注意力机制在CNN中使用总结
目录
2、SE-Net: Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks
摘要
计算机视觉(computer vision)中的注意力机制(attention)的基本思想就是想让系统学会注意力——能够忽略无关信息而关注重点信息。
注意力机制按照关注的域来分:
空间域(spatial domain)
通道域(channel domain)
层域(layer domain)
混合域(mixed domain)
时间域(time domain):还有另一种比较特殊的强注意力实现的注意力域,时间域(time domain),但是因为强注意力是使用reinforcement learning来实现的,训练起来有所不同
1、通道注意力机制和空间注意力机制
Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) 表示卷积模块的注意力机制模块。是一种结合了空间(spatial)和通道(channel)的注意力机制模块。相比于senet只关注通道(channel)的注意力机制可以取得更好的效果。

通道注意力:将输入的featuremap,分别经过基于width和height的global max pooling 和global average pooling,然后分别经过MLP。将MLP输出的特征进行基于elementwise的加和操作,再经过sigmoid激活操作,生成最终的channel attention featuremap。将该channel attention featuremap和input featuremap做elementwise乘法操作,生成Spatial attention模块需要的输入特征。


空间注意力:将Channel attention模块输出的特征图作为本模块的输入特征图。首先做一个基于channel的global max pooling 和global average pooling,然后将这2个结果基于channel 做concat操作。然后经过一个卷积操作,降维为1个channel。再经过sigmoid生成spatial attention feature。最后将该feature和该模块的输入feature做乘法,得到最终生成的特征。
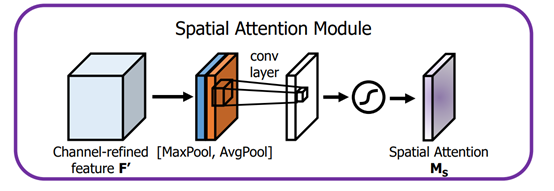
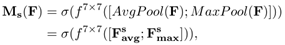
代码如下:
-
import torch.nn as nn
-
import math
-
try:
-
from torch.hub import load_state_dict_from_url
-
except ImportError:
-
from torch.utils.model_zoo import load_url as load_state_dict_from_url
-
import torch
-
#通道注意力机制
-
class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):
-
def __init__(self, in_planes, ratio=16):
-
super(ChannelAttention, self).__init__()
-
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
-
self.max_pool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d(1)
-
-
self.fc1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, in_planes // 16, 1, bias=False)
-
self.relu1 = nn.ReLU()
-
self.fc2 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes // 16, in_planes, 1, bias=False)
-
-
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
-
-
def forward(self, x):
-
avg_out = self.fc2(self.relu1(self.fc1(self.avg_pool(x))))
-
max_out = self.fc2(self.relu1(self.fc1(self.max_pool(x))))
-
out = avg_out + max_out
-
return self.sigmoid(out)
-
-
-
#空间注意力机制
-
class SpatialAttention(nn.Module):
-
def __init__(self, kernel_size=7):
-
super(SpatialAttention, self).__init__()
-
-
assert kernel_size in (3, 7), 'kernel size must be 3 or 7'
-
padding = 3 if kernel_size == 7 else 1
-
-
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(2, 1, kernel_size, padding=padding, bias=False)
-
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
-
-
def forward(self, x):
-
avg_out = torch.mean(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
-
max_out, _ = torch.max(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
-
x = torch.cat([avg_out, max_out], dim=1)
-
x = self.conv1(x)
-
return self.sigmoid(x)
使用举例,在Resnet网络中添加注意力机制
-
class ResNet(nn.Module):
-
-
def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=1000, zero_init_residual=False,
-
groups=1, width_per_group=64, replace_stride_with_dilation=None,
-
norm_layer=None):
-
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
-
if norm_layer is None:
-
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
-
self._norm_layer = norm_layer
-
-
self.inplanes = 64
-
self.dilation = 1
-
if replace_stride_with_dilation is None:
-
# each element in the tuple indicates if we should replace
-
# the 2x2 stride with a dilated convolution instead
-
replace_stride_with_dilation = [False, False, False]
-
if len(replace_stride_with_dilation) != 3:
-
raise ValueError("replace_stride_with_dilation should be None "
-
"or a 3-element tuple, got {}".format(replace_stride_with_dilation))
-
self.groups = groups
-
self.base_width = width_per_group
-
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.inplanes, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3,
-
bias=False)
-
self.bn1 = norm_layer(self.inplanes)
-
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
-
-
# 网络的第一层加入注意力机制
-
self.ca = ChannelAttention(self.inplanes)
-
self.sa = SpatialAttention()
-
-
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
-
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0])
-
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2,
-
dilate=replace_stride_with_dilation[0])
-
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2,
-
dilate=replace_stride_with_dilation[1])
-
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2,
-
dilate=replace_stride_with_dilation[2])
-
# 网络的卷积层的最后一层加入注意力机制
-
self.ca1 = ChannelAttention(self.inplanes)
-
self.sa1 = SpatialAttention()
-
-
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
-
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
-
-
for m in self.modules():
-
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
-
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
-
elif isinstance(m, (nn.BatchNorm2d, nn.GroupNorm)):
-
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
-
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
-
-
# Zero-initialize the last BN in each residual branch,
-
# so that the residual branch starts with zeros, and each residual block behaves like an identity.
-
# This improves the model by 0.2~0.3% according to https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.02677
-
if zero_init_residual:
-
for m in self.modules():
-
if isinstance(m, Bottleneck):
-
nn.init.constant_(m.bn3.weight, 0)
-
elif isinstance(m, BasicBlock):
-
nn.init.constant_(m.bn2.weight, 0)
-
-
def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, dilate=False):
-
norm_layer = self._norm_layer
-
downsample = None
-
previous_dilation = self.dilation
-
if dilate:
-
self.dilation *= stride
-
stride = 1
-
if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
-
downsample = nn.Sequential(
-
conv1x1(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion, stride),
-
norm_layer(planes * block.expansion),
-
)
-
-
layers = []
-
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample, self.groups,
-
self.base_width, previous_dilation, norm_layer))
-
self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
-
for _ in range(1, blocks):
-
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, groups=self.groups,
-
base_width=self.base_width, dilation=self.dilation,
-
norm_layer=norm_layer))
-
-
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
-
-
def forward(self, x):
-
x = self.conv1(x)
-
x = self.bn1(x)
-
x = self.relu(x)
-
-
x = self.ca(x) * x
-
x = self.sa(x) * x
-
-
x = self.maxpool(x)
-
-
x = self.layer1(x)
-
x = self.layer2(x)
-
x = self.layer3(x)
-
x = self.layer4(x)
-
-
x = self.ca1(x) * x
-
x = self.sa1(x) * x
-
-
-
x = self.avgpool(x)
-
x = x.reshape(x.size(0), -1)
-
x = self.fc(x)
-
-
return x
注意点:因为不能改变ResNet的网络结构,所以CBAM不能加在block里面,因为加进去网络结构发生了变化,所以不能用预训练参数。加在最后一层卷积和第一层卷积不改变网络,可以用预训练参数。
添加位置:
-
# 网络的第一层加入注意力机制
-
self.ca = ChannelAttention(self.inplanes)
-
self.sa = SpatialAttention()
和
-
# 网络的卷积层的最后一层加入注意力机制
-
self.ca1 = ChannelAttention(self.inplanes)
-
self.sa1 = SpatialAttention()
forWord部分代码
-
x = self.ca(x) * x
-
x = self.sa(x) * x
-
-
x = self.maxpool(x)
-
-
x = self.layer1(x)
-
x = self.layer2(x)
-
x = self.layer3(x)
-
x = self.layer4(x)
-
-
x = self.ca1(x) * x
-
x = self.sa1(x) * x
2、SE-Net: Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.01507
代码地址:https://github.com/hujie-frank/SENet
PyTorch代码地址:https://github.com/miraclewkf/SENet-PyTorch
SE-Net赢得了最后一届ImageNet 2017竞赛分类任务的冠军,其基本原理是对于每个输出channel,预测一个常数权重,对每个channel加权一下。结构如下图:

第一步每个通道H*W个数全局平均池化得到一个标量,称之为Squeeze,然后两个FC得到01之间的一个权重值,对原始的每个HxW的每个元素乘以对应通道的权重,得到新的feature map,称之为Excitation。任意的原始网络结构,都可以通过这个Squeeze-Excitation的方式进行feature recalibration,如下图。

具体实现上就是一个Global Average Pooling-FC-ReLU-FC-Sigmoid,第一层的FC会把通道降下来,然后第二层FC再把通道升上去,得到和通道数相同的C个权重,每个权重用于给对应的一个通道进行加权。上图中的r就是缩减系数,实验确定选取16,可以得到较好的性能并且计算量相对较小。SENet的核心思想在于通过网络根据loss去学习特征权重,使得有效的feature map权重大,无效或效果小的feature map权重小的方式训练模型达到更好的结果。
SE模块的实现
这里给出PyTorch版本的实现(参考senet.pytorch):
-
class SELayer(nn.Module):
-
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=16):
-
super(SELayer, self).__init__()
-
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
-
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
-
nn.Linear(channel, channel // reduction, bias=False),
-
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
-
nn.Linear(channel // reduction, channel, bias=False),
-
nn.Sigmoid()
-
)
-
-
def forward(self, x):
-
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
-
y = self.avg_pool(x).view(b, c)
-
y = self.fc(y).view(b, c, 1, 1)
-
return x * y.expand_as(x)
将SE模块用在Resnet网络,只需要将SE模块加入到残差单元(应用在残差学习那一部分)就可以:
-
class SEBottleneck(nn.Module):
-
expansion = 4
-
-
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, reduction=16):
-
super(SEBottleneck, self).__init__()
-
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
-
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
-
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
-
padding=1, bias=False)
-
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
-
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes * 4, kernel_size=1, bias=False)
-
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * 4)
-
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
-
self.se = SELayer(planes * 4, reduction)
-
self.downsample = downsample
-
self.stride = stride
-
-
def forward(self, x):
-
residual = x
-
-
out = self.conv1(x)
-
out = self.bn1(out)
-
out = self.relu(out)
-
-
out = self.conv2(out)
-
out = self.bn2(out)
-
out = self.relu(out)
-
-
out = self.conv3(out)
-
out = self.bn3(out)
-
out = self.se(out)
-
-
if self.downsample is not None:
-
residual = self.downsample(x)
-
-
out += residual
-
out = self.relu(out)
-
-
return out
SE的另一种实现方式
该方式使用卷积替代全连接。
-
class SEBlock(nn.Module):
-
-
-
-
def __init__(self, input_channels, internal_neurons):
-
-
super(SEBlock, self).__init__()
-
-
self.down = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=input_channels, out_channels=internal_neurons, kernel_size=1, stride=1,
-
-
bias=True, padding_mode='same')
-
-
self.up = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=internal_neurons, out_channels=input_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1,
-
-
bias=True, padding_mode='same')
-
-
-
-
def forward(self, inputs):
-
-
x = F.avg_pool2d(inputs, kernel_size=inputs.size(3))
-
-
x = self.down(x)
-
-
x = F.leaky_relu(x)
-
-
x = self.up(x)
-
-
x = F.sigmoid(x)
-
-
x = x.repeat(1, 1, inputs.size(2), inputs.size(3))
-
-
return inputs * x
3、轻量模块ECANet(通道注意力超强改进)
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.03151
代码地址:https://github.com/BangguWu/ECANet
论文翻译:https://wanghao.blog.csdn.net/article/details/113073026
ECANet主要对SENet模块进行了一些改进,提出了一种不降维的局部跨信道交互策略(ECA模块)和自适应选择一维卷积核大小的方法,从而实现了性能上的提优。
ECANet的实现:
-
class eca_layer(nn.Module):
-
"""Constructs a ECA module.
-
Args:
-
channel: Number of channels of the input feature map
-
k_size: Adaptive selection of kernel size
-
"""
-
def __init__(self, channel, k_size=3):
-
super(eca_layer, self).__init__()
-
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
-
self.conv = nn.Conv1d(1, 1, kernel_size=k_size, padding=(k_size - 1) // 2, bias=False)
-
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
-
-
def forward(self, x):
-
# x: input features with shape [b, c, h, w]
-
b, c, h, w = x.size()
-
-
# feature descriptor on the global spatial information
-
y = self.avg_pool(x)
-
-
# Two different branches of ECA module
-
y = self.conv(y.squeeze(-1).transpose(-1, -2)).transpose(-1, -2).unsqueeze(-1)
-
-
# Multi-scale information fusion
-
y = self.sigmoid(y)
-
-
return x * y.expand_as(x)
ECANet在模型中的调用
-
channelNum=64
-
class CRBlock(nn.Module):
-
def __init__(self):
-
super(CRBlock, self).__init__()
-
self.convban = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
-
("conv3x3_bn", ConvBN(channelNum, channelNum, 3)),
-
]))
-
self.path1 = Encoder_conv(channelNum, 2)
-
self.path2 = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
-
('conv1x5', ConvBN(channelNum, channelNum, [1, 3])),
-
('conv5x1', ConvBN(channelNum, channelNum, 3)),
-
('ac', ACBlock(channelNum, channelNum, kernel_size=3)),
-
('eca', eca_layer(channelNum, 3)),
-
# ('ac', ACBlock(channelNum, channelNum, kernel_size=3)),
-
]))
-
self.path2 = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
-
('conv1x5', ConvBN(channelNum, channelNum, [1, 5])),
-
('conv5x1', ConvBN(channelNum, channelNum, [5, 1])),
-
("conv9x1_bn", ConvBN(channelNum, channelNum, 1)),
-
('eca', eca_layer(channelNum, 3)),
-
]))
-
self.encoder_conv = Encoder_conv(channelNum * 4)
-
self.encoder_conv1 = ConvBN(channelNum * 4, channelNum, 1)
-
self.identity = nn.Identity()
-
self.relu = Mish()
-
self.ca1 = eca_layer(channelNum * 4, 3)
-
# self.ca2 = eca_layer(channelNum*4, 1)
-
-
def forward(self, x):
-
identity = self.identity(x)
-
x = self.convban(x)
-
out1 = self.path1(x)
-
out2 = self.path2(x)
-
out3 = self.path2(x)
-
out = torch.cat((out1, out2, out3, x), dim=1)
-
out = self.relu(out)
-
out = self.encoder_conv(out)
-
out = self.ca1(out)
-
out = self.encoder_conv1(out)
-
out = self.relu(out + identity)
-
return out
4、Coordinate Attention
论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.02907
代码链接:https://github.com/Andrew-Qibin/CoordAttention
Coordinate Attention通过精确的位置信息对通道关系和长期依赖性进行编码,具体操作分为Coordinate信息嵌入和Coordinate Attention生成2个步骤。
网络结构如下图:

详见:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/zQoo_IRfqVa2WzFOU_de1Q
Coordinate Attention的pytorch实现。
-
import torch
-
from torch import nn
-
-
-
class CA_Block(nn.Module):
-
def __init__(self, channel, h, w, reduction=16):
-
super(CA_Block, self).__init__()
-
-
self.h = h
-
self.w = w
-
-
self.avg_pool_x = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((h, 1))
-
self.avg_pool_y = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, w))
-
-
self.conv_1x1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=channel, out_channels=channel//reduction, kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False)
-
-
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
-
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(channel//reduction)
-
-
self.F_h = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=channel//reduction, out_channels=channel, kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False)
-
self.F_w = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=channel//reduction, out_channels=channel, kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False)
-
-
self.sigmoid_h = nn.Sigmoid()
-
self.sigmoid_w = nn.Sigmoid()
-
-
def forward(self, x):
-
-
x_h = self.avg_pool_x(x).permute(0, 1, 3, 2)
-
x_w = self.avg_pool_y(x)
-
-
x_cat_conv_relu = self.relu(self.conv_1x1(torch.cat((x_h, x_w), 3)))
-
-
x_cat_conv_split_h, x_cat_conv_split_w = x_cat_conv_relu.split([self.h, self.w], 3)
-
-
s_h = self.sigmoid_h(self.F_h(x_cat_conv_split_h.permute(0, 1, 3, 2)))
-
s_w = self.sigmoid_w(self.F_w(x_cat_conv_split_w))
-
-
out = x * s_h.expand_as(x) * s_w.expand_as(x)
-
-
return out
-
-
-
if __name__ == '__main__':
-
x = torch.randn(1, 16, 128, 64) # b, c, h, w
-
ca_model = CA_Block(channel=16, h=128, w=64)
-
y = ca_model(x)
-
print(y.shape)
参考文章:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/99261200?from=singlemessage
https://blog.csdn.net/chanbo8205/article/details/110880273
文章来源: wanghao.blog.csdn.net,作者:AI浩,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:wanghao.blog.csdn.net/article/details/114449042
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)