关于 Linux中系统调优的一些笔记(二)
【摘要】 我突然又明白,死亡是聪明的兄长,我们可以放心地把自己托付给他,他会知道在我们有所准备的适当时刻前来。我也突然懂得,原来痛苦、失望和悲愁不是为了惹恼我们,使我们气馁或者无地自容;它们的存在,是为了使我们心智成熟,臻于完善。--------—赫尔曼·黑塞《彼得·卡门青》
写在前面
- 推送的的邮件里看到有大佬讲的公共课,听了之后这里整理学习笔记。
- 因为是公开课,所以讲的很浅,没接触过,这里做为了解,长长见识。
- 博文内容包括:
| 内容 |
|---|
| 系统调优原理概述 |
| 如何检测系统的性能瓶颈 |
| 如何进行内核参数调优 |
| 如何限制服务的资源占用 |
| 自定义tuned调优配置集 |
接上篇
我突然又明白,死亡是聪明的兄长,我们可以放心地把自己托付给他,他会知道在我们有所准备的适当时刻前来。我也突然懂得,原来痛苦、失望和悲愁不是为了惹恼我们,使我们气馁或者无地自容;它们的存在,是为了使我们心智成熟,臻于完善。--------—赫尔曼·黑塞《彼得·卡门青》
内核调优之清理缓存
如何使用帮助调整内核参数
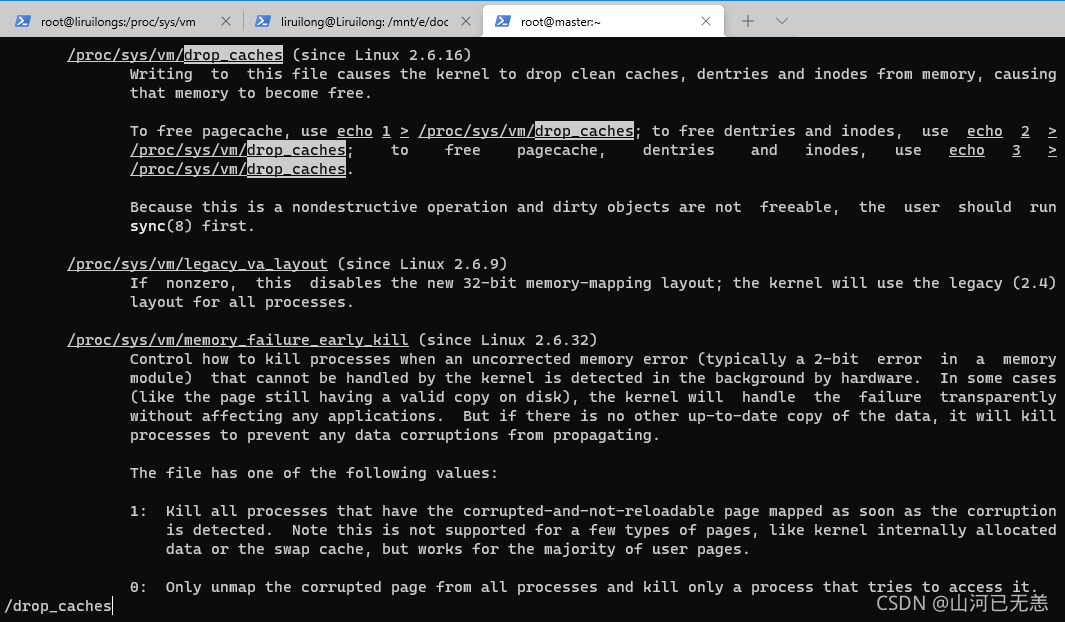
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/proc/sys/vm]
└─$ man -K drop_caches
--Man-- next: proc(5) [ view (return) | skip (Ctrl-D) | quit (Ctrl-C) ]
| 清理缓存 |
|---|
 |
 |
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/proc/sys/vm]
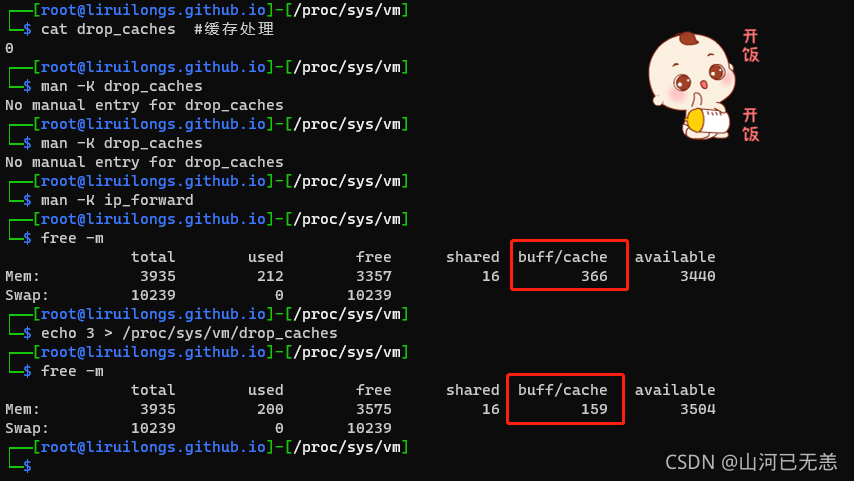
└─$ cat drop_caches #缓存处理
0
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/proc/sys/vm]
└─$ man -K drop_caches
No manual entry for drop_caches
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/proc/sys/vm]
└─$ man -K drop_caches
No manual entry for drop_caches
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/proc/sys/vm]
└─$ man -K ip_forward
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/proc/sys/vm]
└─$ free -m
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 3935 212 3357 16 366 3440
Swap: 10239 0 10239
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/proc/sys/vm]
└─$ echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/proc/sys/vm]
└─$ free -m
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 3935 200 3575 16 159 3504
Swap: 10239 0 10239
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/proc/sys/vm]
└─$
调整内核模块参数:lsmod、modinfo、modprobe
加载的内核模块列表 lsmod
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/proc/sys/vm]
└─$ lsmod # 大小 调用次数
Module Size Used by
binfmt_misc 17468 1
xt_conntrack 12760 2
ipt_MASQUERADE 12678 2
nf_nat_masquerade_ipv4 13412 1 ipt_MASQUERADE
nf_conntrack_netlink 40449 0
nfnetlink 14696 2 nf_conntrack_netlink
xt_addrtype 12676 2
iptable_filter 12810 1
iptable_nat 12875 1
nf_conntrack_ipv4 15053 3
nf_defrag_ipv4 12729 1 nf_conntrack_ipv4
。。。。。
。。。。。。
crct10dif_common 12595 3 crct10dif_pclmul,crct10dif_generic,crc_t10dif
crc32c_intel 22079 1
ahci 34042 0
drm 370825 2 ttm,drm_kms_helper
libahci 31992 1 ahci
mptspi 22542 2
ata_piix 35038 0
scsi_transport_spi 30732 1 mptspi
mptscsih 40150 1 mptspi
libata 238896 5 ahci,pata_acpi,libahci,ata_generic,ata_piix
e1000 137500 0
serio_raw 13413 0
mptbase 105960 2 mptspi,mptscsih
i2c_core 40756 3 drm,i2c_piix4,drm_kms_helper
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/proc/sys/vm]
└─$
查看内核模块参数 modinfo
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/proc/sys/vm]
└─$ modinfo kvm # 查看内核模块参数
filename: /lib/modules/3.10.0-693.el7.x86_64/kernel/arch/x86/kvm/kvm.ko.xz
license: GPL
author: Qumranet
rhelversion: 7.4
srcversion: FA3AAB0FB1DD5C7B9D69811
depends: irqbypass
intree: Y
vermagic: 3.10.0-693.el7.x86_64 SMP mod_unload modversions
signer: CentOS Linux kernel signing key
sig_key: DA:18:7D:CA:7D:BE:53:AB:05:BD:13:BD:0C:4E:21:F4:22:B6:A4:9C
sig_hashalgo: sha256
parm: ignore_msrs:bool
parm: min_timer_period_us:uint
parm: kvmclock_periodic_sync:bool
parm: tsc_tolerance_ppm:uint
parm: lapic_timer_advance_ns:uint
parm: vector_hashing:bool
parm: halt_poll_ns:uint
parm: halt_poll_ns_grow:uint
parm: halt_poll_ns_shrink:uint
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/proc/sys/vm]
└─$
内核模块调优之嵌套虚拟化设置
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/proc/sys/vm]
└─$ modinfo kvm
filename: /lib/modules/3.10.0-693.el7.x86_64/kernel/arch/x86/kvm/kvm.ko.xz
license: GPL
author: Qumranet
rhelversion: 7.4
srcversion: FA3AAB0FB1DD5C7B9D69811
depends: irqbypass
intree: Y
vermagic: 3.10.0-693.el7.x86_64 SMP mod_unload modversions
signer: CentOS Linux kernel signing key
sig_key: DA:18:7D:CA:7D:BE:53:AB:05:BD:13:BD:0C:4E:21:F4:22:B6:A4:9C
sig_hashalgo: sha256
parm: ignore_msrs:bool
parm: min_timer_period_us:uint
parm: kvmclock_periodic_sync:bool
parm: tsc_tolerance_ppm:uint
parm: lapic_timer_advance_ns:uint
parm: vector_hashing:bool
parm: halt_poll_ns:uint
parm: halt_poll_ns_grow:uint
parm: halt_poll_ns_shrink:uint
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/proc/sys/vm]
└─$ modinfo kvm | grep ignore_msrs # 设置允许嵌套虚拟化
parm: ignore_msrs:bool
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/etc/modprobe.d]
└─$ echo "options kvm ignore_msrs=1" >> /etc/modprobe.d/kvm.conf ##从起机器
如何限制服务的资源占用
资源消耗分为用户和服务,消耗:CPU,内存和 I/O
经典的限制通过 pam_limit 模块配合 /etc/security/limits.conf 实现(用户)
用户登录会加载pam_limit模块,pam_limit模块读取配置文件 /etc/security/limits.conf限制用户资源的占用
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/etc/modprobe.d]
└─$ cat /etc/security/limits.conf
# /etc/security/limits.conf
#
#This file sets the resource limits for the users logged in via PAM.
#It does not affect resource limits of the system services.
#
#Also note that configuration files in /etc/security/limits.d directory,
#which are read in alphabetical order, override the settings in this
#file in case the domain is the same or more specific.
#That means for example that setting a limit for wildcard domain here
#can be overriden with a wildcard setting in a config file in the
#subdirectory, but a user specific setting here can be overriden only
#with a user specific setting in the subdirectory.
#
#Each line describes a limit for a user in the form:
#
#<domain> <type> <item> <value>
#
#Where:
#<domain> can be:
# - a user name
# - a group name, with @group syntax
# - the wildcard *, for default entry
# - the wildcard %, can be also used with %group syntax,
# for maxlogin limit
#
#<type> can have the two values:
# - "soft" for enforcing the soft limits
# - "hard" for enforcing hard limits
#
#<item> can be one of the following:
# - core - limits the core file size (KB) 核心文件大小
# - data - max data size (KB)
# - fsize - maximum filesize (KB)
# - memlock - max locked-in-memory address space (KB)
# - nofile - max number of open file descriptors # 访问文件数量
# - rss - max resident set size (KB)
# - stack - max stack size (KB)
# - cpu - max CPU time (MIN) # cup时间
# - nproc - max number of processes
# - as - address space limit (KB)
# - maxlogins - max number of logins for this user #最多的登录数
# - maxsyslogins - max number of logins on the system
# - priority - the priority to run user process with
# - locks - max number of file locks the user can hold
# - sigpending - max number of pending signals
# - msgqueue - max memory used by POSIX message queues (bytes)
# - nice - max nice priority allowed to raise to values: [-20, 19]
# - rtprio - max realtime priority
#
#<domain> <type> <item> <value>
#
#* soft core 0
#* hard rss 10000
#@student hard nproc 20
#@faculty soft nproc 20
#@faculty hard nproc 50
#ftp hard nproc 0
#@student - maxlogins 4
# End of file
限制服务的资源之限制用户通过ssh的登录数
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/etc/modprobe.d]
└─$vim /etc/security/limits.conf
student hard maxlogins 4
也可以通过 cgroup 实现资源的限制(服务)
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/etc/modprobe.d]
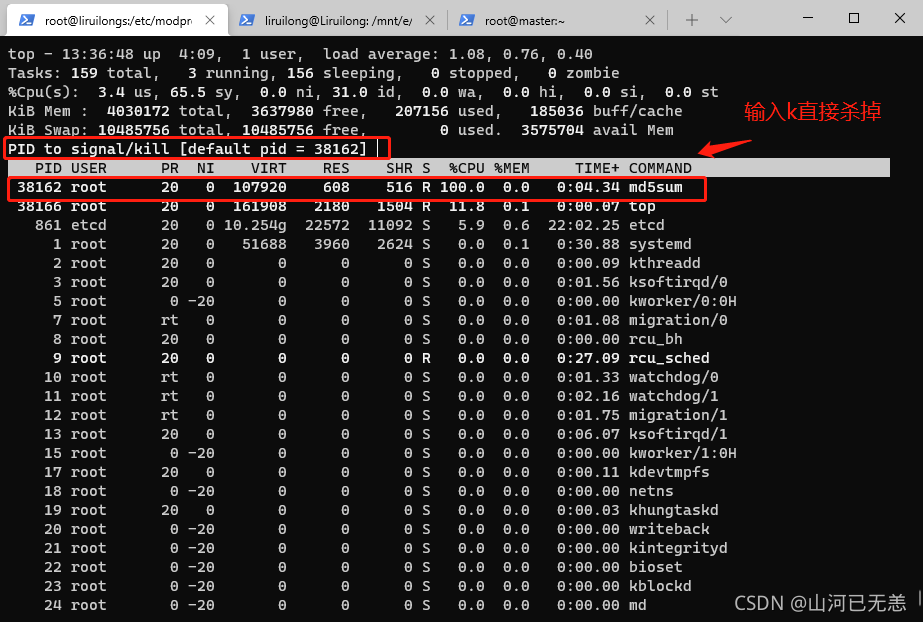
└─$ md5sum /dev/urandom & #启动一个进程 cpu100%
[1] 38162
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/etc/modprobe.d]
└─$ top
top - 13:37:42 up 4:10, 1 user, load average: 1.03, 0.80, 0.43
Tasks: 158 total, 2 running, 156 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombie
%Cpu(s): 2.0 us, 53.9 sy, 0.0 ni, 43.3 id, 0.0 wa, 0.0 hi, 0.8 si, 0.0 st
KiB Mem : 4030172 total, 3637840 free, 207252 used, 185080 buff/cache
KiB Swap: 10485756 total, 10485756 free, 0 used. 3575580 avail Mem
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
861 etcd 20 0 10.254g 22572 11092 S 9.7 0.6 22:07.49 etcd
9 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 1.7 0.0 0:28.00 rcu_sched
595 root 20 0 298868 6260 4916 S 1.6 0.2 2:27.63 vmtoolsd
371 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.4 0.0 1:23.11 xfsaild/sda1
1 root 20 0 51688 3960 2624 S 0.4 0.1 0:31.08 systemd
36765 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.2 0.0 0:03.13 kworker/1:0
583 root 20 0 21616 1284 972 S 0.2 0.0 0:09.59 irqbalance
857 root 20 0 573468 16760 6020 S 0.2 0.4 0:14.24 tuned
13 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.2 0.0 0:06.16 ksoftirqd/1
864 root 20 0 1015116 42652 13740 S 0.1 1.1 0:22.33 containerd
853 root 20 0 228220 5128 3240 S 0.1 0.1 0:09.13 httpd
594 root 20 0 224504 12424 3348 S 0.1 0.3 0:08.61 rsyslogd
649 chrony 20 0 117704 1772 1312 S 0.1 0.0 0:03.47 chronyd
7604 root 20 0 151984 5352 4088 R 0.1 0.1 0:05.89 sshd
38166 root 20 0 161908 2264 1556 R 0.1 0.1 0:00.10 top
1055 root 20 0 81744 3132 2168 S 0.0 0.1 0:10.09 pmdalinux
8095 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:01.54 kworker/u256:0
11 root rt 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:02.17 watchdog/1
1051 root 20 0 81628 2700 1912 S 0.0 0.1 0:03.07 pmdaproc
2 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.09 kthreadd
3 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:01.56 ksoftirqd/0
5 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 kworker/0:0H
7 root rt 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:01.08 migration/0
[1]+ Terminated md5sum /dev/urandom
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/etc/modprobe.d]
└─$
现在我们把这个写成一个服务,然后通过cgroup做简单限制。
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ vim /etc/systemd/system/md5sum.service
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ cat /etc/systemd/system/md5sum.service
[Unit]
Description=MD5 Demo
[Service]
CPUQuota=40%
ExecStart=/usr/bin/md5sum /dev/urandom
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ systemctl daemon-reload
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ systemctl start md5sum.service
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ top
top - 19:12:14 up 9:44, 1 user, load average: 0.29, 0.20, 0.11
Tasks: 159 total, 2 running, 157 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 zombie
%Cpu(s): 0.5 us, 20.3 sy, 0.0 ni, 78.8 id, 0.0 wa, 0.0 hi, 0.4 si, 0.0 st
KiB Mem : 4030172 total, 3606960 free, 209832 used, 213380 buff/cache
KiB Swap: 10485756 total, 10485756 free, 0 used. 3558764 avail Mem
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM TIME+ COMMAND
59598 root 20 0 107920 612 516 R 39.7 0.0 0:02.54 md5sum ##CPU限制为40%
861 etcd 20 0 10.254g 22572 11092 S 6.3 0.6 51:24.88 etcd
59601 root 20 0 161908 2268 1560 R 1.0 0.1 0:00.08 top
595 root 20 0 298868 6260 4916 S 0.7 0.2 5:35.80 vmtoolsd
1 root 20 0 51688 4000 2648 S 0.3 0.1 1:15.99 systemd
9 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.3 0.0 0:50.90 rcu_sched
371 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.3 0.0 3:02.41 xfsaild/sda1
6671 root 20 0 1309148 66444 25620 S 0.3 1.6 0:48.35 dockerd
2 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.13 kthreadd
3 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:04.25 ksoftirqd/0
5 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 kworker/0:0H
7 root rt 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:02.39 migration/0
8 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 rcu_bh
10 root rt 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:03.13 watchdog/0
11 root rt 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:04.80 watchdog/1
12 root rt 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:02.72 migration/1
13 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:11.18 ksoftirqd/1
15 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 kworker/1:0H
17 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.11 kdevtmpfs
18 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 netns
19 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.08 khungtaskd
20 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 writeback
21 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0 0:00.00 kintegrityd
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$
这个具体小伙伴可以看看这篇博客: https://blog.csdn.net/sanhewuyang/article/details/120735766
关于cgroup参数设置可以使用帮助文档
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ man -k systemd
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ man systemd.resource-control
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$
为 systemd unit 实现资源限制
这个老师没讲,以后研究下,应该也和cgroup有关
自定义tuned调优配置集:
tuned 实现系统傻瓜化和集成化调优,操作系统预装多个调优场景配置集,这是一道RHCAS的考试题
查看调优策略
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ tuned-adm list
Available profiles:
- balanced - General non-specialized tuned profile
- desktop - Optimize for the desktop use-case
- latency-performance - Optimize for deterministic performance at the cost of increased power consumption
- network-latency - Optimize for deterministic performance at the cost of increased power consumption, focused on low latency network performance
- network-throughput - Optimize for streaming network throughput, generally only necessary on older CPUs or 40G+ networks
- powersave - Optimize for low power consumption
- throughput-performance - Broadly applicable tuning that provides excellent performance across a variety of common server workloads
- virtual-guest - Optimize for running inside a virtual guest
- virtual-host - Optimize for running KVM guests
Current active profile: virtual-guest
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ tuned-adm recommend # 查看推荐的策略
virtual-guest
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ tuned-adm profile virtual-guest
调优策略位置
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ cd /usr/lib/tuned/;ls ## 调优参数
balanced latency-performance powersave virtual-guest
desktop network-latency recommend.conf virtual-host
functions network-throughput throughput-performance
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/usr/lib/tuned]
└─$ cd virtual-guest/
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/usr/lib/tuned/virtual-guest]
└─$ ls
tuned.conf
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/usr/lib/tuned/virtual-guest]
└─$ cat tuned.conf
#
# tuned configuration
#
[main]
summary=Optimize for running inside a virtual guest
include=throughput-performance
[sysctl]
# If a workload mostly uses anonymous memory and it hits this limit, the entire
# working set is buffered for I/O, and any more write buffering would require
# swapping, so it's time to throttle writes until I/O can catch up. Workloads
# that mostly use file mappings may be able to use even higher values.
#
# The generator of dirty data starts writeback at this percentage (system default
# is 20%)
vm.dirty_ratio = 30
# Filesystem I/O is usually much more efficient than swapping, so try to keep
# swapping low. It's usually safe to go even lower than this on systems with
# server-grade storage.
vm.swappiness = 30
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/usr/lib/tuned/virtual-guest]
└─$
在/etc/tuned目录中编辑自定义tuned profile,配置集中的条目可以相互引用,并通过各种plugin自定义
获取 yum仓库的tuned profile
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/usr/lib/tuned/virtual-guest]
└─$ yum list | grep tuned
tuned.noarch 2.8.0-5.el7 @anaconda
tuned.noarch 2.11.0-11.el7_9 updates
tuned-gtk.noarch 2.11.0-11.el7_9 updates
tuned-profiles-atomic.noarch 2.11.0-11.el7_9 updates
tuned-profiles-compat.noarch 2.11.0-11.el7_9 updates
tuned-profiles-cpu-partitioning.noarch 2.11.0-11.el7_9 updates
tuned-profiles-mssql.noarch 2.11.0-11.el7_9 updates
tuned-profiles-oracle.noarch 2.11.0-11.el7_9 updates
tuned-utils.noarch 2.11.0-11.el7_9 updates
tuned-utils-systemtap.noarch 2.11.0-11.el7_9 updates
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/usr/lib/tuned/virtual-guest]
└─$ yum -y install tuned-profiles-oracle.noarch
....
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/usr/lib/tuned/virtual-guest]
└─$ tuned-adm list
Available profiles:
- balanced - General non-specialized tuned profile
- desktop - Optimize for the desktop use-case
- hpc-compute - Optimize for HPC compute workloads
- latency-performance - Optimize for deterministic performance at the cost of increased power consumption
- network-latency - Optimize for deterministic performance at the cost of increased power consumption, focused on low latency network performance
- network-throughput - Optimize for streaming network throughput, generally only necessary on older CPUs or 40G+ networks
- oracle - Optimize for Oracle RDBMS
- powersave - Optimize for low power consumption
- throughput-performance - Broadly applicable tuning that provides excellent performance across a variety of common server workloads
- virtual-guest - Optimize for running inside a virtual guest
- virtual-host - Optimize for running KVM guests
Current active profile: virtual-guest
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[/usr/lib/tuned/virtual-guest]
└─$
通过SystemTap配置内核模块进行系统底层分析:
嗯,这部分有些复杂,有些包需要订阅,先记录下,以后有机会学习
| 通过SystemTap配置内核模块进行系统底层分析: |
|---|
| SystemTap 可以简易的探索测量 kernel 中任意部件 |
| Kernel开发者通过kprobe在kernel功能前后加入测试代码 |
| SystemTap需要gcc,kernel-debuginfo,kernel-devel软件支持 |
| stap命令将*.stp脚本文件编译为kernel模块,通过staprun命令运行 |
【声明】本内容来自华为云开发者社区博主,不代表华为云及华为云开发者社区的观点和立场。转载时必须标注文章的来源(华为云社区)、文章链接、文章作者等基本信息,否则作者和本社区有权追究责任。如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)