中山大学提出SimAM:无参Attention!助力分类/检测/分割涨点!
http://proceedings.mlr.press/v139/yang21o.html
code: https://github.com/ZjjConan/SimAM
在正式介绍本文所提注意力模块之前,我们先对现有代表性注意力模块(比如SE、CBAM、GC)进行简要总结;然后,我们再引出本文所提完全不同架构的注意力模块。
Overview of Existing Attention Modules
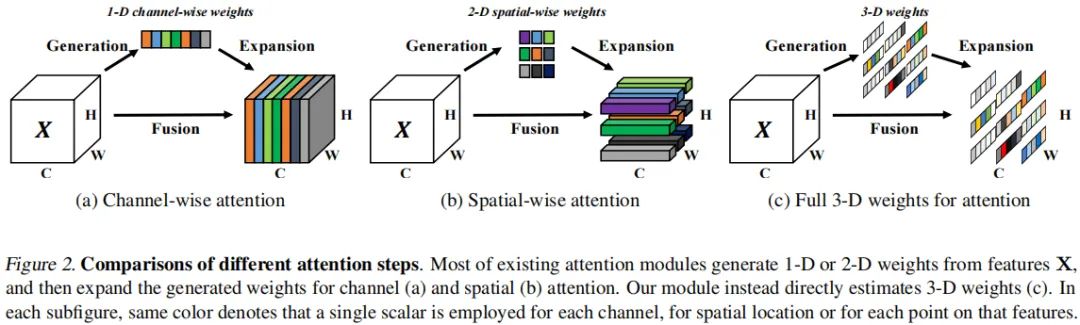
上图a与b列出了现有两种类型的注意力模块:
-
通道注意力:1D注意力,它对不同通道区别对待,对所有位置同等对待;
-
空域注意力:2D注意力,它对不同位置区别对待,对所有通道同等对待。
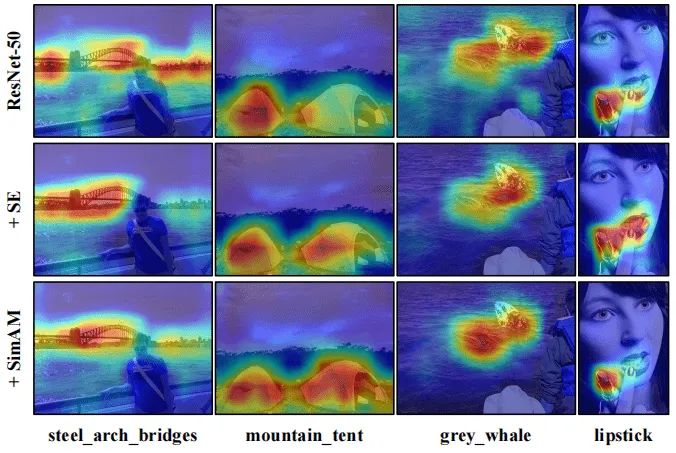
以下图为例,SE缺失了关于"grey_whale"的某些重要成分。我们认为3D注意力比1D和2D更佳,进而提出了上图c的3D注意力模块。

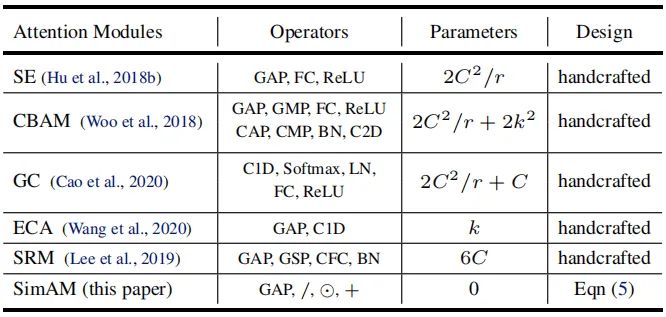
现有注意力模块的另一个重要影响因素:权值生成方法。现有注意力往往采用额外的子网络生成注意力权值,比如SE的GAP+FC+ReLU+FC+Sigmoid。更多注意力模块的操作、参数量可参考下表。总而言之,现有注意力的结构设计需要大量的工程性实验。我们认为:注意力机制的实现应当通过神经科学中的某些统一原则引导设计。
Our Attention Module
已有研究BAM、CBAM分别将空域注意力与通道注意力进行并行或串行组合。然而,人脑的两种注意力往往是协同工作,因此,我们提出了统一权值的注意力模块。
为更好的实现注意力,我们需要评估每个神经元的重要性。在神经科学中,信息丰富的神经元通常表现出与周围神经元不同的放电模式。而且,激活神经元通常会抑制周围神经元,即空域抑制。换句话说,具有空域抑制效应的神经元应当赋予更高的重要性。最简单的寻找重要神经元的方法:度量神经元之间的线性可分性。因此,我们定义了如下能量函数:
其中,。最小化上述公式等价于训练同一通道内神经元t与其他神经元之间的线性可分性。为简单起见,我们采用二值标签,并添加正则项,最终的能量函数定义如下:
理论上,每个通道有个能量函数。幸运的是,上述公式具有如下解析解:
其中,。因此,最小能量可以通过如下公式得到:
上述公式意味着:能量越低,神经元t与周围神经元的区别越大,重要性越高。因此,神经元的重要性可以通过得到。
到目前为止,我们推导了能量函数并挖掘了神经元的重要性。按照注意力机制的定义,我们需要对特征进行增强处理:
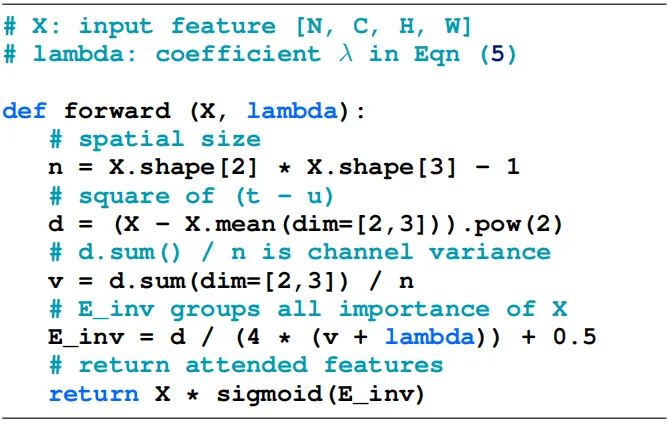
下图给出了SimAM的pytorch风格实现code。
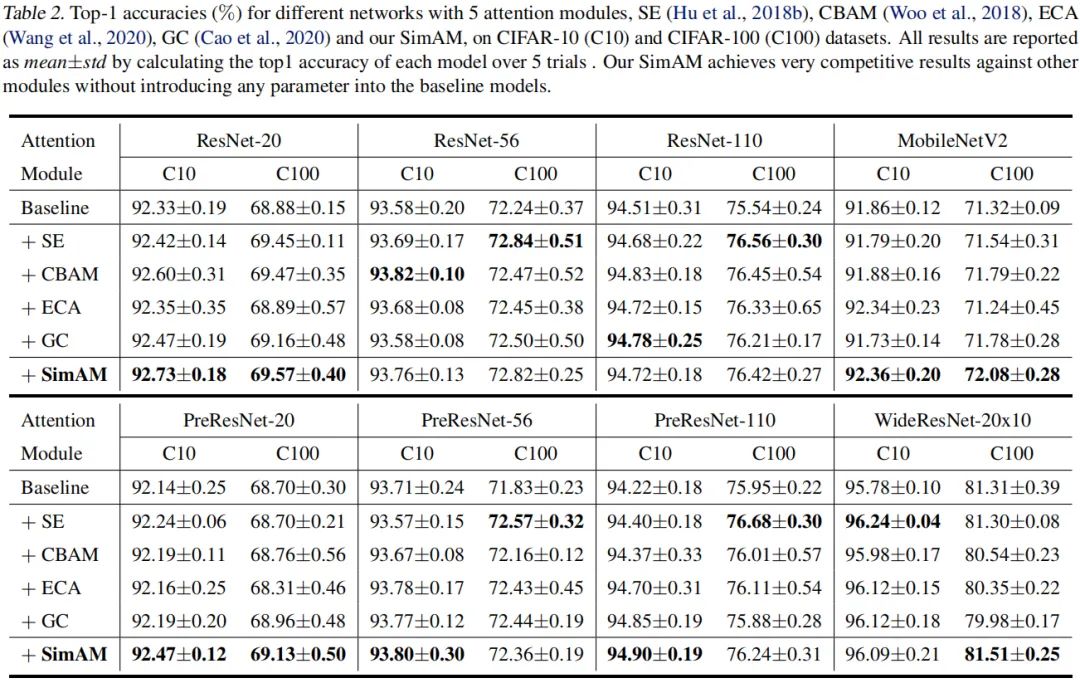
Experiments
我把最后一层改为320,模型6.21m,荣耀9 上64*64 25ms。
测试代码:
-
import functools
-
-
import torch
-
from torch import nn
-
from torch import Tensor
-
# from .utils import load_state_dict_from_url
-
from typing import Callable, Any, Optional, List
-
-
import torch
-
import torch.nn as nn
-
-
-
class Simam_module(torch.nn.Module):
-
def __init__(self, channels = None, e_lambda = 1e-4):
-
super(Simam_module, self).__init__()
-
-
self.activaton = nn.Sigmoid()
-
self.e_lambda = e_lambda
-
-
def __repr__(self):
-
s = self.__class__.__name__ + '('
-
s += ('lambda=%f)' % self.e_lambda)
-
return s
-
-
@staticmethod
-
def get_module_name():
-
return "simam"
-
-
def forward(self, x):
-
-
b, c, h, w = x.size()
-
-
n = w * h - 1
-
-
x_minus_mu_square = (x - x.mean(dim=[2,3], keepdim=True)).pow(2)
-
y = x_minus_mu_square / (4 * (x_minus_mu_square.sum(dim=[2,3], keepdim=True) / n + self.e_lambda)) + 0.5
-
-
return x * self.activaton(y)
-
-
-
-
def _make_divisible(v: float, divisor: int, min_value: Optional[int] = None) -> int:
-
"""
-
This function is taken from the original tf repo.
-
It ensures that all layers have a channel number that is divisible by 8
-
It can be seen here:
-
https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/slim/nets/mobilenet/mobilenet.py
-
:param v:
-
:param divisor:
-
:param min_value:
-
:return:
-
"""
-
if min_value is None:
-
min_value = divisor
-
new_v = max(min_value, int(v + divisor / 2) // divisor * divisor)
-
# Make sure that round down does not go down by more than 10%.
-
if new_v < 0.9 * v:
-
new_v += divisor
-
return new_v
-
-
-
class ConvBNActivation(nn.Sequential):
-
def __init__(self, in_planes: int, out_planes: int, kernel_size: int = 3, stride: int = 1, groups: int = 1,
-
norm_layer: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None,
-
activation_layer: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None,
-
attention_module: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None, ) -> None:
-
padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2
-
if norm_layer is None:
-
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
-
if activation_layer is None:
-
activation_layer = nn.ReLU6
-
if attention_module is not None:
-
if type(attention_module) == functools.partial:
-
module_name = attention_module.func.get_module_name()
-
else:
-
module_name = attention_module.get_module_name()
-
-
if module_name == "simam":
-
super(ConvBNReLU, self).__init__(
-
nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, stride, padding, groups=groups, bias=False),
-
Simam_module(e_lambda=0.1), norm_layer(out_planes), activation_layer(inplace=True))
-
else:
-
super(ConvBNReLU, self).__init__(
-
nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, stride, padding, groups=groups, bias=False),
-
norm_layer(out_planes), activation_layer(inplace=True))
-
else:
-
super(ConvBNReLU, self).__init__(
-
nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, stride, padding, groups=groups, bias=False),
-
norm_layer(out_planes), activation_layer(inplace=True))
-
-
-
# necessary for backwards compatibility
-
ConvBNReLU = ConvBNActivation
-
-
-
class InvertedResidual(nn.Module):
-
def __init__(self, inp: int, oup: int, stride: int, expand_ratio: int,
-
norm_layer: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None,
-
attention_module: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None) -> None:
-
super(InvertedResidual, self).__init__()
-
self.stride = stride
-
assert stride in [1, 2]
-
-
if norm_layer is None:
-
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
-
-
hidden_dim = int(round(inp * expand_ratio))
-
self.use_res_connect = self.stride == 1 and inp == oup
-
-
layers: List[nn.Module] = []
-
if expand_ratio != 1:
-
# pw
-
layers.append(ConvBNReLU(inp, hidden_dim, kernel_size=1, norm_layer=norm_layer))
-
layers.extend([# dw
-
ConvBNReLU(hidden_dim, hidden_dim, stride=stride, groups=hidden_dim, norm_layer=norm_layer,
-
attention_module=attention_module), # pw-linear
-
nn.Conv2d(hidden_dim, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False), norm_layer(oup), ])
-
-
if attention_module is not None:
-
if type(attention_module) == functools.partial:
-
module_name = attention_module.func.get_module_name()
-
else:
-
module_name = attention_module.get_module_name()
-
-
if module_name != "simam":
-
# print(attention_module)
-
layers.append(attention_module(oup))
-
-
self.conv = nn.Sequential(*layers)
-
-
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
-
if self.use_res_connect:
-
return x + self.conv(x)
-
else:
-
return self.conv(x)
-
-
-
class MobileNetV2(nn.Module):
-
def __init__(self, num_classes: int = 1000, width_mult: float = 1.0,
-
inverted_residual_setting: Optional[List[List[int]]] = None, round_nearest: int = 8,
-
-
attention_module: Optional[Callable[..., nn.Module]] = None) -> None:
-
-
super(MobileNetV2, self).__init__()
-
-
block = InvertedResidual
-
-
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
-
-
input_channel = 32
-
last_channel = 320
-
-
if inverted_residual_setting is None:
-
inverted_residual_setting = [# t, c, n, s
-
[1, 16, 1, 1], [6, 32, 3, 2], [6, 64, 4, 2], [6, 96, 3, 1], [6, 160, 2, 2],
-
[6, 320, 1, 1], ]
-
-
# only check the first element, assuming user knows t,c,n,s are required
-
if len(inverted_residual_setting) == 0 or len(inverted_residual_setting[0]) != 4:
-
raise ValueError("inverted_residual_setting should be non-empty "
-
"or a 4-element list, got {}".format(inverted_residual_setting))
-
-
# building first layer
-
input_channel = _make_divisible(input_channel * width_mult, round_nearest)
-
self.last_channel = _make_divisible(last_channel * max(1.0, width_mult), round_nearest)
-
features: List[nn.Module] = [ConvBNReLU(3, input_channel, stride=2, norm_layer=norm_layer)]
-
# building inverted residual blocks
-
for t, c, n, s in inverted_residual_setting:
-
output_channel = _make_divisible(c * width_mult, round_nearest)
-
for i in range(n):
-
stride = s if i == 0 else 1
-
features.append(block(input_channel, output_channel, stride, expand_ratio=t, norm_layer=norm_layer,
-
attention_module=attention_module))
-
input_channel = output_channel
-
# building last several layers
-
features.append(ConvBNReLU(input_channel, self.last_channel, kernel_size=1, norm_layer=norm_layer))
-
# make it nn.Sequential
-
self.features = nn.Sequential(*features)
-
-
# building classifier
-
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(# nn.Dropout(0.2),
-
nn.Linear(self.last_channel, num_classes), )
-
-
# weight initialization
-
for m in self.modules():
-
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
-
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out')
-
if m.bias is not None:
-
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
-
elif isinstance(m, (nn.BatchNorm2d, nn.GroupNorm)):
-
nn.init.ones_(m.weight)
-
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
-
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
-
nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)
-
if m.bias is not None:
-
nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
-
-
def _forward_impl(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
-
# This exists since TorchScript doesn't support inheritance, so the superclass method
-
# (this one) needs to have a name other than `forward` that can be accessed in a subclass
-
x = self.features(x)
-
# Cannot use "squeeze" as batch-size can be 1 => must use reshape with x.shape[0]
-
x = nn.functional.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, (1, 1)).reshape(x.shape[0], -1)
-
x = self.classifier(x)
-
return x
-
-
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
-
return self._forward_impl(x)
-
-
-
if __name__ == '__main__':
-
kwargs = {}
-
kwargs["num_classes"] = 6
-
kwargs["attention_module"] = Simam_module(e_lambda=0.1)
-
-
model = MobileNetV2(**kwargs)
-
-
size = 64
-
-
-
# model.cuda()
-
model.eval()
-
model_path = "dicenet.pth"
-
torch.save(model.state_dict(), model_path)
-
-
import os
-
import time
-
-
fsize = os.path.getsize(model_path)
-
fsize = fsize / float(1024 * 1024)
-
-
print(f"model size {round(fsize, 2)} m")
-
-
input = torch.rand(2, 3, size, size)#.cuda()
-
for i in range(15):
-
t1 = time.time()
-
loc = model(input)
-
-
cnt = time.time() - t1
-
print(cnt, loc.size())
-
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:AI视觉网奇,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/jacke121/article/details/119331832
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)