Java 线程同步(wait、notify、notifyAll)
一、方法介绍
1、void wait()
使得线程进入等待状态,直到它被其他线程通过notify()或者notifyAll唤醒。该方法只能在同步方法(void synchronized methodName( args... ){ ... })或者 “同步块内部“ (synchronized(object){ ... })被调用。如果当前线程不是锁的持有者,该方法会抛出一个IllegalMonitorStateException异常。
即如果锁住的是object,那么你只能调用object的wait()方法。
2、void notify()
随机选择一个在该对象上调用wait方法的线程,解除其阻塞状态。该方法只能在同步方法(void synchronized methodName( args... ){ ... })或者 “同步块内部“ (synchronized(object){ ... })被调用。如果当前线程不是锁的持有者,该方法会抛出一个IllegalMonitorStateException异常。
3、void notifyAll()
解除所有那些在该对象上调用wait方法的线程的阻塞状态。该方法只能在同步方法(void synchronized methodName( args... ){ ... })或者 “同步块内部“ (synchronized(object){ ... })被调用。如果当前线程不是锁的持有者,该方法会抛出一个IllegalMonitorStateException异常。
二、范例讲解( 注意测试类A只能声明为外部类,下面代码在 class A 和 main方法 之间 省略了MainClass { ... } )
1、“同步块”测试
(1)加synchronized(){}
-
class A{}
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
A object = new A();
-
System.out.println("Main Thread Id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
synchronized (object) {
-
try {
-
System.out.println("This Thread Id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
object.wait();
-
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
-
</span>e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
}
-
}
输出

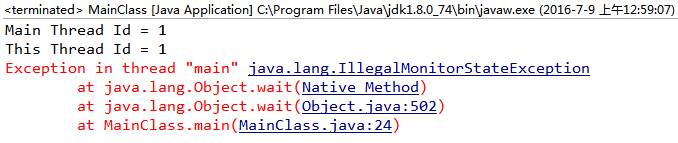
(2)不加synchronized(){}
-
class A{}
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
A object = new A();
-
System.out.println("Main Thread Id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
//synchronized (object) {
-
try {
-
</span>System.out.println("This Thread Id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
</span>object.wait();
-
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
-
</span>e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
//}
-
}
2、同步方法测试
(1)synchronized方法前缀
-
class A
-
{
-
public synchronized void test() throws InterruptedException {
-
//synchronized (this) {
-
System.out.println("Object Thread Id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
wait();
-
//}
-
};
-
}
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
A object = new A();
-
System.out.println("Main Thread Id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
//synchronized (object) {
-
try {
-
System.out.println("This Thread Id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
//object.wait();
-
object.test();
-
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
//}
-
}
输出

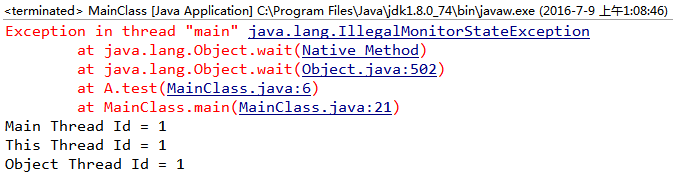
(2)不synchronized方法前缀
-
class A
-
{
-
public void test() throws InterruptedException {
-
//synchronized (this) {
-
System.out.println("Object Thread Id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
wait();
-
//}
-
};
-
}
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
A object = new A();
-
System.out.println("Main Thread Id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
//synchronized (object) {
-
try {
-
System.out.println("This Thread Id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
//object.wait();
-
object.test();
-
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
//}
-
}
输出
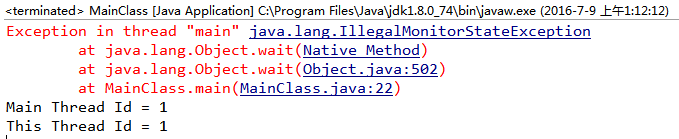
3、使用其它锁对象测试
-
class A{}
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
A object = new A();
-
Object object2 = new Object();
-
System.out.println("Main Thread Id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
synchronized (object) {
-
//synchronized (object2) {
-
try {
-
System.out.println("This Thread Id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
object.wait();
-
//object.test();
-
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
}
-
}
输出:
4、wait、notify进行线程同步
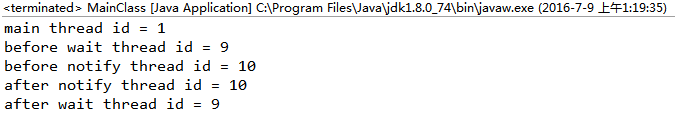
(1)一(wait)对一(notify)模式
-
class A{}
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
final A object = new A();
-
System.out.println("main thread id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
-
new Thread(new Runnable() {
-
-
@Override
-
public void run() {
-
synchronized (object) {
-
try {
-
System.out.println("before wait thread id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
object.wait();
-
System.out.println("after wait thread id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
}).start();
-
-
new Thread(new Runnable() {
-
-
@Override
-
public void run() {
-
try {
-
Thread.sleep(1000);
-
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
synchronized (object) {
-
System.out.println("before notify thread id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
object.notify();
-
System.out.println("after notify thread id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
}
-
}
-
}).start();
-
}
输出
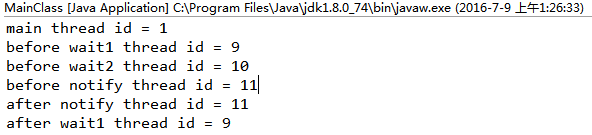
(2)多(wait)对一(notify)模式
-
class A{}
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
final A object = new A();
-
System.out.println("main thread id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
-
new Thread(new Runnable() {
-
-
@Override
-
public void run() {
-
synchronized (object) {
-
try {
-
System.out.println("before wait1 thread id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
object.wait();
-
System.out.println("after wait1 thread id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
}).start();
-
-
new Thread(new Runnable() {
-
-
@Override
-
public void run() {
-
synchronized (object) {
-
try {
-
System.out.println("before wait2 thread id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
object.wait();
-
System.out.println("after wait2 thread id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
}).start();
-
-
new Thread(new Runnable() {
-
-
@Override
-
public void run() {
-
try {
-
Thread.sleep(1000);
-
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
synchronized (object) {
-
System.out.println("before notify thread id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
object.notify();
-
System.out.println("after notify thread id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
}
-
}
-
}).start();
-
}
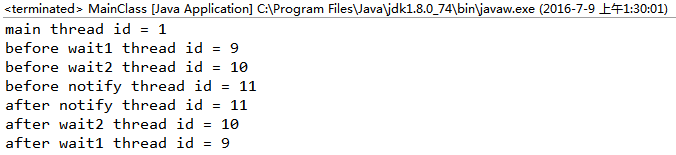
5、notifyAll
-
class A{}
-
public static void main(String[] args) {
-
final A object = new A();
-
System.out.println("main thread id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
-
new Thread(new Runnable() {
-
-
@Override
-
public void run() {
-
synchronized (object) {
-
try {
-
System.out.println("before wait1 thread id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
object.wait();
-
System.out.println("after wait1 thread id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
}).start();
-
-
new Thread(new Runnable() {
-
-
@Override
-
public void run() {
-
synchronized (object) {
-
try {
-
System.out.println("before wait2 thread id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
object.wait();
-
System.out.println("after wait2 thread id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
}).start();
-
-
new Thread(new Runnable() {
-
-
@Override
-
public void run() {
-
try {
-
Thread.sleep(1000);
-
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
synchronized (object) {
-
System.out.println("before notify thread id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
object.notifyAll();
-
System.out.println("after notify thread id = " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
-
}
-
}
-
}).start();
-
}
三、总结:
(1)由1和2可以看出:object.wait()方法只能在同步方法(void synchronized methodName( args... ){ ... })或者 “同步块内部“ (synchronized(object){ ... })被调用,否则会抛出一个IllegalMonitorStateException异常。
(2)由3可以看出:object.wait()方法只能在锁住自己的情况下被调用,否则会抛出一个IllegalMonitorStateException异常。
(3)由4可得:一个notify只能唤醒一个wait的线程
(4)由5可得:一个notifyAll可以唤醒多个wait的线程
四、注意点:(网上很多博客都讲的不清不楚的,龙神我估计他们就没有花时间真正的去测试过)
wait、notify和notifyAll方法是Object类的final native方法。所以这些方法不能被子类重写,Object类是所有类的超类,因此在程序中有以下三种形式调用wait等方法:
1、wait()
2、this.wait()
3、super.wait()
这三个方法是等价的。
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:福州-司马懿,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/chy555chy/article/details/51864773
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)