MongoDB最简单的入门教程之五-通过Restful API访问MongoDB
通过前面四篇的学习,我们已经在本地安装了一个MongoDB数据库,并且通过一个简单的Spring boot应用的单元测试,插入了几条记录到MongoDB中,并通过MongoDB Compass查看到了插入的数据。
本文我们更进一步,通过Spring Boot构造出Restful API,这样可以直接在浏览器里通过调用Restful API对Spring Boot进行增删查改了。

先看效果,假设我本地MongoDB的数据库里有一张表book,只有一条记录,id为1。
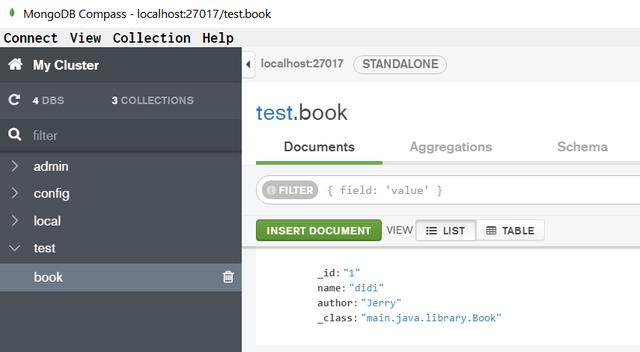
通过浏览器里的这个url根据id读取该记录:http://localhost:8089/bookmanage/read?id=1
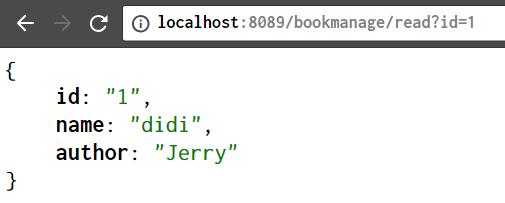
记录的创建:
http://localhost:8089/bookmanage/create?id=2&name=Spring&author=Jerry
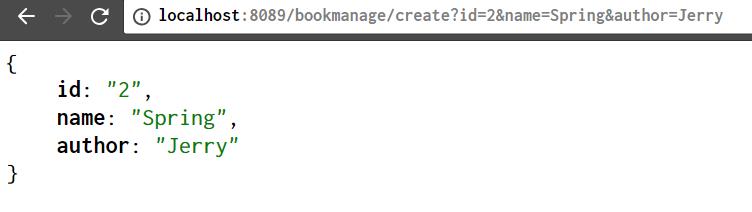
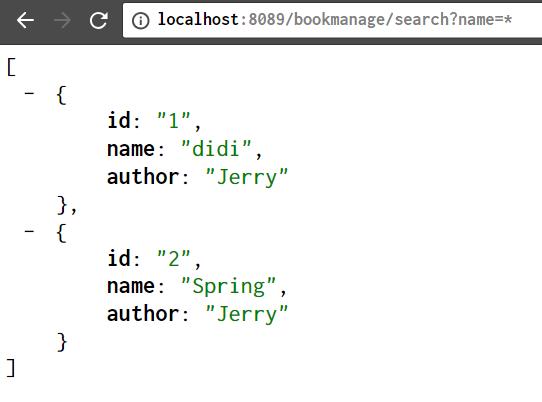
记录的搜索:http://localhost:8089/bookmanage/search?name=*
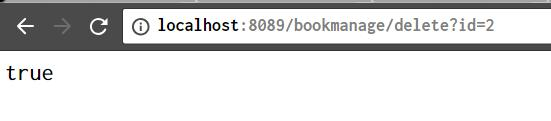
记录的删除:删除id为2的记录
http://localhost:8089/bookmanage/delete?id=2
下面是实现的细节。
1. 创建一个新的controller,位于文件夹src/main/java下。
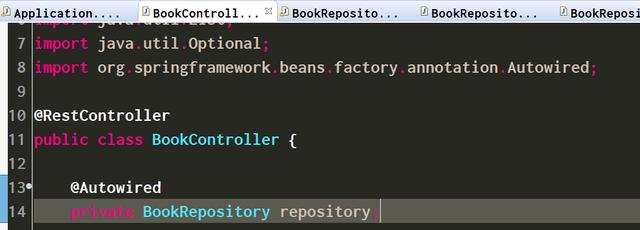
这个controller加上注解@RestController。@RestController注解相当于@ResponseBody和@Controller这两个注解提供的功能的并集。这里有一个知识点就是,如果用注解@RestController定义一个Controller,那么这个Controller里的方法无法返回jsp页面,或者html,因为@ResponseBody注解在起作用,因此即使配置了视图解析器 InternalResourceViewResolver也不会生效,此时返回的内容就是@RestController定义的控制器方法里返回的内容。
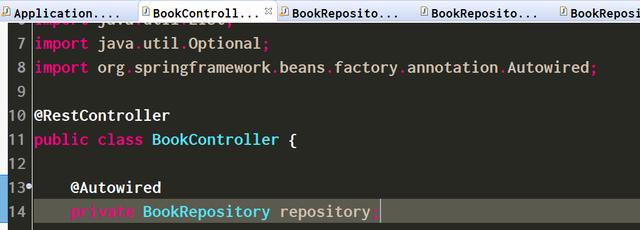
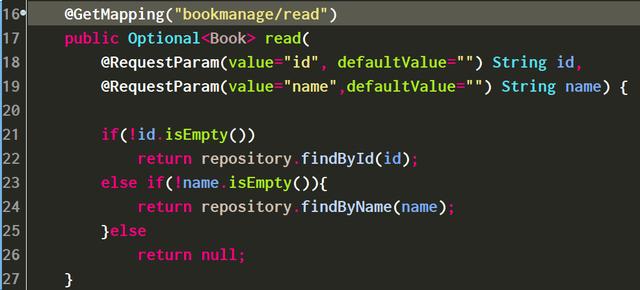
2. 以读操作为例,通过注解@GetMapping定义了读操作Restful API的url为bookmanage/read。
@RequestParam定义了url:bookmanage/read后面的参数为id或者name。读操作最终将会使用我们在MongoDB最简单的入门教程之三 使用Java代码往MongoDB里插入数据里介绍的方法,即通过@Autowired注入的BookRepository实例完成对MongoDB的操作。
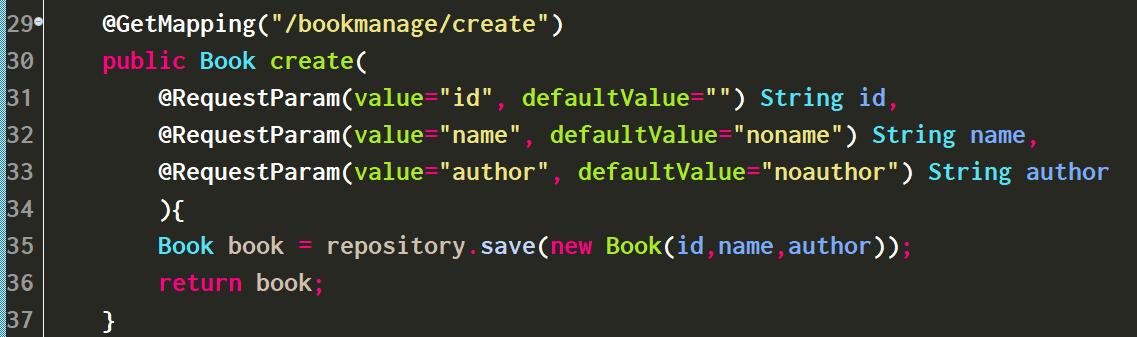
3. 创建操作的源代码:
@GetMapping("/bookmanage/create")
public Book create(
@RequestParam(value="id", defaultValue="") String id,
@RequestParam(value="name", defaultValue="noname") String name,
@RequestParam(value="author", defaultValue="noauthor") String author
){
Book book = repository.save(new Book(id,name,author));
return book;
}
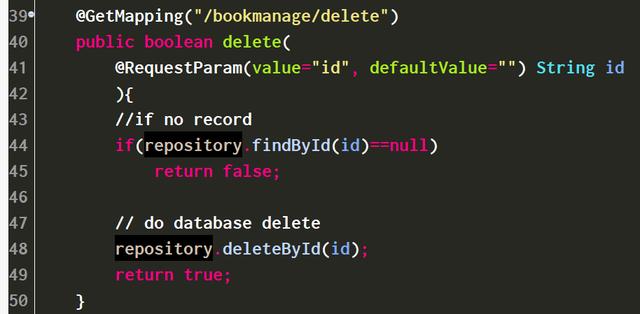
4. 删除操作的源代码:
@GetMapping("/bookmanage/delete")
public boolean delete(
@RequestParam(value="id", defaultValue="") String id
){
//if no record
if(repository.findById(id)==null)
return false;
// do database delete
repository.deleteById(id);
return true;
}
Spring Boot 是一个轻量级框架,可以完成基于 Spring 的应用程序的大部分配置工作。Spring Boot的目的是提供一组工具,以便快速构建容易配置的Spring应用程序,省去大量传统Spring项目的繁琐配置。
MongoDB是一个基于分布式文件存储的数据库。由 C++ 语言编写。旨在为 WEB 应用提供可扩展的高性能数据存储解决方案。
本文介绍如何使用Spring Boot操作MongoDB,通过Java代码在MongoDB里插入数据。
首先按照这个教程的第一篇文章的介绍,在本地搭建好MongoDB的环境:
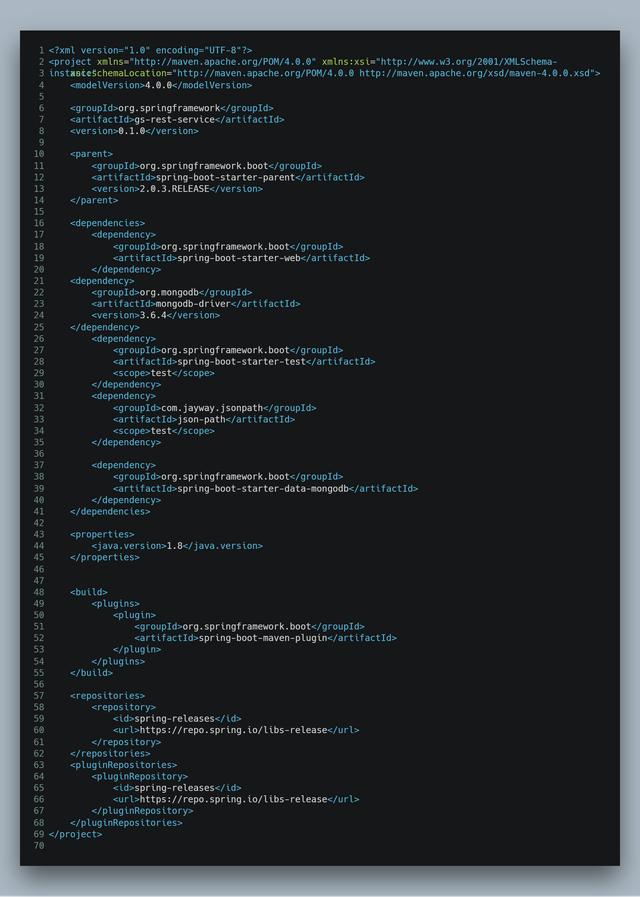
新建一个Java项目,pom.xml的内容如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>gs-rest-service</artifactId>
<version>0.1.0</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.3.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mongodb</groupId>
<artifactId>mongodb-driver</artifactId>
<version>3.6.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jayway.jsonpath</groupId>
<artifactId>json-path</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>spring-releases</id>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/libs-release</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-releases</id>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/libs-release</url>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
</project>
其中这个dependency的作用是为SpringBoot应用提供操作MongoDB的功能:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
这个dependent能让您的Spring Boot应用支持junit:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
在src/main/test文件夹下创建一个以Tests结尾的.java文件,我的例子里是ApplicationTests.java:
将如下代码粘贴进去:
package main.test;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import main.java.library.Application;
import main.java.library.Book;
import main.java.library.BookRepository;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes=Application.class)
public class ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private BookRepository bookRepository;
@Before
public void setUp() {
bookRepository.deleteAll();
}
@Test
public void test() throws Exception {
bookRepository.save(new Book("1", "didi", "Jerry"));
}
}
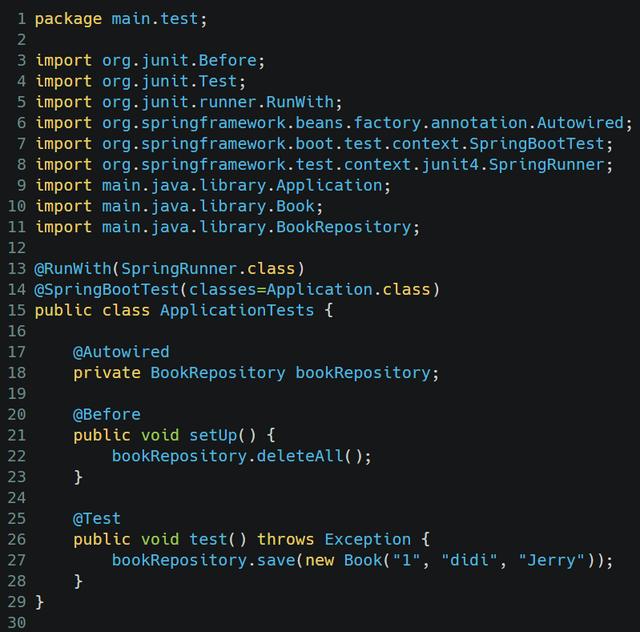
第27行代码,新建了一个Book对象,id为1,name为didi,作者为Jerry。然后通过bookRepository加入到MongoDB里。
BookRepository的实现:
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.MongoRepository;
public interface BookRepository extends MongoRepository<Book, String>, BookRepositoryCustom {
public Optional<Book> findByName(String name);
}
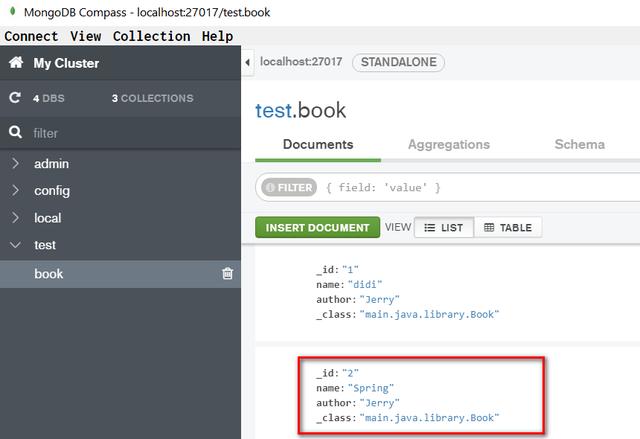
这个JUnit单元测试运行成功后,
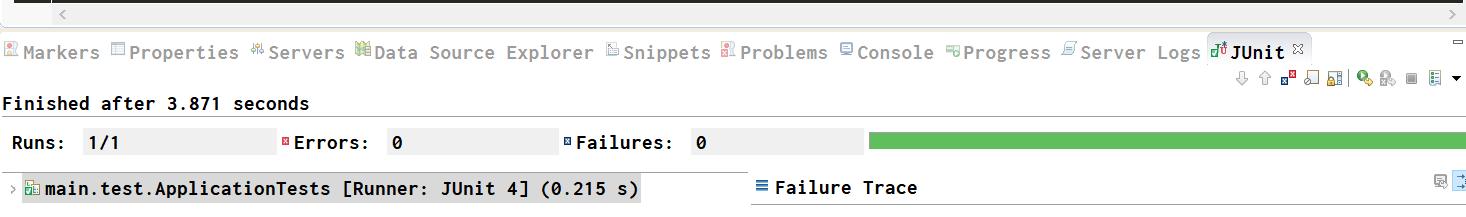
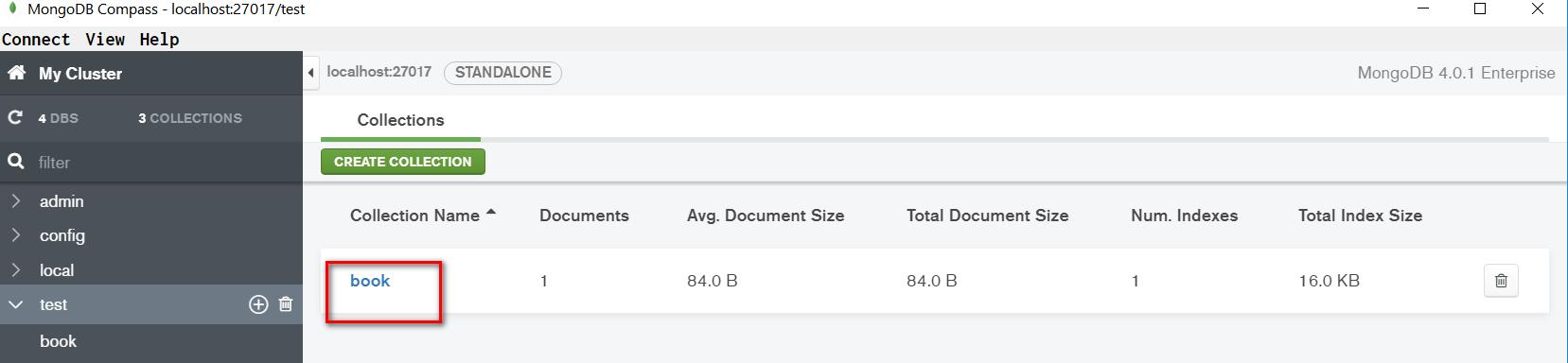
在MongoDB Compass里成功看到这条插入的记录:
要获取更多Jerry的原创技术文章,请关注公众号"汪子熙"。
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)