlugin();
-
-
Dims getOutputDimensions(int index, const Dims* inputs, int nbInputDims);
-
int enqueue(int batchSize, const void* const* inputs, void** outputs, void*, cudaStream_t stream);
-
int getNbOutputs() const override
-
{
-
return 1;
-
};
-
-
void configure(const Dims* inputs, int nbInputs, const Dims* outputs, int nbOutputs, int) override;
-
void serialize(void* buffer) override;
-
size_t getSerializationSize() override;
-
-
inline size_t getWorkspaceSize(int) const override
-
{
-
return 0;
-
}
-
-
int initialize() override;
-
-
void terminate() override;
-
-
protected:
-
int m_input_c;
-
int m_input_h;
-
int m_input_w;
-
int m_input_count;
-
bool m_channel_shared {false};
-
Weights m_weights;
-
void* m_device_kernel{nullptr};
-
-
private:
-
void deserializeToDevice(const char*& hostBuffer, void*& deviceWeights, size_t size)
-
{
-
deviceWeights = copyToDevice(hostBuffer, size);
-
hostBuffer += size;
-
}
-
-
// 将 host 的 buffer 上的值拷贝到 device (还会开辟设备内存)上
-
void* copyToDevice(const void* data, size_t count)
-
{
-
void* deviceData;
-
cudaMalloc(&deviceData, count);
-
cudaMemcpy(deviceData, data, count, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
-
return deviceData;
-
}
-
-
template<typename T> void read(const char*& buffer, T& val)
-
{
-
val = *reinterpret_cast<const T*>(buffer);
-
buffer += sizeof(T);
-
}
-
-
template<typename T> void write(char*& buffer, const T& val)
-
{
-
*reinterpret_cast<T*>(buffer) = val;
-
buffer += sizeof(T);
-
}
-
-
size_t type2size(nvinfer1::DataType type)
-
{
-
// return sizeof(float);
-
return type == nvinfer1::DataType::kFLOAT ? sizeof(float) : sizeof(__half);
-
}
-
-
// 将 Weights 的 values 中的值拷贝到 host 的 buffer 上
-
void convertAndCopyToBuffer(char*& buffer, const Weights& weights)
-
{
-
memcpy(buffer, weights.values, weights.count * type2size(weights.type));
-
buffer += weights.count * type2size(weights.type);
-
}
-
};
-
-
-
-
#endif // PRELU_PLUGIN_H
prelu_plugin.cpp
-
#include "prelu_plugin.h"
-
#include <iostream>
-
-
using namespace nvinfer1;
-
using namespace nvcaffeparser1;
-
//using namespace plugin;
-
-
PreluPlugin::PreluPlugin(const Weights* weights, int nbWeights)
-
{
-
assert(nbWeights == 1);
-
m_weights = weights[0];
-
assert(m_weights.type == DataType::kFLOAT || m_weights.type == DataType::kHALF);
-
// 为 values 开辟空间
-
m_weights.values = malloc(m_weights.count * type2size(m_weights.type));
-
// weights[0].values -> m_weights.values
-
memcpy(const_cast<void*>(m_weights.values), weights[0].values, m_weights.count * type2size(m_weights.type));
-
}
-
-
PreluPlugin::PreluPlugin(const void* buffer, size_t size)
-
{
-
// 反序列化:和序列化的顺序相同,注意不同的数据类型
-
const char* d = reinterpret_cast<const char*>(buffer), *a = d;
-
read<int>(d, m_input_c);
-
read<int>(d, m_input_h);
-
read<int>(d, m_input_w);
-
read<int>(d, m_input_count);
-
read<bool>(d, m_channel_shared);
-
read<int64_t>(d, m_weights.count);
-
read<DataType>(d, m_weights.type);
-
-
// m_weights.values = nullptr;
-
m_weights.values = malloc(m_weights.count * type2size(m_weights.type));
-
-
//deserializeToDevice(d,m_device_kernel,m_weights.count);
-
// d -> m_weights.values
-
memcpy(const_cast<void*>(m_weights.values), d, m_weights.count * type2size(m_weights.type));
-
d += m_weights.count * type2size(m_weights.type); // 指针继续向后
-
-
assert(d == a + size);
-
}
-
-
PreluPlugin::~PreluPlugin()
-
{
-
// std::cout << "~PreluPlugin "<< std::endl;
-
// if (m_weights.values)
-
// {
-
// free(const_cast<void*>(m_weights.values));
-
// }
-
}
-
-
// 仅在序列化时调用该方法
-
Dims PreluPlugin::getOutputDimensions(int index, const Dims* inputs, int nbInputDims)
-
{
-
// std::cout << "0~getOutputDimensions " << std::endl;
-
assert(index == 0 && nbInputDims == 1 && inputs[0].nbDims == 3);
-
return DimsCHW(inputs[0].d[0], inputs[0].d[1], inputs[0].d[2]);
-
}
-
-
// 仅在序列化时调用该方法
-
void PreluPlugin::configure(const Dims* inputs, int nbInputs, const Dims* outputs, int nbOutputs, int)
-
{
-
// std::cout << "1~configure " << std::endl;
-
m_input_c = inputs[0].d[0];
-
m_input_h = inputs[0].d[1];
-
m_input_w = inputs[0].d[2];
-
m_input_count = m_input_c * m_input_h * m_input_w;
-
}
-
-
size_t PreluPlugin::getSerializationSize()
-
{
-
return 4 * sizeof(int) + sizeof(bool) +
-
sizeof(m_weights.count)
-
+ sizeof(m_weights.type)
-
+ m_weights.count * type2size(m_weights.type);
-
}
-
-
void PreluPlugin::serialize(void* buffer)
-
{
-
char* d = static_cast<char*>(buffer), *a = d;
-
write(d, m_input_c);
-
write(d, m_input_h);
-
write(d, m_input_w);
-
write(d, m_input_count);
-
write(d, m_channel_shared);
-
write(d, m_weights.count);
-
write(d, m_weights.type);
-
-
convertAndCopyToBuffer(d, m_weights);
-
assert(d == a + getSerializationSize());
-
}
-
-
int PreluPlugin::enqueue(int batchSize, const void* const* inputs, void** outputs, void*, cudaStream_t stream)
-
{
-
const float* bottom_data = reinterpret_cast<const float*>(inputs[0]);
-
float* top_data = reinterpret_cast<float*>(outputs[0]);
-
-
const int count = batchSize * m_input_count;
-
const int dim = m_input_h * m_input_w;
-
const int channels = m_input_c;
-
const int div_factor = m_channel_shared ? channels : 1; //m_channel_shared default is false
-
-
pReLUForward(count, channels, dim, bottom_data, top_data, m_device_kernel, div_factor, stream);
-
-
return 0;
-
}
-
-
int PreluPlugin::initialize()
-
{
-
// std::cout << "2~initialize~0 "<< m_device_kernel << std::endl;
-
cudaMalloc(&m_device_kernel, m_weights.count * type2size(m_weights.type));
-
cudaMemcpy(m_device_kernel, m_weights.values, m_weights.count * type2size(m_weights.type), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
-
return 0;
-
}
-
-
// engine 销毁时会调用
-
void PreluPlugin::terminate()
-
{
-
// std::cout << "~terminate "<< m_device_kernel << std::endl;
-
-
if (m_weights.values)
-
{
-
free(const_cast<void*>(m_weights.values));
-
}
-
-
if (m_device_kernel)
-
{
-
cudaFree(m_device_kernel);
-
m_device_kernel = nullptr;
-
}
-
}
kernel.cu
-
__global__ void pReLU(const int n, const int channels, const int dim,
-
const float* in, float* out, const float* slope_data, const int div_factor)
-
{
-
CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(index, n)
-
{
-
int c = (index / dim) % channels / div_factor;
-
out[index] = in[index] > 0 ? in[index] : in[index] * slope_data[c];
-
}
-
}
-
-
void pReLUForward(const int count, const int channels, const int dim, const float* bottom_data,
-
float* top_data, void* mDeviceKernel, const int div_factor, cudaStream_t stream)
-
{
-
pReLU <<< CAFFE_GET_BLOCKS(count), CAFFE_CUDA_NUM_THREADS, 0, stream>>>(count, channels, dim,
-
bottom_data, top_data,
-
static_cast<const float*>(mDeviceKernel), // slope_data
-
div_factor);
-
-
CUDA_POST_KERNEL_CHECK;
-
}
继而通过 Valgrind 和 gProf 进行性能分析可以发现,


如果优化 nms 和 image2Matrix 方法的话,可以进一步提高性能;
由于多个 Pnet 的检测也是相互独立的,所以还可以使用多线程并行,然后多个流在 GPU (最好支持 HyperQ)上的 Overlap 可以再进一步提高性能。

上图是我没用 TensorRT,直接用原生的 CUDA 加速的效果,迭代 20 次,平均每次仅花费 60 ms 左右。
经过进一步优化纯 CUDA 的算法,一次迭代仅需 44 ms( 仍然是在 min_size = 30, thresh_p = 0.7, thresh_r = 0.7, thresh_o = 0.7, thresh_nms_p = 0.5, thresh_nms_r = 0.5, thresh_nms_o = 0.5 的条件下)
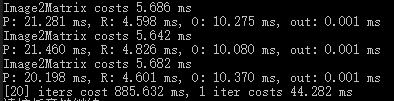
如果通过 TensorRT 加速应该会取得更优的性能。
最后是检测的结果:

文章来源: panda1234lee.blog.csdn.net,作者:panda1234lee,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:panda1234lee.blog.csdn.net/article/details/87201073
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)