使用Scratch2和ROS进行机器人图形化编程学习
【摘要】 使用Scratch3和ROS进行机器人编程学习(适用于中小学机器人编程Scratch和ROS)
Scratch是一款由麻省理工学院(MIT)设计开发的少儿编程工具,Python是近年来非常流行的机器人和人工智能编程语言,ROS是机器人操作系统。
参考JdeRobot的一篇详细介绍,就可以实现上述的功能,需要安装Scratch2、ROS Kinetic、Gazebo 7、J...
使用Scratch3和ROS进行机器人编程学习(适用于中小学机器人编程Scratch和ROS)
Scratch是一款由麻省理工学院(MIT)设计开发的少儿编程工具,Python是近年来非常流行的机器人和人工智能编程语言,ROS是机器人操作系统。
参考JdeRobot的一篇详细介绍,就可以实现上述的功能,需要安装Scratch2、ROS Kinetic、Gazebo 7、JdeRobot、Python2.7等。
通过将Scratch2图形化编程语言转为Python,然后通过ROS消息机制控制Gazebo或实际机器人。
codelab-adapter-docs.codelab.club + github.com/wwj718 +
~~信息化智能化时代下平等受教育的权利~~
1 先看如下一个简单的示例
1.1 新建hiros.bz2,如下:
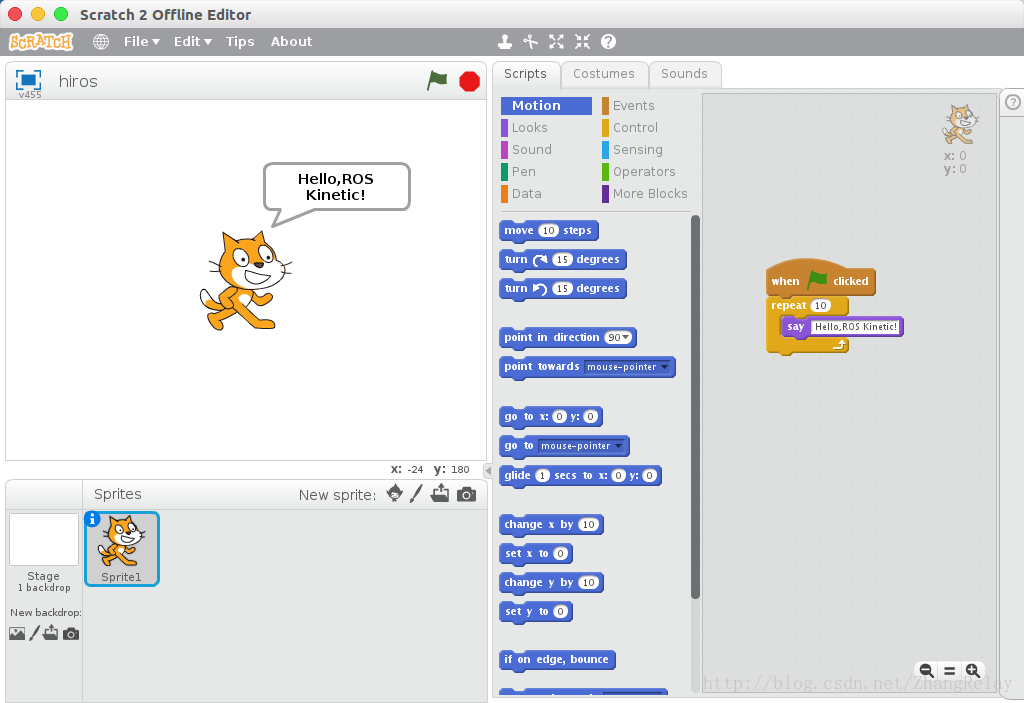
1.2 通过下面命令将其转为Python:
-
$ python scratch2python.py hiros.sb2
-
Stringify:
-
when @greenFlag clicked
-
repeat 10
-
say 'Hello,ROS Kinetic!'
-
end
-
[WARN] Block <when @greenFlag clicked> not included yet
-
-
-------------------
-
#!/usr/bin/env python
-
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
-
-
import time
-
import config
-
import sys
-
import comm
-
import os
-
import yaml
-
-
from drone import Drone
-
from robot import Robot
-
-
def execute(robot):
-
try:
-
-
for i in range(10):
-
print('Hello,ROS Kinetic!')
-
-
except KeyboardInterrupt:
-
raise
-
-
if __name__ == '__main__':
-
if len(sys.argv) == 2:
-
path = os.getcwd()
-
open_path = path[:path.rfind('src')] + 'cfg/'
-
filename = sys.argv[1]
-
-
else:
-
sys.exit("ERROR: Example:python my_generated_script.py cfgfile.yml")
-
-
# loading the ICE and ROS parameters
-
cfg = config.load(open_path + filename)
-
stream = open(open_path + filename, "r")
-
yml_file = yaml.load(stream)
-
-
for section in yml_file:
-
if section == 'drone':
-
#starting comm
-
jdrc = comm.init(cfg,'drone')
-
-
# creating the object
-
robot = Drone(jdrc)
-
-
break
-
elif section == 'robot':
-
#starting comm
-
jdrc = comm.init(cfg,'robot')
-
-
# creating the object
-
robot = Robot(jdrc)
-
-
break
-
# executing the scratch program
-
execute(robot)
-
-
-
-------------------
-
2 控制机器人示例
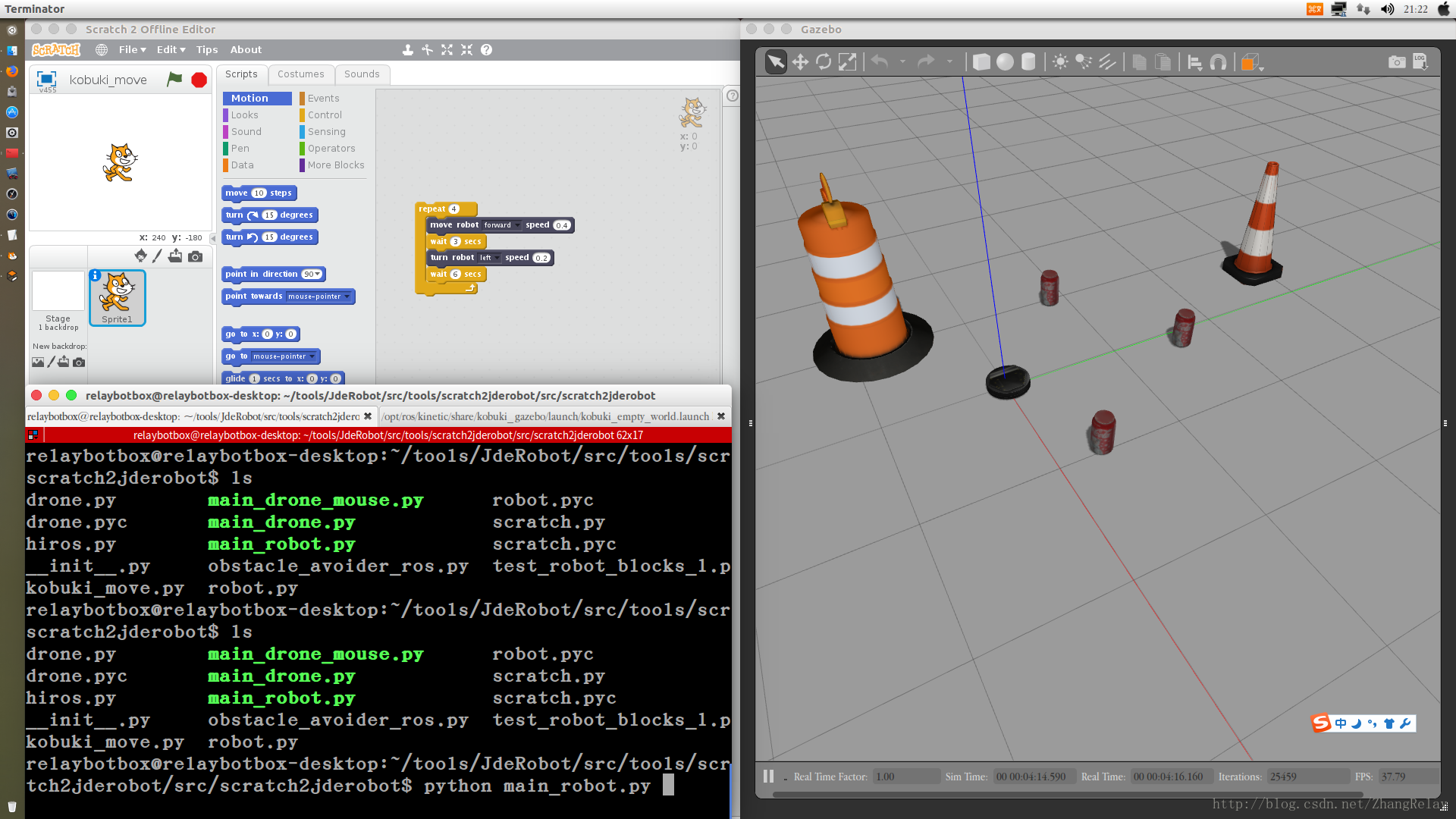
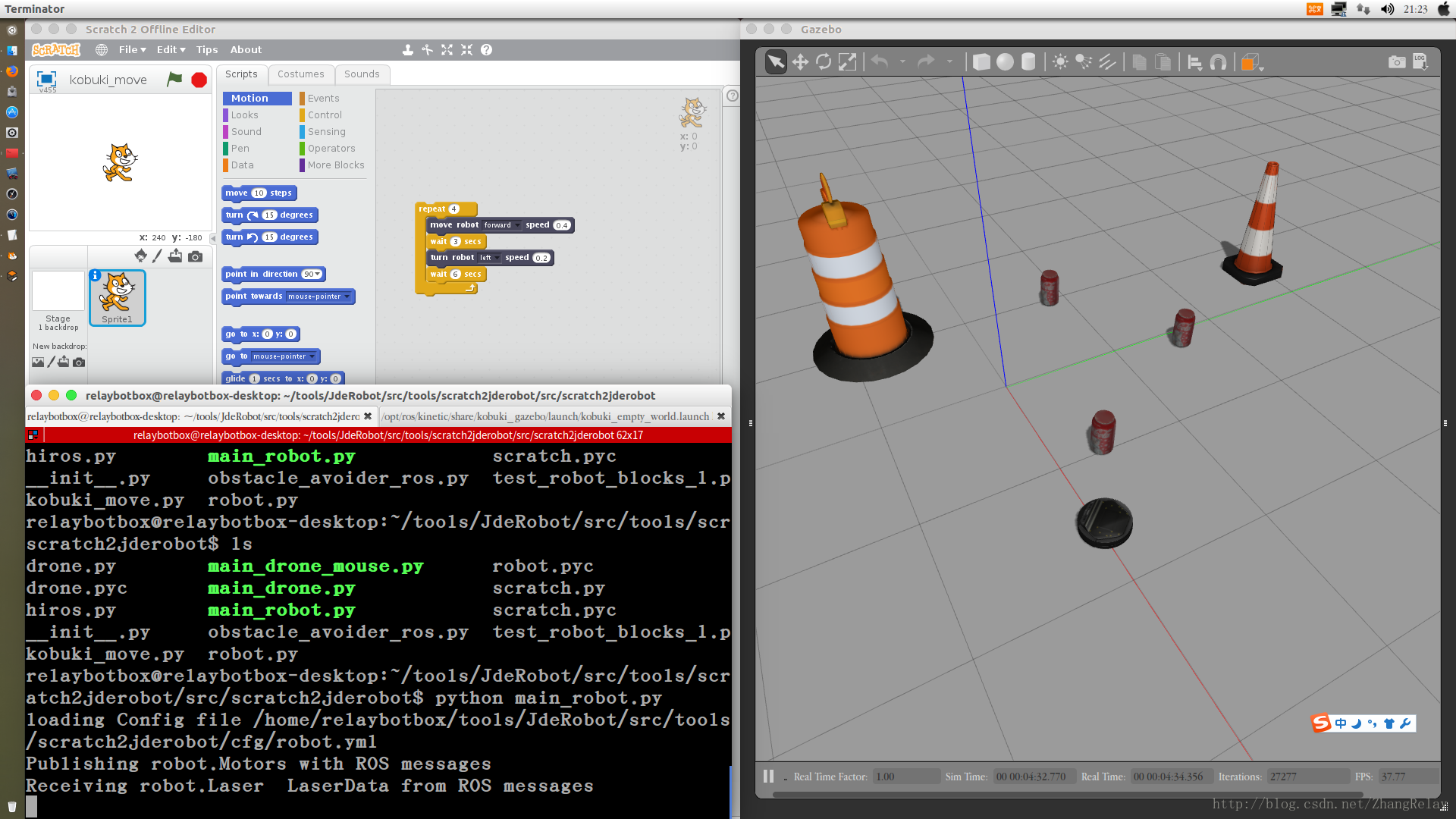
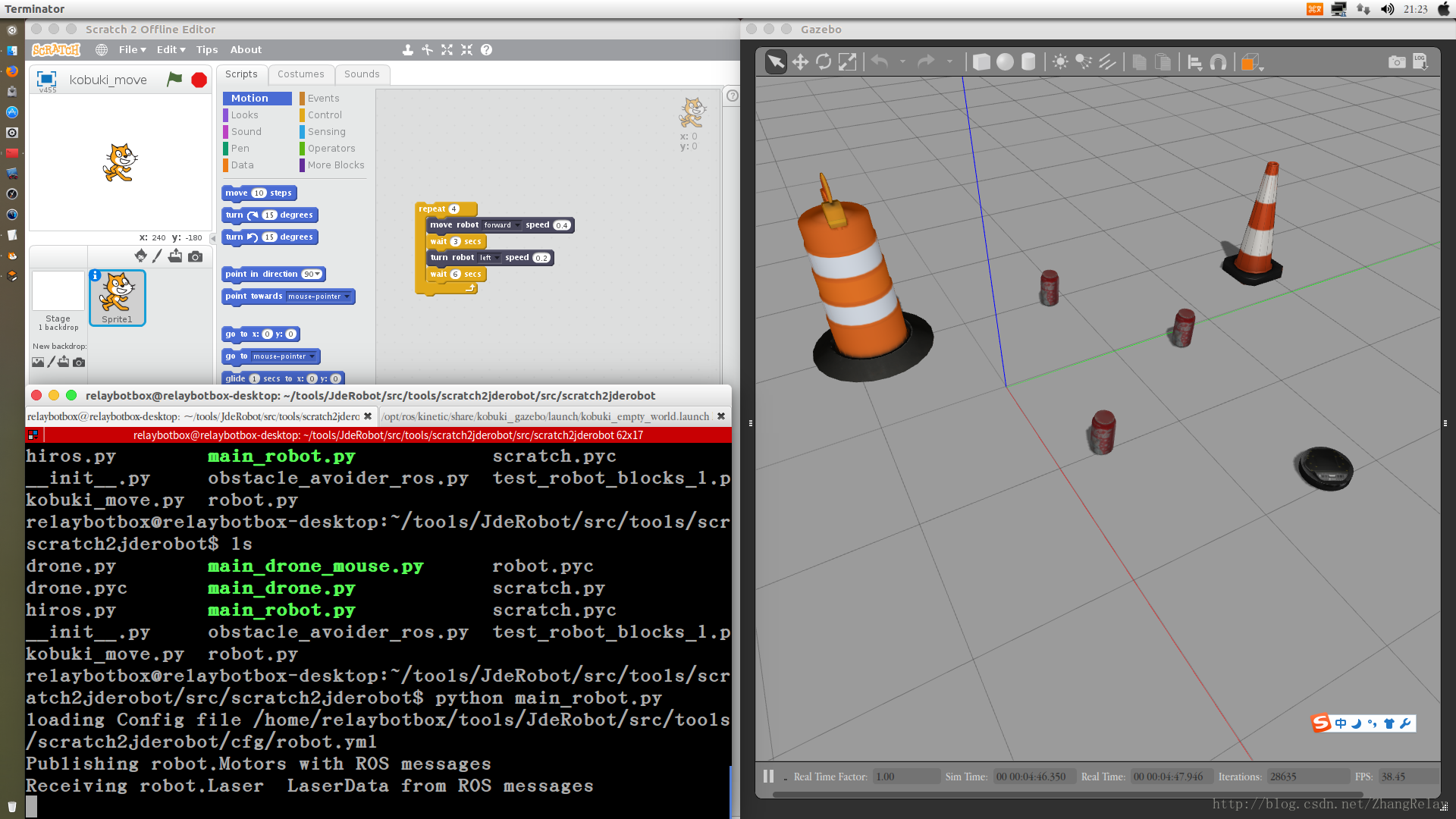
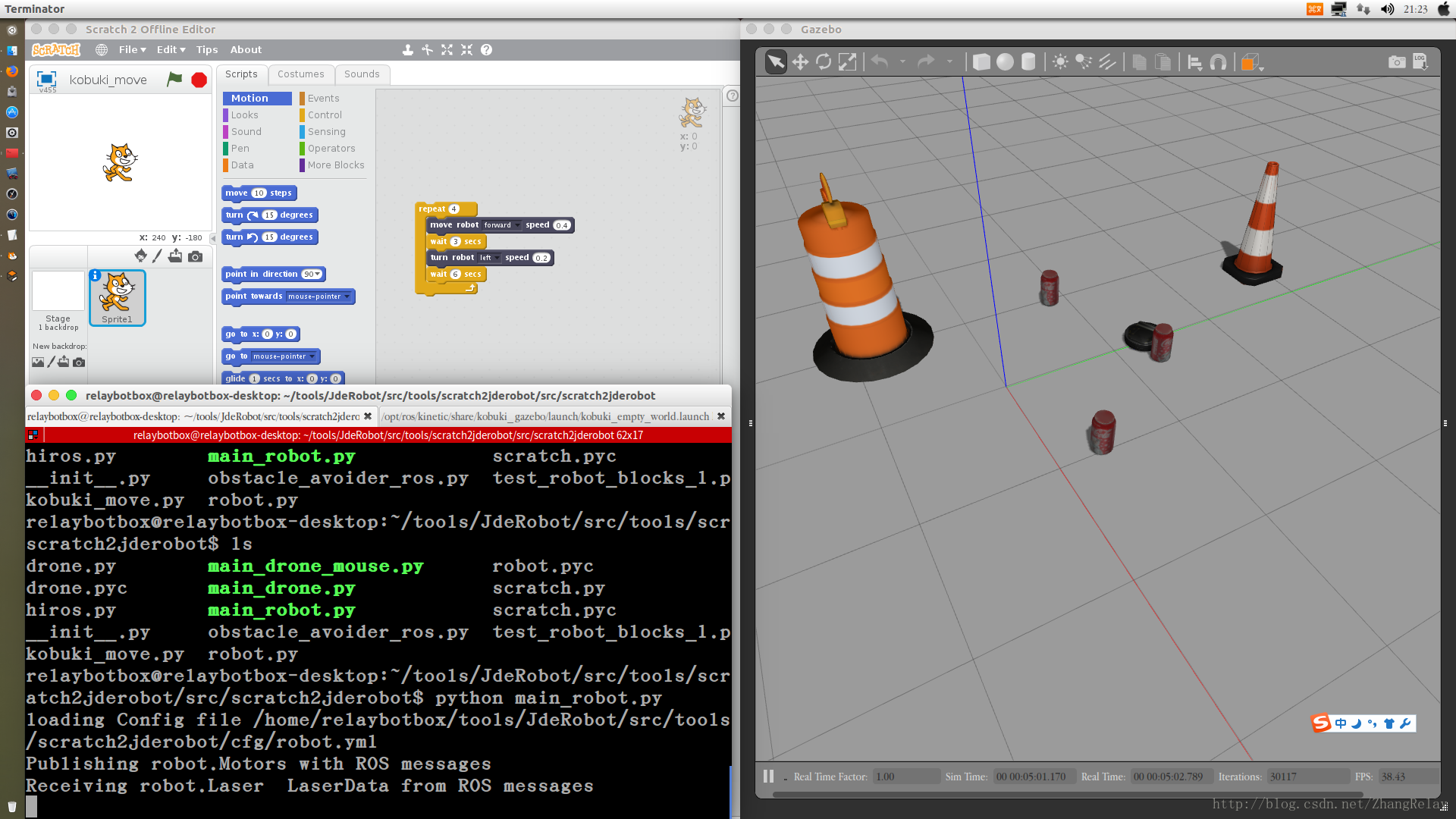
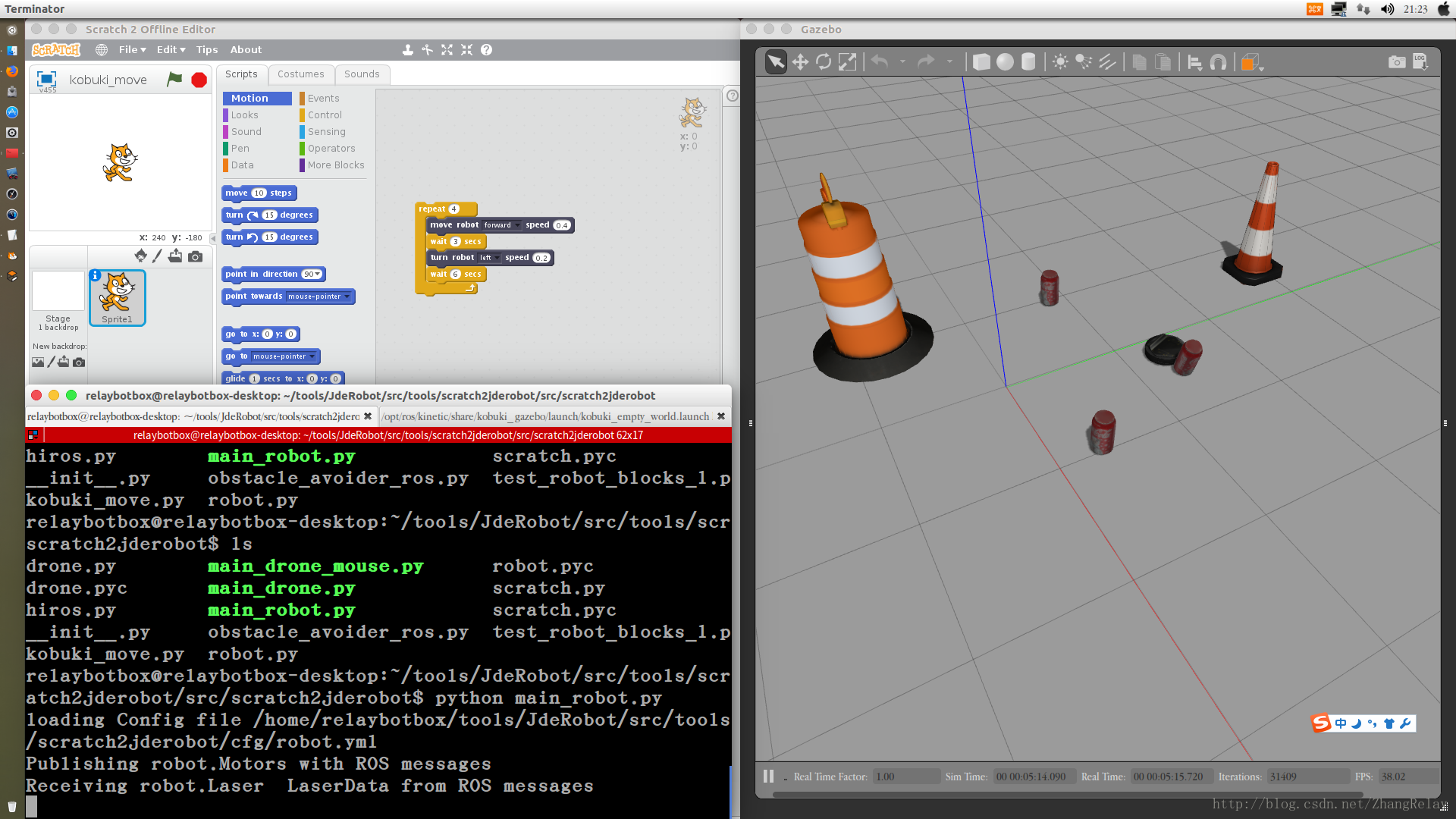
是不是比较有趣,在不需购买任何设备的情况下,就可以用Scratch2进行ROS机器人编程。小学用Scratch2学习简单编程,中学用Python学习简单编程,大学用Python和C++学习复杂机器人编程,无缝衔接。
3 scratch2python.py
-
#!/usr/bin/env python
-
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
-
-
__author__ = "Raul Perula-Martinez"
-
__copyright__ = "JdeRobot project"
-
__credits__ = ["Raul Perula-Martinez"]
-
__license__ = "GPL v3"
-
__version__ = "0.0.0"
-
__maintainer__ = "Raul Perula-Martinez"
-
__email__ = "raules@gmail.com"
-
__status__ = "Development"
-
-
import kurt
-
import os
-
import sys
-
-
from difflib import SequenceMatcher
-
from parse import parse, compile
-
from termcolor import cprint
-
-
-
GENERAL = [
-
['end', ''],
-
['forever', 'while True:'],
-
['if {} then', 'if %s:'],
-
['else', 'else:'],
-
['repeat {}', 'for i in range(%s):'],
-
['say {}', 'print(%s)'],
-
['set {} to {}', '%s = %s'],
-
['wait {} secs', 'time.sleep(%s)'],
-
]
-
-
ROBOTICS = [
-
['move robot {}', 'robot.move("%s")'],
-
['move drone {}', 'robot.move("%s")'],
-
['move robot {} speed {}', 'robot.move("%s", %s)'],
-
['stop robot-drone', 'robot.stop()'],
-
['turn robot-drone {}', 'robot.turn("%s")'],
-
['turn robot {} speed {}', 'robot.turn("%s", %s)'],
-
['take off drone', 'robot.take_off()'],
-
['land drone', 'robot.land()'],
-
['frontal laser distance', 'robot.get_laser_distance()'],
-
]
-
-
def is_conditional(sentence):
-
"""
-
Returns if a sentence is conditional or not.
-
-
@param sentence: The sentence to check.
-
@return: True if it has a conditional, False otherwise.
-
"""
-
-
if "if" in sentence:
-
return True
-
-
return False
-
-
-
def similar(a, b):
-
"""
-
Returns the ratio value comparing two sentences.
-
-
@param a: First sentence.
-
@param b: Second sentence.
-
@return: The ratio of the similarity.
-
"""
-
-
return SequenceMatcher(None, a, b).ratio()
-
-
-
def sentence_mapping(sentence, threshold=None):
-
"""
-
Maps a sentence and returns the original and the mapped.
-
-
@param sentence: The sentence to map.
-
@return: The original sentence and the mapped sentence.
-
"""
-
-
found = False
-
options = []
-
original = None
-
translation = None
-
-
# first look for general blocks
-
for elem in GENERAL:
-
if elem[0][:3] == sentence.replace(' ', '')[:3]:
-
options.append(elem)
-
found = True
-
-
# then look for robotics blocks
-
for elem in ROBOTICS:
-
if elem[0][:3] == sentence.replace(' ', '').replace('(', '')[:3]:
-
options.append(elem)
-
found = True
-
if found:
-
# select the option that better fits
-
l = [(m[0], m[1], similar(sentence, m[0])) for m in options]
-
original, translation, score = max(l, key=lambda item: item[2])
-
if threshold and score < threshold:
-
return None, None
-
-
# extract arguments
-
p = compile(original)
-
args = p.parse(sentence.replace(' ', ''))
-
if args:
-
args_aux = list(args)
-
-
# look for more blocks
-
for idx in range(len(args_aux)):
-
new_ori, new_trans = sentence_mapping(args_aux[idx]) #sentence_mapping(args_aux[idx],0.8) --old
-
if new_trans != None:
-
args_aux[idx] = args_aux[idx].replace(new_ori, new_trans) #replace(args_aux[idx], new_trans)
-
translation = translation % tuple(args_aux)
-
return original, translation
-
-
-
if __name__ == "__main__":
-
# get current working directory
-
path = os.getcwd()
-
open_path = path[:path.rfind('scripts')] + 'data/'
-
save_path = path[:path.rfind('scripts')] + 'src/scratch2jderobot/'
-
-
if len(sys.argv) == 2:
-
# template creation
-
-
template = "\
-
#!/usr/bin/env python\n\
-
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-\n\n\
-
import time\n\
-
import config\n\
-
import sys\n\
-
import comm\n\
-
import os\n\
-
import yaml\n\n\
-
from drone import Drone\n\
-
from robot import Robot\n\n\
-
def execute(robot):\n\
-
\ttry:\n\
-
\t%s\
-
except KeyboardInterrupt:\n\
-
\t\traise\n\n\
-
if __name__ == '__main__':\n\
-
\tif len(sys.argv) == 2:\n\
-
\t\tpath = os.getcwd()\n\
-
\t\topen_path = path[:path.rfind('src')] + 'cfg/'\n\
-
\t\tfilename = sys.argv[1]\n\n\
-
\telse:\n\
-
\t\tsys.exit(\"ERROR: Example:python my_generated_script.py cfgfile.yml\")\n\n\
-
\t# loading the ICE and ROS parameters\n\
-
\tcfg = config.load(open_path + filename)\n\
-
\tstream = open(open_path + filename, \"r\")\n\
-
\tyml_file = yaml.load(stream)\n\n\
-
\tfor section in yml_file:\n\
-
\t\tif section == 'drone':\n\
-
\t\t\t#starting comm\n\
-
\t\t\tjdrc = comm.init(cfg,'drone')\n\n\
-
\t\t\t# creating the object\n\
-
\t\t\trobot = Drone(jdrc)\n\n\
-
\t\t\tbreak\n\
-
\t\telif section == 'robot':\n\
-
\t\t\t#starting comm\n\
-
\t\t\tjdrc = comm.init(cfg,'robot')\n\n\
-
\t\t\t# creating the object\n\
-
\t\t\trobot = Robot(jdrc)\n\n\
-
\t\t\tbreak\n\
-
\t# executing the scratch program\n\
-
\texecute(robot)\n\n\
-
"
-
-
# load the scratch project
-
p = kurt.Project.load(open_path + sys.argv[1])
-
-
# show the blocks included
-
for scriptable in p.sprites + [p.stage]:
-
for script in scriptable.scripts:
-
# exclude definition scripts
-
if "define" not in script.blocks[0].stringify():
-
s = script
-
print("Stringify:")
-
sentences = []
-
for b in s.blocks:
-
print(b.stringify())
-
sentences += b.stringify().split('\n')
-
tab_seq = "\t"
-
python_program = ""
-
-
for s in sentences:
-
# count number of tabs
-
num_tabs = s.replace(' ', tab_seq).count(tab_seq)
-
python_program += tab_seq * (num_tabs + 1)
-
-
# pre-processing if there is a condition (operators and types)
-
if is_conditional(s):
-
s = s.replace("'", "").replace("=", "==")
-
-
# mapping
-
original, translation = sentence_mapping(s)
-
-
# set the code
-
if translation != None:
-
python_program += translation
-
else:
-
cprint("[WARN] Block <%s> not included yet" % s, 'yellow')
-
python_program += "\n" + tab_seq
-
-
# join the template with the code and replace the tabs
-
file_text = template % python_program
-
file_text = file_text.replace(tab_seq, ' ' * 4)
-
-
print("\n-------------------")
-
cprint(file_text, 'green')
-
print("-------------------\n")
-
-
# save the code in a python file with the same name as sb2 file
-
file_name = sys.argv[1].replace('.sb2','.py')
-
f = open(save_path + file_name, "w")
-
f.write(file_text)
-
f.close()
-
-
else:
-
print(
-
"ERROR: Number of parameters incorrect. Example:\n\tpython scratch2python.py hello_world.sb2")
----
文章来源: zhangrelay.blog.csdn.net,作者:zhangrelay,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:zhangrelay.blog.csdn.net/article/details/78857311
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)