【 MATLAB 】信号处理工具箱之 fft 案例分析
【摘要】 上篇博文:【 MATLAB 】信号处理工具箱之fft简介及案例分析介绍了MATLAB信号处理工具箱中的信号变换 fft 并分析了一个案例,就是被噪声污染了的信号的频谱分析。
这篇博文继续分析几个小案例:
Gaussian Pulse
这个案例是将高斯脉冲从时域变换到频域,高斯脉冲的信息在下面的程序中都有注释:
clcclearclose all% Convert a ...
上篇博文:【 MATLAB 】信号处理工具箱之fft简介及案例分析介绍了MATLAB信号处理工具箱中的信号变换 fft 并分析了一个案例,就是被噪声污染了的信号的频谱分析。
这篇博文继续分析几个小案例:
Gaussian Pulse
这个案例是将高斯脉冲从时域变换到频域,高斯脉冲的信息在下面的程序中都有注释:
-
clc
-
clear
-
close all
-
% Convert a Gaussian pulse from the time domain to the frequency domain.
-
%
-
% Define signal parameters and a Gaussian pulse, X.
-
-
Fs = 100; % Sampling frequency
-
t = -0.5:1/Fs:0.5; % Time vector
-
L = length(t); % Signal length
-
-
X = 1/(4*sqrt(2*pi*0.01))*(exp(-t.^2/(2*0.01)));
-
% Plot the pulse in the time domain.
-
figure();
-
plot(t,X)
-
title('Gaussian Pulse in Time Domain')
-
xlabel('Time (t)')
-
ylabel('X(t)')
-
-
% To use the fft function to convert the signal to the frequency domain,
-
% first identify a new input length that is the next power of 2 from the original signal length.
-
% This will pad the signal X with trailing zeros in order to improve the performance of fft.
-
-
n = 2^nextpow2(L);
-
% Convert the Gaussian pulse to the frequency domain.
-
%
-
Y = fft(X,n);
-
% Define the frequency domain and plot the unique frequencies.
-
-
f = Fs*(0:(n/2))/n;
-
P = abs(Y/n);
-
-
figure();
-
plot(f,P(1:n/2+1))
-
title('Gaussian Pulse in Frequency Domain')
-
xlabel('Frequency (f)')
-
ylabel('|P(f)|')
-
-
-
高斯脉冲在时域的图像:
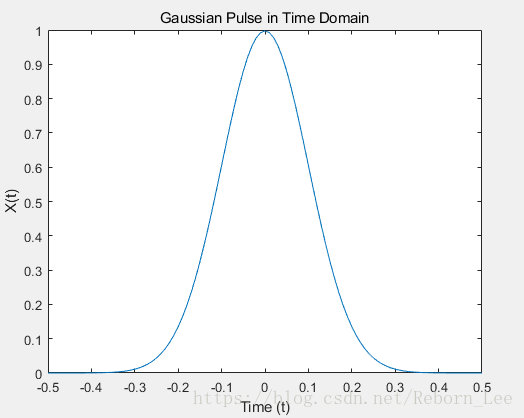
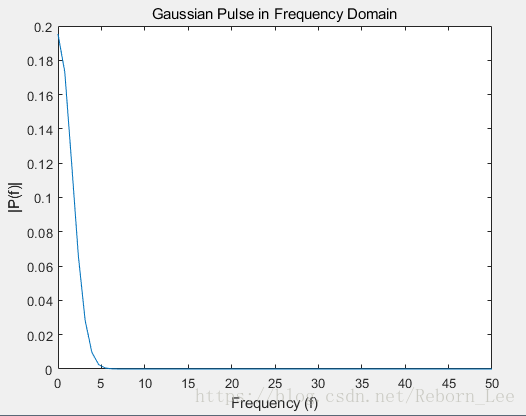
高斯脉冲在频域的图像:
Cosine Waves
这个例子比较简单,就是不同频率的余弦波在时域以及频域的比较:
-
clc
-
clear
-
close all
-
% Compare cosine waves in the time domain and the frequency domain.
-
%
-
% Specify the parameters of a signal with a sampling frequency of 1kHz and a signal duration of 1 second.
-
-
Fs = 1000; % Sampling frequency
-
T = 1/Fs; % Sampling period
-
L = 1000; % Length of signal
-
t = (0:L-1)*T; % Time vector
-
% Create a matrix where each row represents a cosine wave with scaled frequency.
-
% The result, X, is a 3-by-1000 matrix. The first row has a wave frequency of 50,
-
% the second row has a wave frequency of 150, and the third row has a wave frequency of 300.
-
-
x1 = cos(2*pi*50*t); % First row wave
-
x2 = cos(2*pi*150*t); % Second row wave
-
x3 = cos(2*pi*300*t); % Third row wave
-
-
X = [x1; x2; x3];
-
% Plot the first 100 entries from each row of X in a single figure in order and compare their frequencies.
-
-
figure();
-
for i = 1:3
-
subplot(3,1,i)
-
plot(t(1:100),X(i,1:100))
-
title(['Row ',num2str(i),' in the Time Domain'])
-
end
-
-
% For algorithm performance purposes, fft allows you to pad the input with trailing zeros.
-
% In this case, pad each row of X with zeros so that the length of each row is the next higher power of 2 from the current length.
-
% Define the new length using the nextpow2 function.
-
-
n = 2^nextpow2(L);
-
% Specify the dim argument to use fft along the rows of X, that is, for each signal.
-
-
dim = 2;
-
% Compute the Fourier transform of the signals.
-
-
Y = fft(X,n,dim);
-
% Calculate the double-sided spectrum and single-sided spectrum of each signal.
-
-
P2 = abs(Y/L);
-
P1 = P2(:,1:n/2+1);
-
P1(:,2:end-1) = 2*P1(:,2:end-1);
-
% In the frequency domain, plot the single-sided amplitude spectrum for each row in a single figure.
-
-
figure();
-
for i=1:3
-
subplot(3,1,i)
-
plot(0:(Fs/n):(Fs/2-Fs/n),P1(i,1:n/2))
-
title(['Row ',num2str(i),' in the Frequency Domain'])
-
end
-
-
下图是频率为50Hz,150Hz以及300Hz的余弦波在时域的图像:
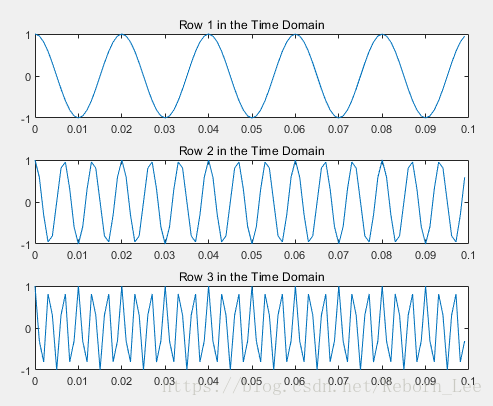
下图分别为其fft:
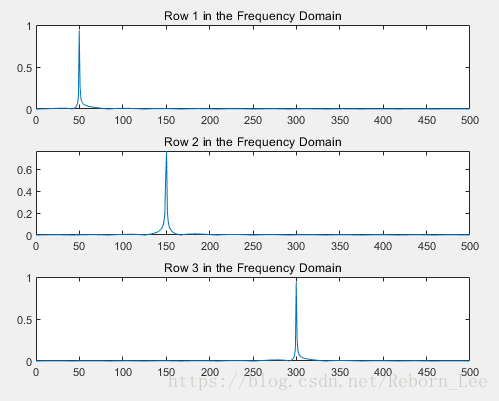
从频域图中可以清晰的看到它们的频率成分位于何处。
文章来源: reborn.blog.csdn.net,作者:李锐博恩,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:reborn.blog.csdn.net/article/details/83060448
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)