ALGORITHMS FOR SOURCE LOCALIZATION
Two approaches for source localization, namely, nonlinear and linear, are presented in Sections 2.3.1 and 2.3.2 , respectively. Generally speaking, the nonlinear methodology [13 – 16] directly employs Equation 2.1 to solve for x by minimizing the least squares ( LS ) or the weighted least squares ( WLS ) cost function constructed from the following error function:
![]()
where ![bold{tilde x} = [tilde x, tilde y]^T](https://res-hd.hc-cdn.cn/ecology/9.3.196/v2_resources/ydcomm/libs/images/loading.gif) is the optimization variable for x , which corresponds to the NLS or ML estimator, respectively. On the other hand, the linear techniques convert Equation 2.1 into a set of linear equations in
is the optimization variable for x , which corresponds to the NLS or ML estimator, respectively. On the other hand, the linear techniques convert Equation 2.1 into a set of linear equations in  :
:
![]()
where b and A are available, while q is the transformed noise vector. Based on Equation 2.37 , we construct
![]()
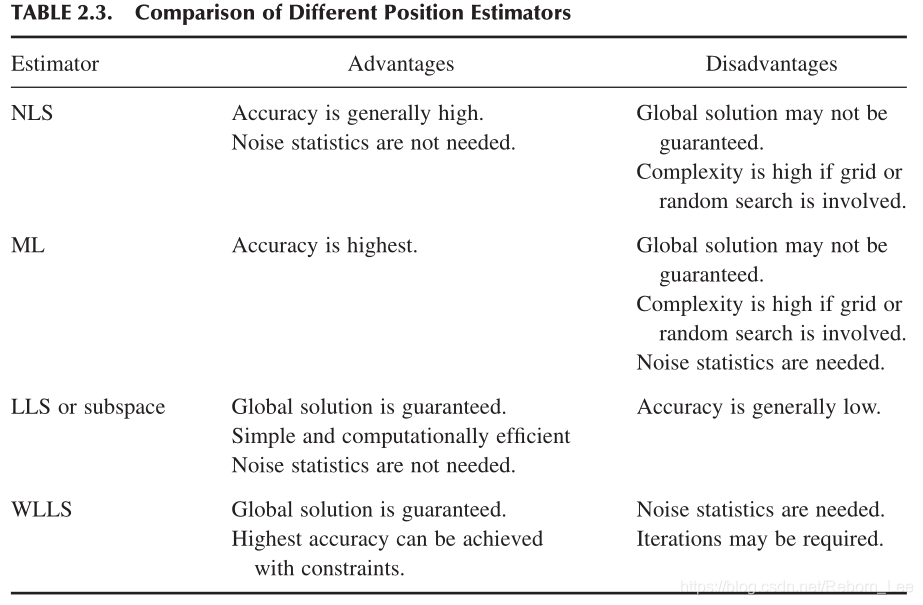
Applying the LS or WLS techniques on Equation 2.38 results in the LLS [17, 18] ,WLLS [19 – 22] and subspace [23 – 26] estimators. A comparison summary for the position estimators examined in this chapter is provided in Table 2.3 .
文章来源: reborn.blog.csdn.net,作者:李锐博恩,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:reborn.blog.csdn.net/article/details/83585354
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)