write_cfgmem 产生存储器配置文件?
write_cfgmem命令用于产生存储器配置文件,用于配置FPGA。在Vivado的tools工具下的Create a configuration file to program the device中,其GUI界面如下:
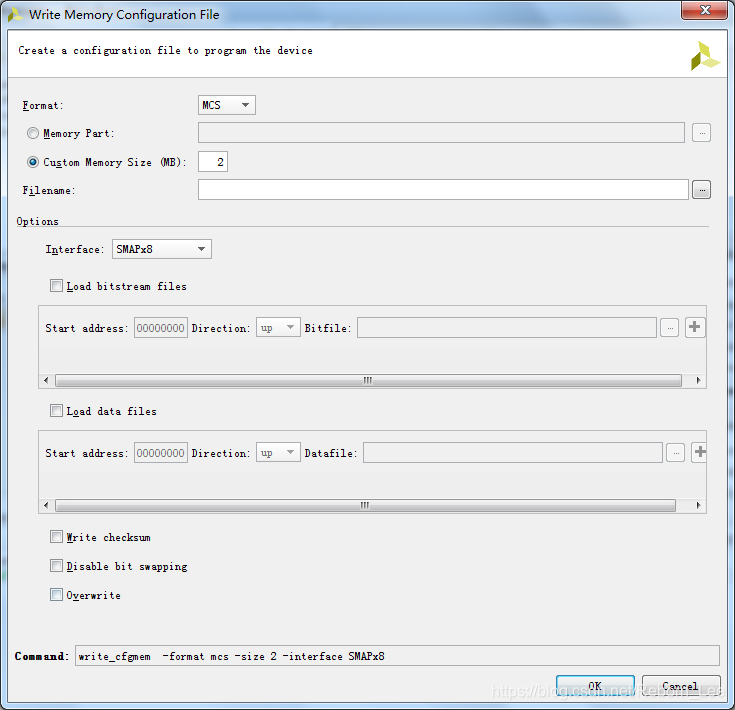
也可以使用Tcl命令来使用,如下实例。
实例:
write_cfgmem -format mcs -size 128 -interface BPIx16 -loadbit "up 0x00000000 G:/Vivado_file/MultiBoot/MultiBoot.runs/impl_1/Golden_image.bit up 0x45000000 G:/Vivado_file/MultiBoot_Update/MultiBoot_Update.runs/impl_1/Update_image.bit " -file C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/multiboot_test.mcs
在Vivado的Tcl Console中输入write_cfgmem -help,得到如下的解释:
Description:
Create file(s) for programming flash memory.
Syntax:
write_cfgmem [-force] -format <arg> -size <arg> [-interface <arg>] [-checksum]
[-disablebitswap] [-loadbit <arg>] [-loaddata <arg>] [-quiet]
[-verbose] <file>
Usage:
Name Description
------------------------------
[-force] Overwrite existing file
-format Format of the file to generate
-size Size of memory that is being targeted in M Bytes (must
be power of 2).
[-interface] Interface used to program device.
Default: SMAPx8
[-checksum] Calculate a 32-bit checksum for each file. Memory will
be filed with value of 0xFF unless a different byte
value is specified.
Default: 0xFF
[-disablebitswap] Disable bit swapping in a byte for bitfiles.
[-loadbit] Load bit files into memory from given address.
[-loaddata] Load data into memory from given address.
[-quiet] Ignore command errors
[-verbose] Suspend message limits during command execution
<file> The name of the file to generate
Categories:
FileIO
Description:
This command formats a design specific configuration bitstream (.bit) file,
and any specified data files, into a specified memory configuration file
format to program into a flash memory device using the program_hw_cfgmem
command. Supported memory configuration file formats are MCS, BIN, and HEX.
Note: When you generate a cfgmem file with write_cfgmem, by default the
bits within a byte are bit-swapped, or mirrored, compared to bytes in the
original input bitstream. You can disable bitswap using the -disablebitswap
option as described below.
The process whereby the design specific data is loaded or programmed into
the Xilinx FPGA is called configuration. The create_hw_cfgmem command
defines a flash memory device used for configuring and booting the hardware
device.
After the hw_cfgmem object is created, and associated with the hw_device,
the configuration memory can be programmed with the bitstream and other
data from a memory configuration file created with the write_cfgmem
command. The hw_cfgmem object is programmed using the program_hw_cfgmem
command.
The write_cfgmem -loadbit command loads one or more specified bitstream
files into the memory configuration file, filling the available memory of
the device in an upward or downward direction from a specified starting
address. You can also add data files to the memory configuration file, by
specifying the starting address to load the file with -loaddata.
Note: When using -loadbit and -loaddata to fill the memory of the device,
you must exercise care to insure that the bitstream and data files fit into
the available memory and do not overwrite each other. Any data collisions
will cause the write_cfgmem command to fail with an error
The write_cfgmem command returns a transcript of its process when
successful, or returns an error if it fails.
Arguments:
-force - (Optional) Overwrite a file of the same name if one exists.
-format [ BIN | HEX | MCS ] - (Required) The format of the memory
configuration file to write. Supported values include BIN, HEX, and MCS.
-size <arg> - (Required) Specify the size limit in MBytes of the PROM
device that is being targeted. The size must be specified as a power of 2.
-interface <arg> - (Optional) Specify the interface used to program the
PROM device. Valid values include SMAPx8 (default), SMAPx16, SMAPx32,
SERIALx1, SPIx1, SPIx2, SPIx4, SPIx8, BPIx8, BPIx16. This also determines
if byte swapping is enabled or disabled. The default interface is SMAPx8.
Note: The specified interface format of the configuration memory file is
critical to properly programming the flash memory device with the
program_hw_cfgmem command. You should be careful to use this option to
match the generated file with the target cfgmem_part
-checksum - (Optional) Calculate a 32-bit checksum for the PROM file. The
device memory will be filled with the default value of 0xFF unless a
different byte value is specified. This option generates a checksum value
appearing in the memory configuration file. This value should match the
checksum in the device programmer. Use this option to verify that correct
data was programmed into the flash memory.
-disablebitswap - (Optional) Disable the default bit swapping for bytes in
the bitstream files. By default, in the files written by write_cfgmem, the
bits within a byte are bit-swapped, or mirrored, compared to bytes in the
original input BIT files. This option disables the bit swapping in the
output files.
-loadbit <arg> - (Optional) Specify the starting address of the PROM device
to begin loading one or more bitstream files. The option is specified as a
string with the form:
"up|down 0x0 bitfile.bit <bitfile2.bit>"
Where:
* up | down - This option loads one or more BIT files into memory,
starting from the specified address, in either and upward or a downward
direction.
* 0x0 - The starting address to load the bitstream, specified as a
hexadecimal value.
* <bitfile.bit> - The bitstream (.bit) file to load into the flash memory
device. You can specify multiple bitfiles, causing the files to be
concatenated in a daisy chain.
Note: You can only specify the -loadbit option once, but you can repeat the
arguments as needed to load multiple bitstream files from different
starting addresses:
-loadbit "up 0 bitfile1.bit up 0xFFFFFF bitfile2.bit"
-loaddata <arg> - (Optional) Load the specified data files into the memory
of the configuration device from the starting address. The -loaddata option
is a string in the same form as the -loadbit argument, specifying the
direction, starting address, and data file names to add into the memory
configuration file. Data files will be added to the flash memory device as
is, with no additional formatting.
* up | down - This option loads one or more DATA files into memory,
starting from the specified address, in either and upward or a downward
direction.
* 0x0 - The starting address to load the data file, specified as a
hexadecimal value.
* <data_file> - A data file to load into the flash memory device. You can
specify multiple data files, causing the files to be concatenated in a
daisy chain.
Note: Although both -loadbit and -loaddata are marked as optional, at least
one argument must be used to provide the data for the memory configuration
file
-quiet - (Optional) Execute the command quietly, returning no messages from
the command. The command also returns TCL_OK regardless of any errors
encountered during execution.
Note: Any errors encountered on the command-line, while launching the
command, will be returned. Only errors occurring inside the command will be
trapped.
-verbose - (Optional) Temporarily override any message limits and return
all messages from this command.
Note: Message limits can be defined with the set_msg_config command.
<file> - (Required) The filename of the memory configuration file to write.
The file extension will match the format specified (.mcs), and is not
required as part of the file name.
Note: If the path is not specified as part of the file name, the file will
be written into the current working directory, or the directory from which
the tool was launched.
Example:
The following example writes the specified memory configuration file in the
MCS format, with a size limit of 64 MB, loading the specified bitstream
file moving up from the starting address:
write_cfgmem -format MCS -size 64 -loadbit "up 0x0 \
C:/Data/Vivado_Debug/project_debug/project_debug.runs/impl_1/sinegen_demo.bit" \
config_memory1
文章来源: reborn.blog.csdn.net,作者:李锐博恩,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:reborn.blog.csdn.net/article/details/88951035
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)