UI5和WebUI的View和Controller是如何绑定的
UI5
例如我在UI5的界面上画一个按钮,点击之后弹出一个Alert dialog。
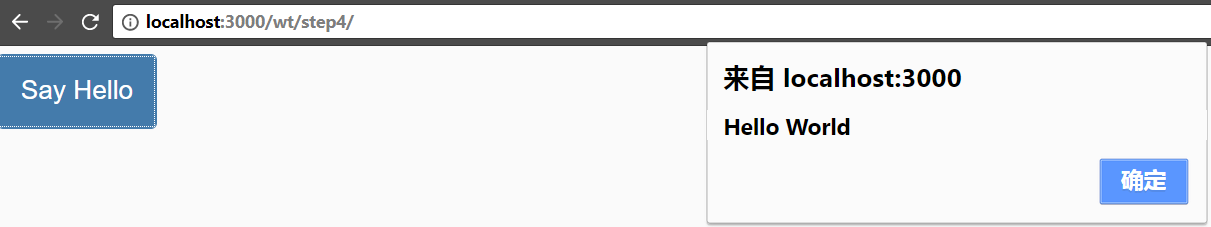
在XML view里只定义了controller的名称和事件处理函数的名称。那么按钮被点击之后,controller的onShowHello被触发。但是,这个controller的实例是什么时候被创建, 并且关联到这个申明它的XML view里呢?
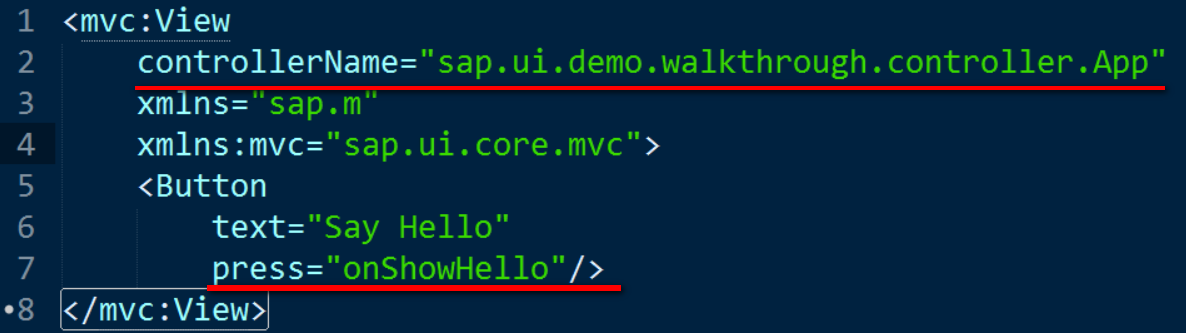
在XMLView.js里,我定义的XML view的源代码被加载之后,XMLView会调用XMLTemplateProcessor, 解析XML view的内容,根据里面的control申明创建对应的UI5控件实例。下图的变量_xContent.innerHTML即为上图XML view的源代码。
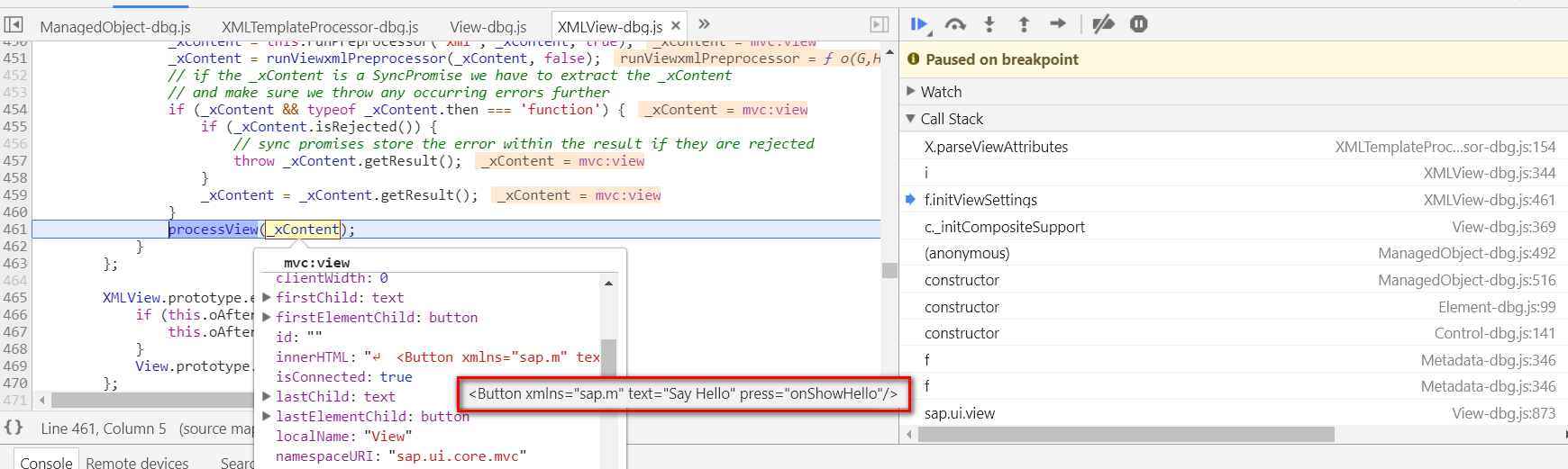
XMLView的实例通过工厂模式创建之后,XMLView源代码里定义的controller名称sap.ui.demo.walkthrough.controller.App,会赋到oView实例的字段_controllerName上。
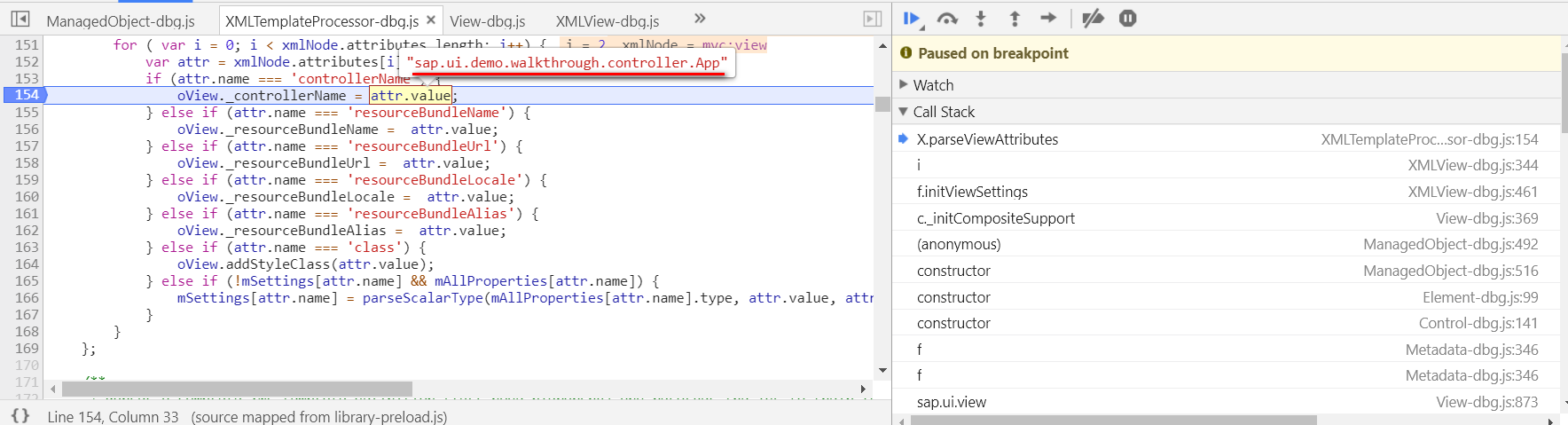
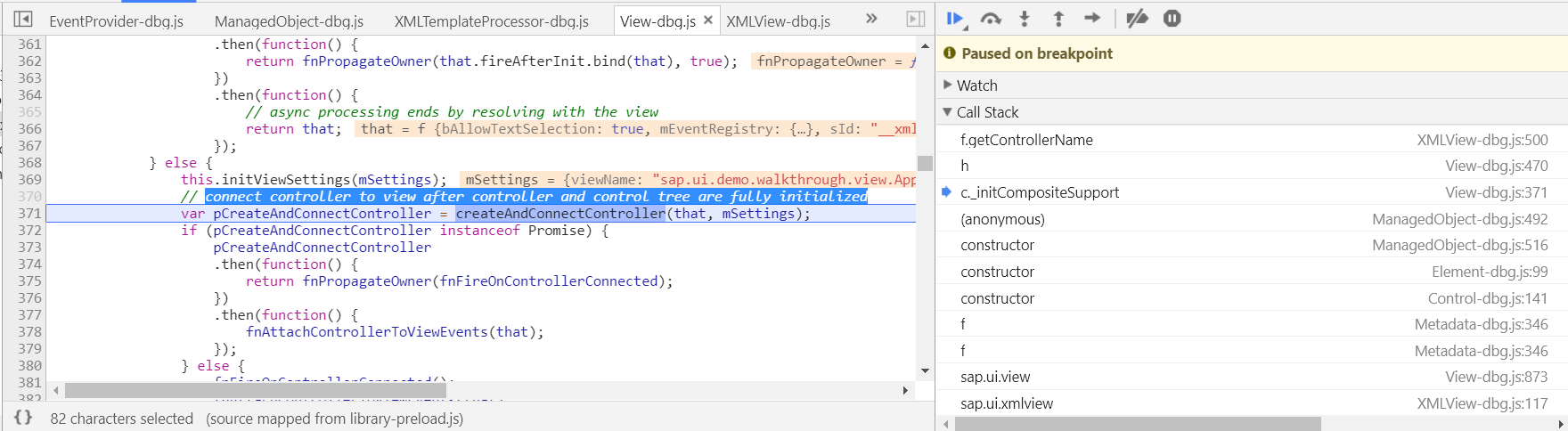
View和Controller的绑定是通过这个方法createAndConnectController完成:
connect controller to view after controller and control tree are fully initialized
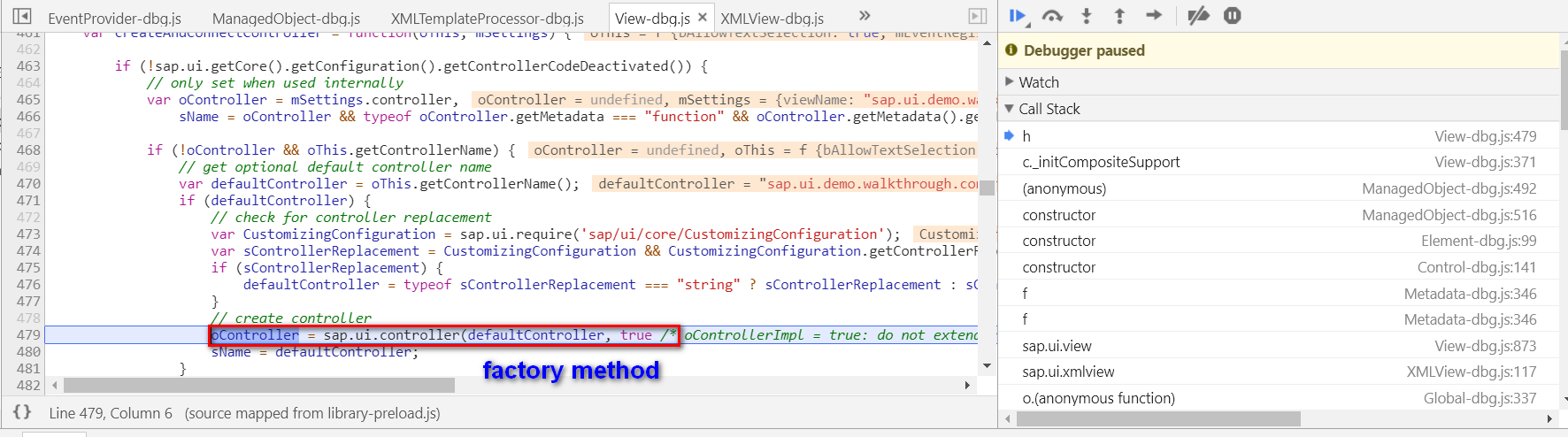
Controller的实例也通过工厂模式创建:
一旦connectToView执行之后,
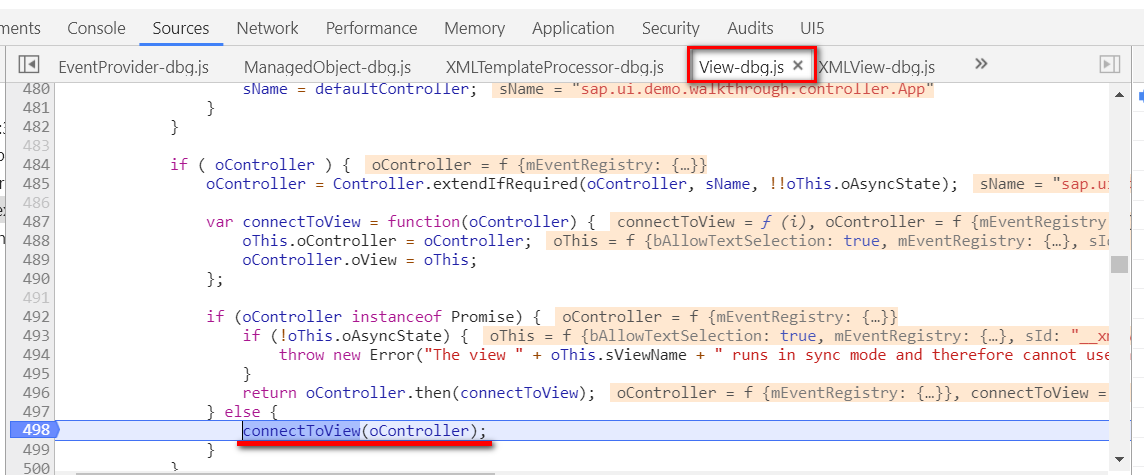
oView和oController的关联关系就建立起来了。

CRM WebClient UI
每个UI component view里有一个built-in的属性controller, 指向这个view对应的controller实例。
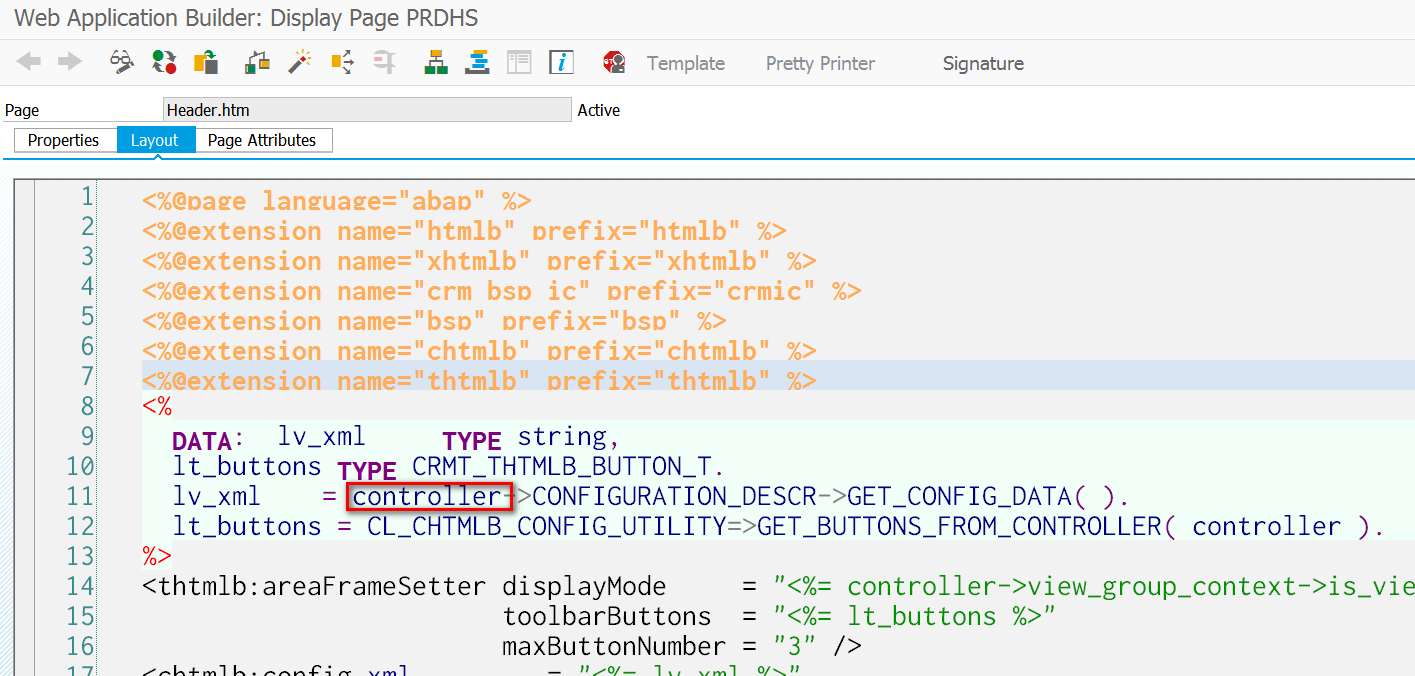
在BSP的编程环境里,开发人员根本无需操心这个controller实例的初始化,直接用就行。
那么View的controller实例究竟在什么时候被框架初始化的?
要自己搞清楚这个问题,可以随便找个BSP UI component做个实验。我找的是PRDHS。在其View的controller CL_PRDHS_HEADER_IMPL的构造函数里设置断点:
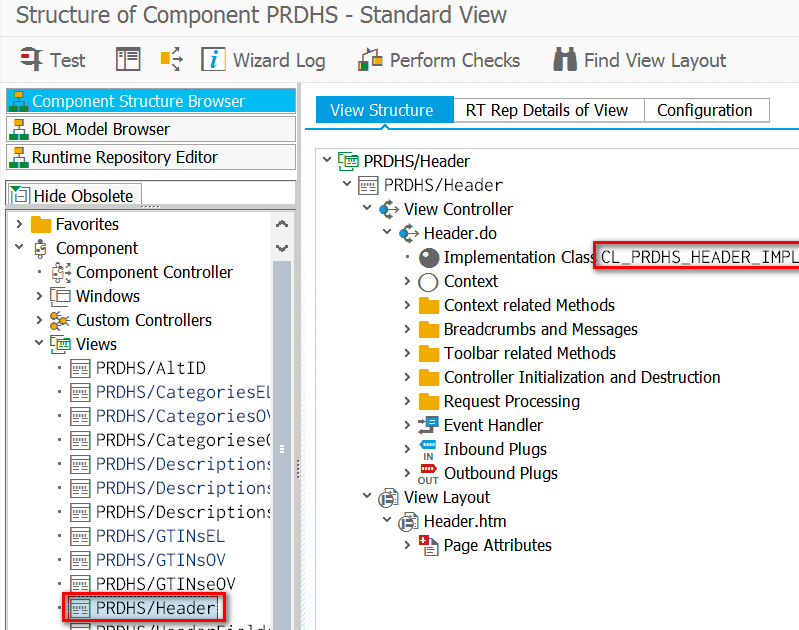
打开该view,从调用栈上下文即可得知BSP框架在什么地方初始化controller实例的。记下这个实例在ABAP runtime的地址编号4633:
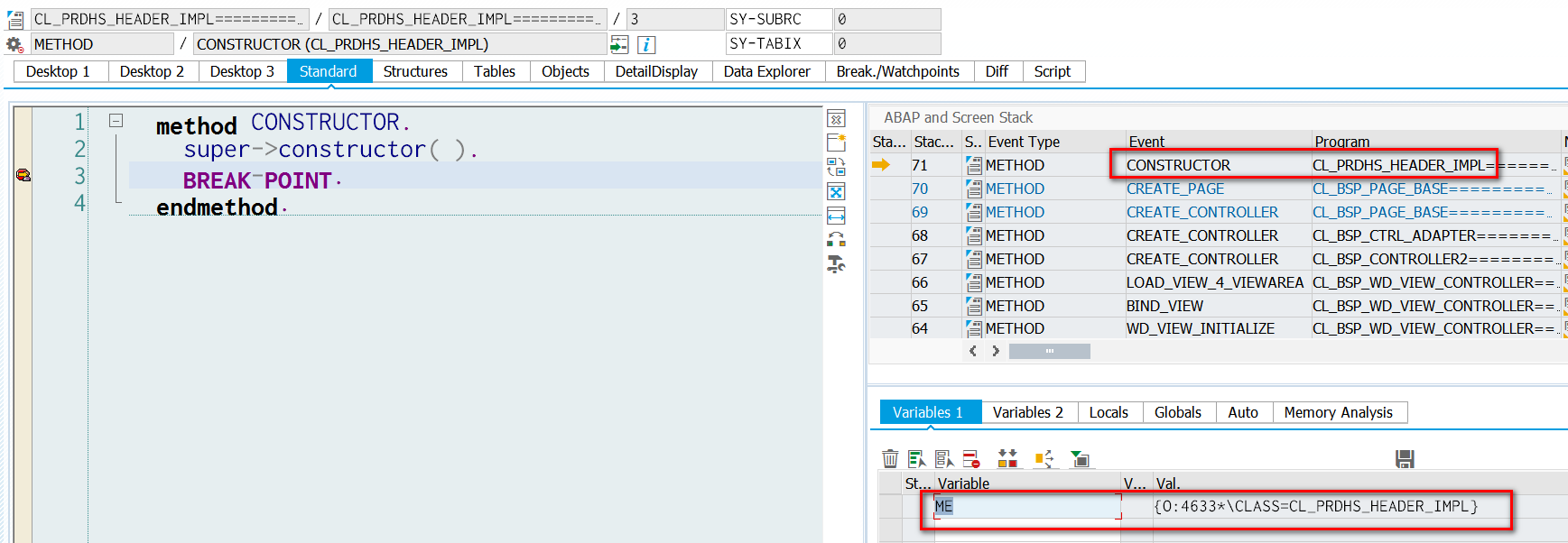
同UI5逻辑类似,在CL_BSP_PAGE_BASE~CREATE_PAGE内部,第190行创建controller的实例并将其同View实例建立关联关系。
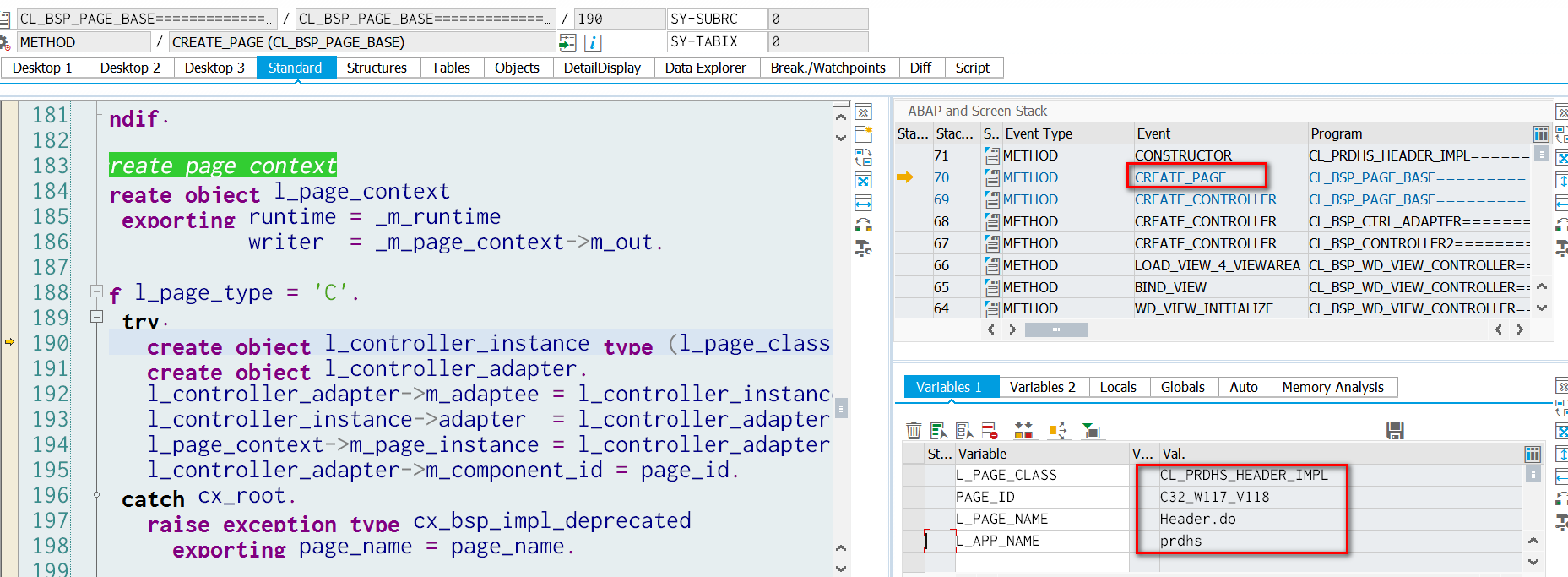
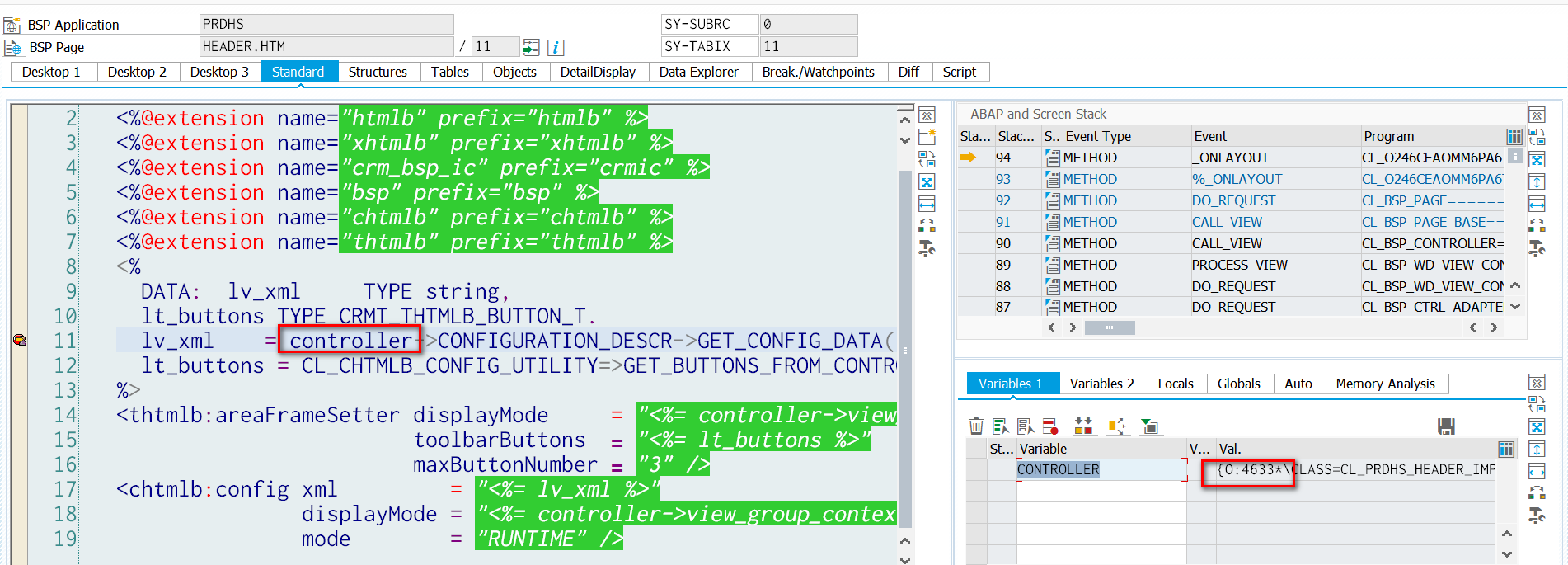
最后运行时View的controller实例4633和之前我们在PRDHS/Header的controller CL_PRDHS_HEADER_IMPL的构造函数中的me指针4633一样,证明两个变量指向的是同一个实例。
另外,UML 模型里的 association, aggregation 和 composition 的区别,大家能分清吗?
UI5
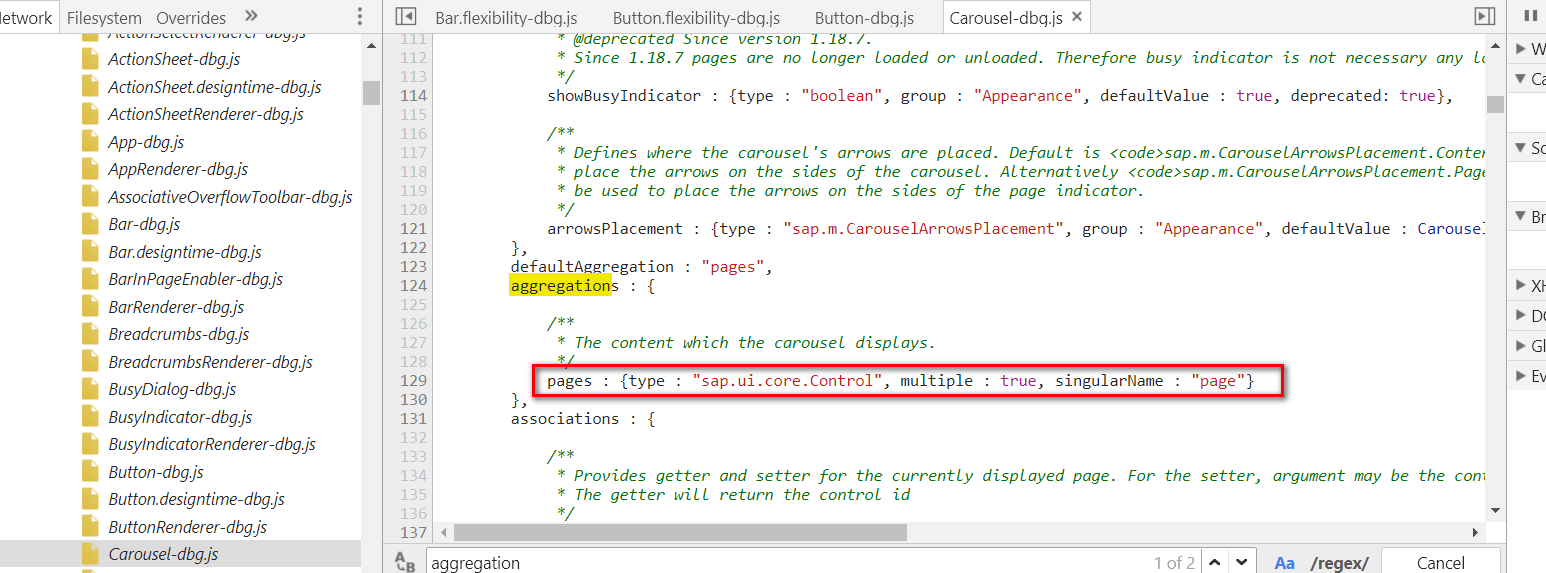
UI5使用Association和Aggregation描述控件之间的关系。
Aggregation:parent和子控件在lifecycle上存在依赖关系:
When a ManagedObject is destroyed, all aggregated objects are destroyed as well and the object itself is removed from its parent. That is, aggregations won’t contain destroyed objects or null/undefined.
比如UI5的转盘控件Carousel: 一旦转盘被析构,里面显示的page当然也没有继续存在的意义了,需要跟着被析构。
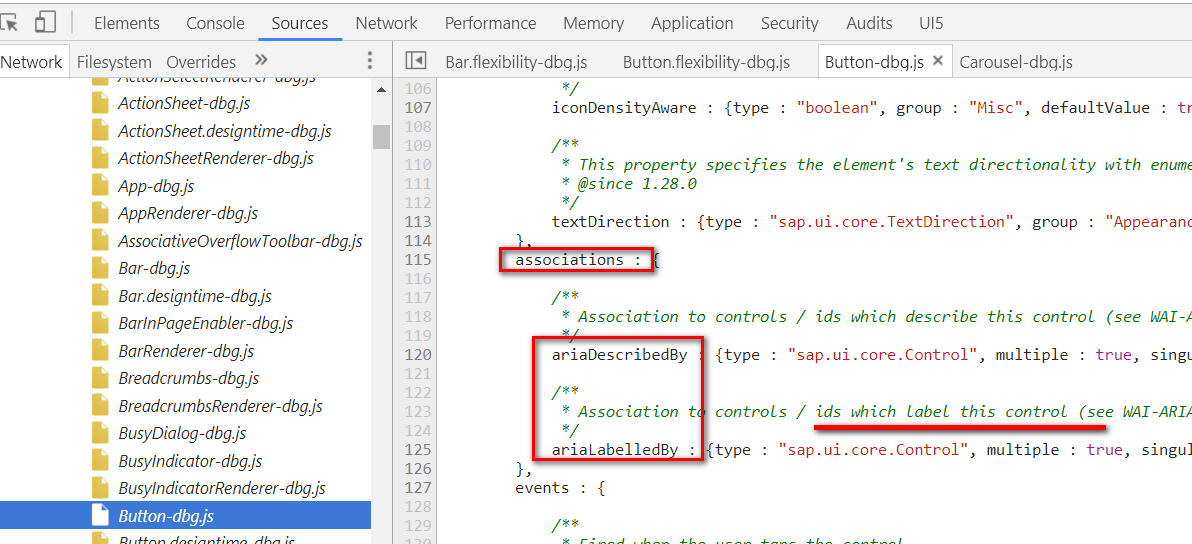
而Association描述了在lifecycle层面的一种soft dependency关系:
Managed associations also form a relationship between objects, but they don’t define a lifecycle for the associated objects. They even can ‘break’ in the sense that an associated object might have been destroyed already although it is still referenced in an association.
最明显的例子就是控件和其label的关系,比如button和label:技术上来说,可以彼此分开独立存在。
CRM
CRM的Genil model存在三种类型的relation,可以在doman CRM_RELATION_KIND里查看:
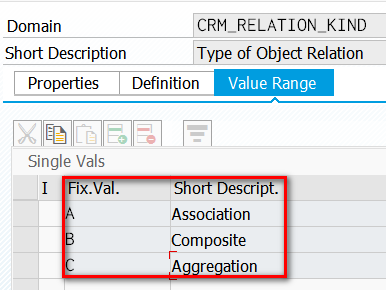
区别:
-
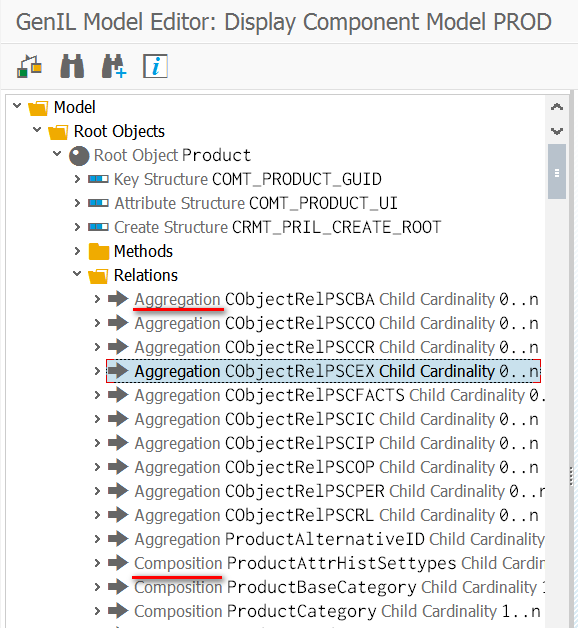
Association: Link between any kind of objects. Can also be defined across components with root or access object as target. 依赖关系最为loose的一种relation,可以用来连接跨model之间的节点。
-
Aggregation: Binds child objects to a root object. Only access and dependent objects can be aggregated. 只适用于同一模型的节点之间的关联。
-
Composition: Like an aggregation, but composed child objects always exist. 特殊类型的Aggregation。目标节点的Cardinality为1或者1…n
S/4HANA
只有两种:association或者composition。Composition的含义同CRM里的aggregation,而association的含义同UI5和CRM中的association一致。
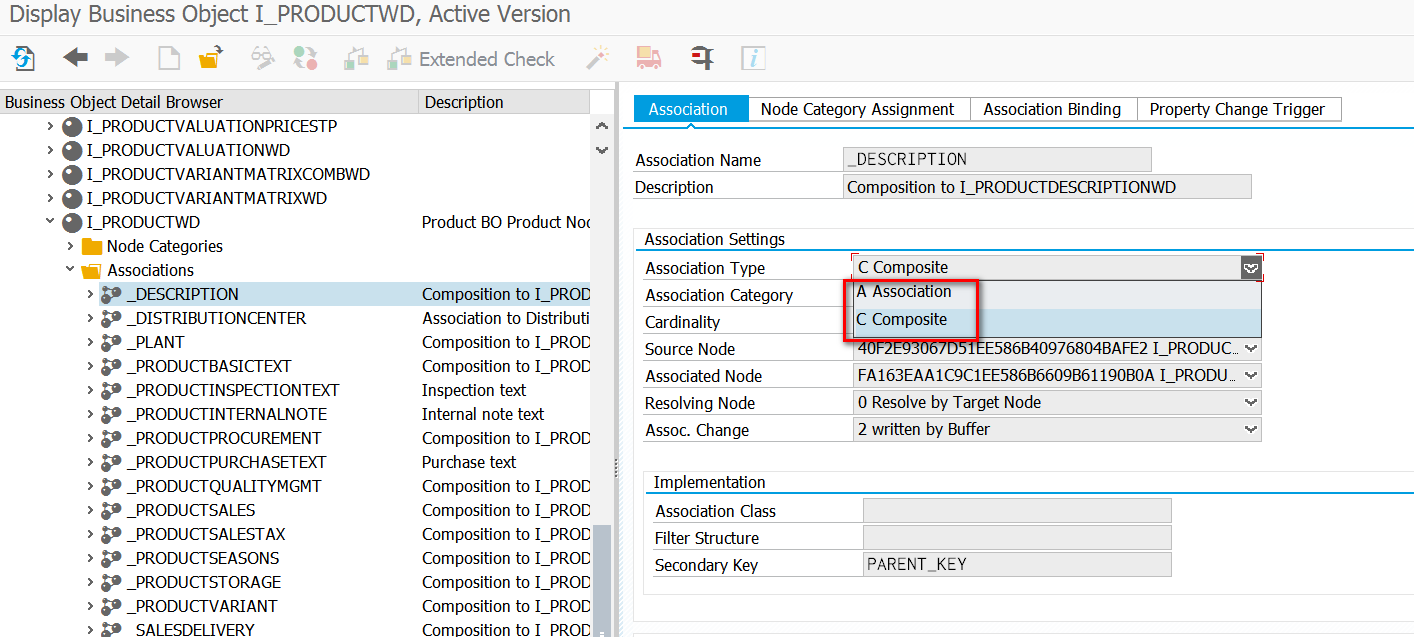
C4C
只有两种: association或者composition。C4C的这两种relation多了一个限制:relation的目标BO必须和源BO在同一个部署单元Deployment Unit,或者目标BO位于Foundation部署单元内。
Association的语法如下图:
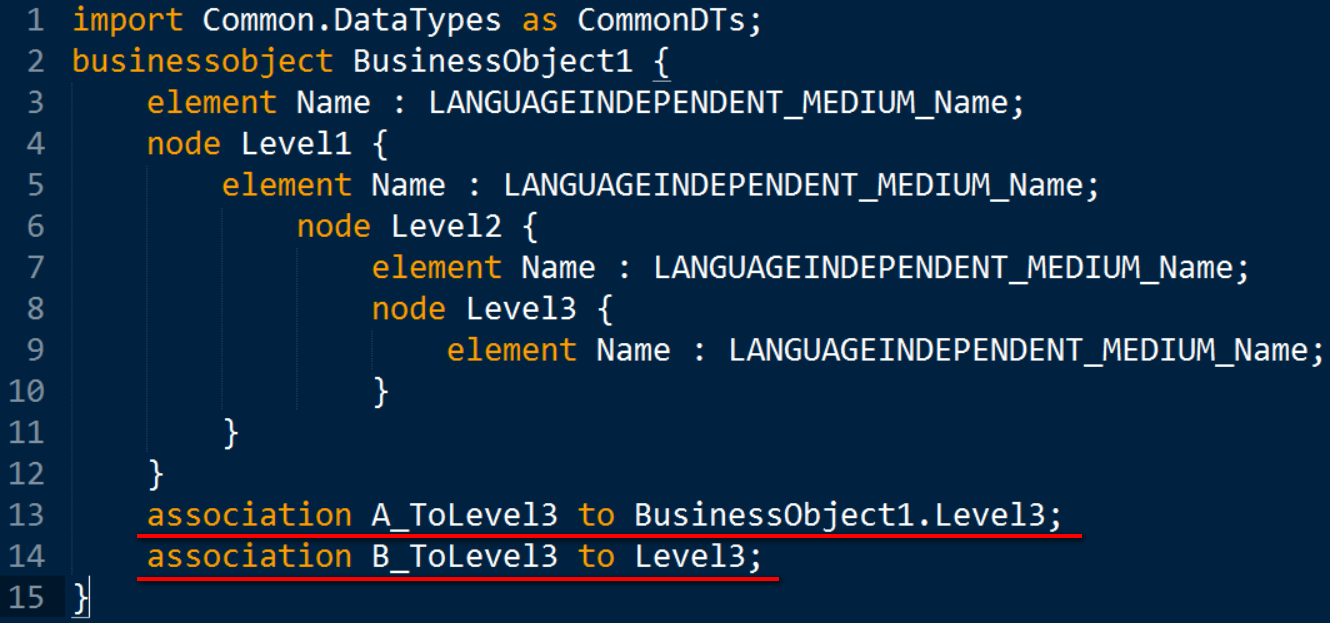
association的multiplicity只支持[0,1]或者[1,1], 如果不显式指定,默认为[1,1].
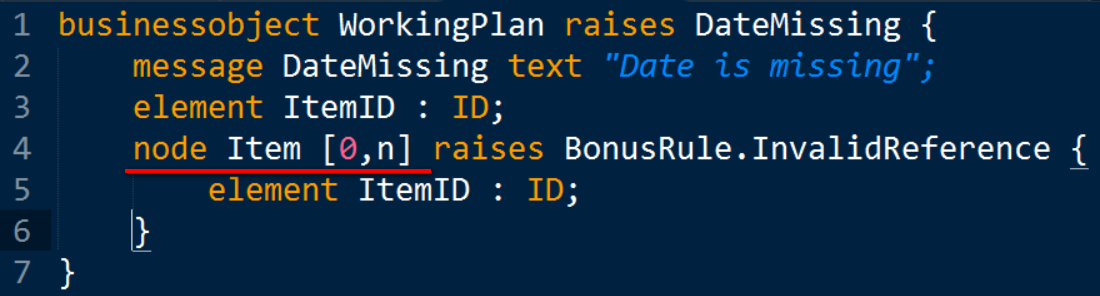
C4C relation的一个特色是,一旦申明了一个子节点之后,系统会默认生成一个对应的composition。
下图第4行代码会自动生成一个[0,n]的从root节点到Item节点的composition。
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)