【 MATLAB 】信号处理工具箱之fft简介及案例分析
目录
Syntax
Y = fft(X)
Y = fft(X,n)
Y = fft(X,n,dim)
Description
Y = fft(X)
Y = fft(X)
-
如果 X 是一个向量,那么 fft(X) 返回向量的傅里叶变换;
-
如果 X 是一个矩阵,则 fft(X) 视X的列为向量,然后返回每列的傅里叶变换;
Y = fft(X,n)
Y = fft(X,n)Y = fft(X,n)
-
如果X是向量并且X的长度小于n,则用尾随零填充X到长度n。
-
如果X是向量并且X的长度大于n,则X被截断为长度n。
-
如果X是矩阵,那么每个列都被视为向量情况。
-
如果X是多维数组,则大小不等于1的第一个数组维度将被视为向量的情况。
Y = fft(X,n,dim)
Y = fft(X,n,dim)沿维度dim返回傅立叶变换。 例如,如果X是矩阵,则fft(X,n,2)返回每行的n点傅立叶变换。
Examples
Noisy Signal
使用傅立叶变换来查找隐藏在噪声中的信号的频率分量。
指定采样频率为1 kHz且信号持续时间为1.5秒的信号参数。
-
clc
-
clear
-
close all
-
% Use Fourier transforms to find the frequency components of a signal buried in noise.
-
% Specify the parameters of a signal with a sampling frequency of 1 kHz and a signal duration of 1.5 seconds.
-
-
Fs = 1000; % Sampling frequency
-
T = 1/Fs; % Sampling period
-
L = 1500; % Length of signal
-
t = (0:L-1)*T; % Time vector
-
-
% Form a signal containing a 50 Hz sinusoid of amplitude 0.7 and a 120 Hz sinusoid of amplitude 1.
-
-
S = 0.7*sin(2*pi*50*t) + sin(2*pi*120*t);
-
% Corrupt the signal with zero-mean white noise with a variance of 4.
-
-
X = S + 2*randn(size(t));
-
-
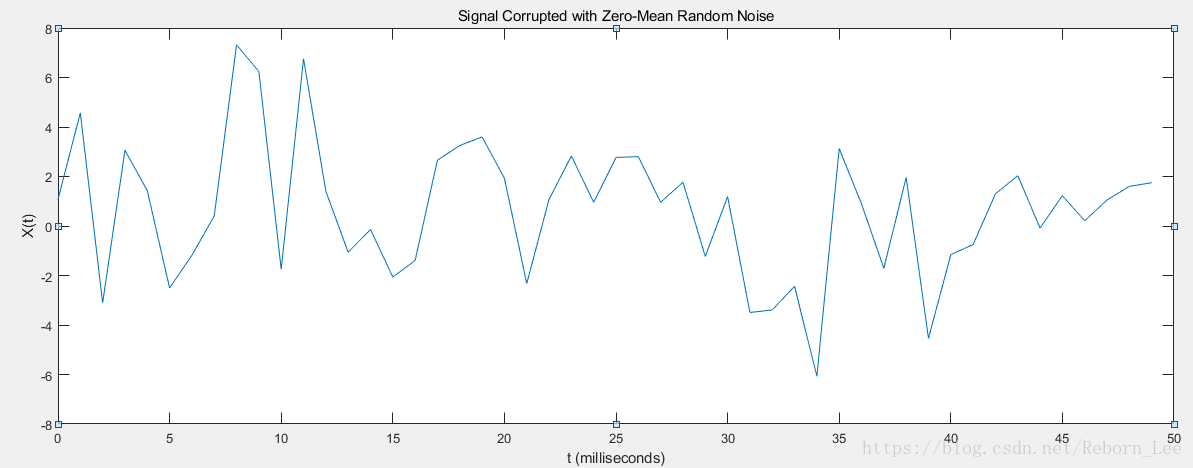
% Plot the noisy signal in the time domain. It is difficult to identify the frequency components by looking at the signal X(t).
-
figure();
-
plot(1000*t(1:50),X(1:50))
-
title('Signal Corrupted with Zero-Mean Random Noise')
-
xlabel('t (milliseconds)')
-
ylabel('X(t)')
-
-
% Compute the Fourier transform of the signal.
-
Y = fft(X);
-
-
% Compute the two-sided spectrum P2. Then compute the single-sided spectrum P1 based on P2 and the even-valued signal length L.
-
P2 = abs(Y/L);
-
P1 = P2(1:L/2+1);
-
P1(2:end-1) = 2*P1(2:end-1);
-
-
% Define the frequency domain f and plot the single-sided amplitude spectrum P1.
-
% The amplitudes are not exactly at 0.7 and 1, as expected, because of the added noise. On average,
-
% longer signals produce better frequency approximations.
-
figure();
-
f = Fs*(0:(L/2))/L;
-
plot(f,P1)
-
title('Single-Sided Amplitude Spectrum of X(t)')
-
xlabel('f (Hz)')
-
ylabel('|P1(f)|')
-
-
% Now, take the Fourier transform of the original, uncorrupted signal and retrieve the exact amplitudes, 0.7 and 1.0.
-
%
-
-
Y = fft(S);
-
P2 = abs(Y/L);
-
P1 = P2(1:L/2+1);
-
P1(2:end-1) = 2*P1(2:end-1);
-
-
figure();
-
plot(f,P1)
-
title('Single-Sided Amplitude Spectrum of S(t)')
-
xlabel('f (Hz)')
-
ylabel('|P1(f)|')
-
figure(1)是加上零均值的随机噪声后的信号时域图形,通过观察这幅图很难辨别其频率成分。
figure(2)是X(t)的单边幅度谱,通过这幅图其实已经能够看出信号的频率成分,分别为50Hz和120Hz,其他的频率成分都会噪声的频率分量。

figure(3)是信号S(t)的单边幅度谱,用作和figure(2)的幅度谱对比,原信号确实只有两个频率成分。

上面三幅图画到一起:

更多案例见下篇博文:【 MATLAB 】信号处理工具箱之 fft 案例分析
文章来源: reborn.blog.csdn.net,作者:李锐博恩,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:reborn.blog.csdn.net/article/details/83059170
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)