Cozmo人工智能机器人SDK使用笔记(3)-视觉部分vision
【摘要】 关于机器人感知-视觉部分,有过一次公开分享,讲稿全文和视屏实录,参考如下CSDN链接:
机器人感知-视觉部分(Robotic Perception-Vision Section):
https://blog.csdn.net/ZhangRelay/article/details/81352622
Cozmo视觉Vision也可以完成很多功能,宠物、方块、人脸等识别和跟...
关于机器人感知-视觉部分,有过一次公开分享,讲稿全文和视屏实录,参考如下CSDN链接:
机器人感知-视觉部分(Robotic Perception-Vision Section):
https://blog.csdn.net/ZhangRelay/article/details/81352622
Cozmo视觉Vision也可以完成很多功能,宠物、方块、人脸等识别和跟踪等,非常有趣。
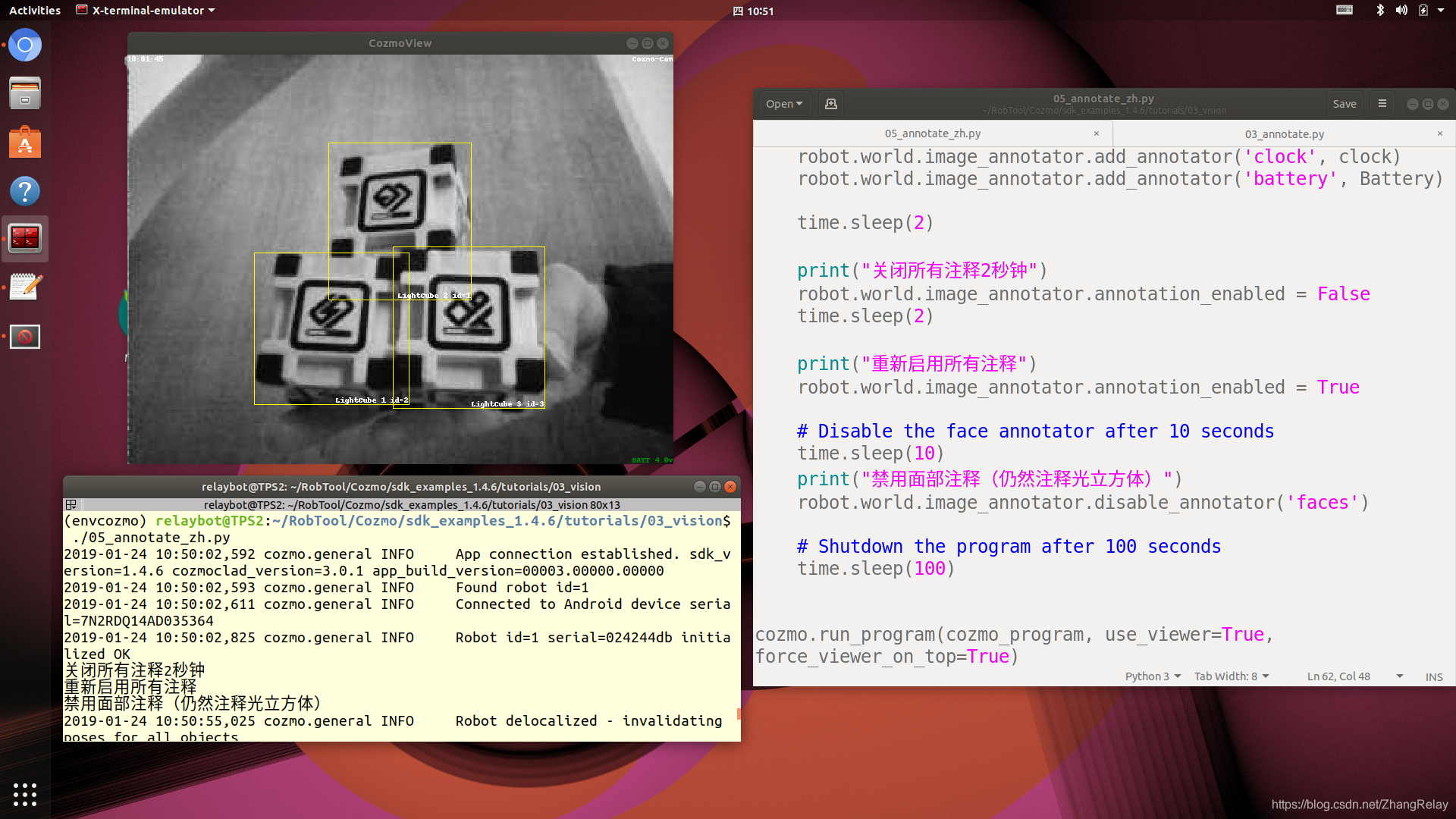
中文
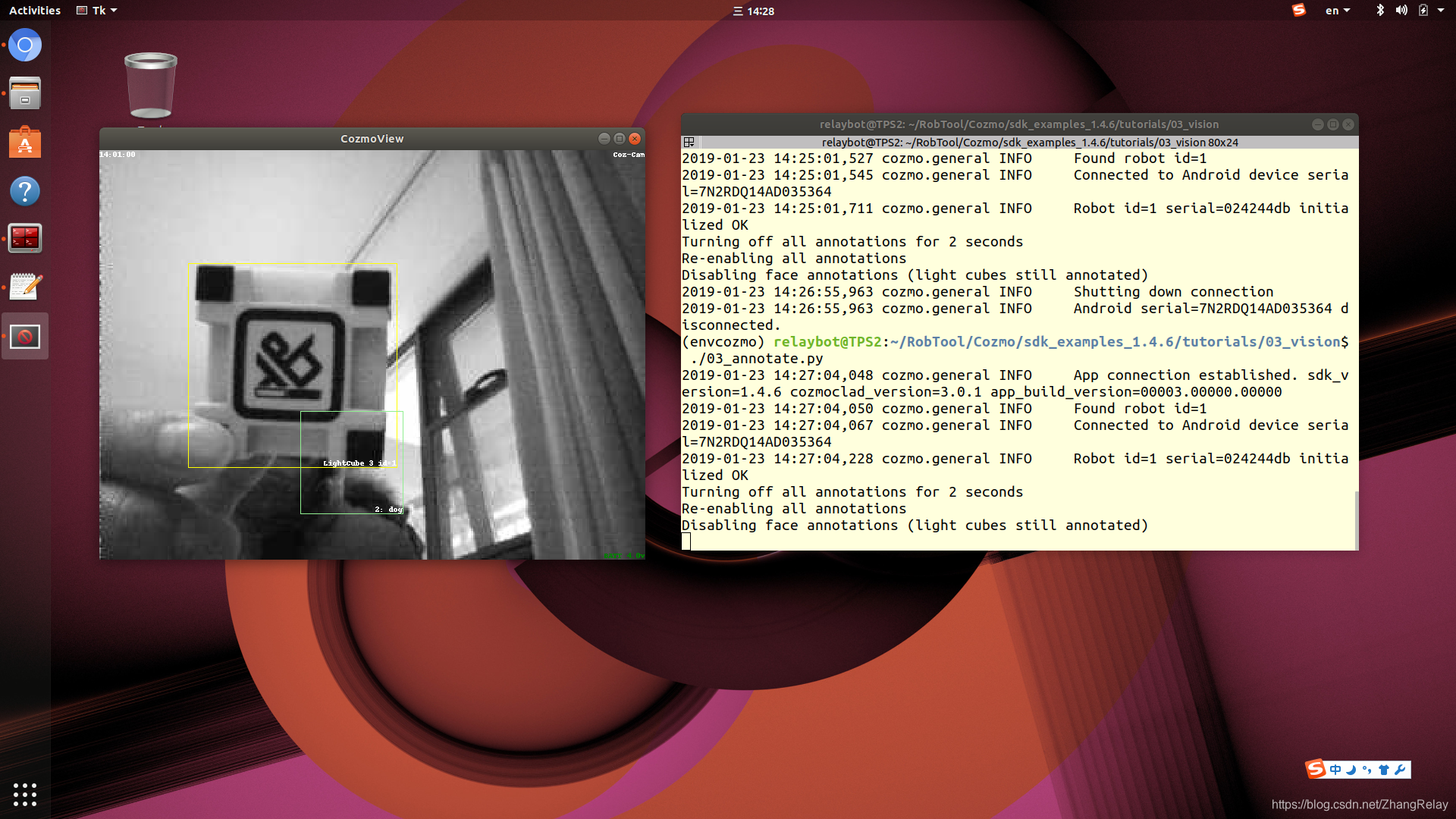
英文
这就是教程tutorials中第三部分vision中的内容。

1. light when face
当检测到人脸在图像中识别并点亮cozmo背部的LED灯。
-
#!/usr/bin/env python3
-
-
# Copyright (c) 2016 Anki, Inc.
-
#
-
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
-
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
-
# You may obtain a copy of the License in the file LICENSE.txt or at
-
#
-
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
-
#
-
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
-
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
-
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
-
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
-
# limitations under the License.
-
-
'''Wait for Cozmo to see a face, and then turn on his backpack light.
-
-
This is a script to show off faces, and how they are easy to use.
-
It waits for a face, and then will light up his backpack when that face is visible.
-
'''
-
-
import asyncio
-
import time
-
-
import cozmo
-
-
-
def light_when_face(robot: cozmo.robot.Robot):
-
'''The core of the light_when_face program'''
-
-
# Move lift down and tilt the head up
-
robot.move_lift(-3)
-
robot.set_head_angle(cozmo.robot.MAX_HEAD_ANGLE).wait_for_completed()
-
-
face = None
-
-
print("Press CTRL-C to quit")
-
while True:
-
if face and face.is_visible:
-
robot.set_all_backpack_lights(cozmo.lights.blue_light)
-
else:
-
robot.set_backpack_lights_off()
-
-
# Wait until we we can see another face
-
try:
-
face = robot.world.wait_for_observed_face(timeout=30)
-
except asyncio.TimeoutError:
-
print("Didn't find a face.")
-
return
-
-
time.sleep(.1)
-
-
-
cozmo.run_program(light_when_face, use_viewer=True, force_viewer_on_top=True)
2. face follower
识别人脸并跟随,控制头部角度和履带运动调整是人脸处于采集图像的中间位置(x,y两轴)。
-
#!/usr/bin/env python3
-
-
# Copyright (c) 2016 Anki, Inc.
-
#
-
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
-
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
-
# You may obtain a copy of the License in the file LICENSE.txt or at
-
#
-
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
-
#
-
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
-
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
-
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
-
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
-
# limitations under the License.
-
-
'''Make Cozmo turn toward a face.
-
-
This script shows off the turn_towards_face action. It will wait for a face
-
and then constantly turn towards it to keep it in frame.
-
'''
-
-
import asyncio
-
import time
-
-
import cozmo
-
-
-
def follow_faces(robot: cozmo.robot.Robot):
-
'''The core of the follow_faces program'''
-
-
# Move lift down and tilt the head up
-
robot.move_lift(-3)
-
robot.set_head_angle(cozmo.robot.MAX_HEAD_ANGLE).wait_for_completed()
-
-
face_to_follow = None
-
-
print("Press CTRL-C to quit")
-
while True:
-
turn_action = None
-
if face_to_follow:
-
# start turning towards the face
-
turn_action = robot.turn_towards_face(face_to_follow)
-
-
if not (face_to_follow and face_to_follow.is_visible):
-
# find a visible face, timeout if nothing found after a short while
-
try:
-
face_to_follow = robot.world.wait_for_observed_face(timeout=30)
-
except asyncio.TimeoutError:
-
print("Didn't find a face - exiting!")
-
return
-
-
if turn_action:
-
# Complete the turn action if one was in progress
-
turn_action.wait_for_completed()
-
-
time.sleep(.1)
-
-
-
cozmo.run_program(follow_faces, use_viewer=True, force_viewer_on_top=True)
3. annotate
此示例使用tkviewer在屏幕上显示带注释的摄像头图像并使用两种不同的方法添加了一些自己的自定义注释。
-
#!/usr/bin/env python3
-
-
# Copyright (c) 2016 Anki, Inc.
-
#
-
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
-
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
-
# You may obtain a copy of the License in the file LICENSE.txt or at
-
#
-
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
-
#
-
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
-
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
-
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
-
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
-
# limitations under the License.
-
-
'''Display a GUI window showing an annotated camera view.
-
-
Note:
-
This example requires Python to have Tkinter installed to display the GUI.
-
It also requires the Pillow and numpy python packages to be pip installed.
-
-
The :class:`cozmo.world.World` object collects raw images from Cozmo's camera
-
and makes them available as a property (:attr:`~cozmo.world.World.latest_image`)
-
and by generating :class:`cozmo.world.EvtNewCamerImages` events as they come in.
-
-
Each image is an instance of :class:`cozmo.world.CameraImage` which provides
-
access both to the raw camera image, and to a scalable annotated image which
-
can show where Cozmo sees faces and objects, along with any other information
-
your program may wish to display.
-
-
This example uses the tkviewer to display the annotated camera on the screen
-
and adds a couple of custom annotations of its own using two different methods.
-
'''
-
-
-
import sys
-
import time
-
-
try:
-
from PIL import ImageDraw, ImageFont
-
except ImportError:
-
sys.exit('run `pip3 install --user Pillow numpy` to run this example')
-
-
import cozmo
-
-
-
# Define an annotator using the annotator decorator
-
@cozmo.annotate.annotator
-
def clock(image, scale, annotator=None, world=None, **kw):
-
d = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
-
bounds = (0, 0, image.width, image.height)
-
text = cozmo.annotate.ImageText(time.strftime("%H:%m:%S"),
-
position=cozmo.annotate.TOP_LEFT)
-
text.render(d, bounds)
-
-
# Define another decorator as a subclass of Annotator
-
class Battery(cozmo.annotate.Annotator):
-
def apply(self, image, scale):
-
d = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
-
bounds = (0, 0, image.width, image.height)
-
batt = self.world.robot.battery_voltage
-
text = cozmo.annotate.ImageText('BATT %.1fv' % batt, color='green')
-
text.render(d, bounds)
-
-
-
def cozmo_program(robot: cozmo.robot.Robot):
-
robot.world.image_annotator.add_static_text('text', 'Coz-Cam', position=cozmo.annotate.TOP_RIGHT)
-
robot.world.image_annotator.add_annotator('clock', clock)
-
robot.world.image_annotator.add_annotator('battery', Battery)
-
-
time.sleep(2)
-
-
print("Turning off all annotations for 2 seconds")
-
robot.world.image_annotator.annotation_enabled = False
-
time.sleep(2)
-
-
print('Re-enabling all annotations')
-
robot.world.image_annotator.annotation_enabled = True
-
-
# Disable the face annotator after 10 seconds
-
time.sleep(10)
-
print("Disabling face annotations (light cubes still annotated)")
-
robot.world.image_annotator.disable_annotator('faces')
-
-
# Shutdown the program after 100 seconds
-
time.sleep(100)
-
-
-
cozmo.run_program(cozmo_program, use_viewer=True, force_viewer_on_top=True)
4. exposure
此示例演示了使用自动曝光和手动曝光Cozmo的摄像头图像。当前的摄像头设置会叠加到PC上查看器窗口。
-
#!/usr/bin/env python3
-
-
# Copyright (c) 2017 Anki, Inc.
-
#
-
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
-
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
-
# You may obtain a copy of the License in the file LICENSE.txt or at
-
#
-
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
-
#
-
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
-
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
-
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
-
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
-
# limitations under the License.
-
-
'''Demonstrate the manual and auto exposure settings of Cozmo's camera.
-
-
This example demonstrates the use of auto exposure and manual exposure for
-
Cozmo's camera. The current camera settings are overlayed onto the camera
-
viewer window.
-
'''
-
-
-
import sys
-
import time
-
-
try:
-
from PIL import ImageDraw, ImageFont
-
import numpy as np
-
except ImportError:
-
sys.exit('run `pip3 install --user Pillow numpy` to run this example')
-
-
import cozmo
-
-
-
# A global string value to display in the camera viewer window to make it more
-
# obvious what the example program is currently doing.
-
example_mode = ""
-
-
-
# An annotator for live-display of all of the camera info on top of the camera
-
# viewer window.
-
@cozmo.annotate.annotator
-
def camera_info(image, scale, annotator=None, world=None, **kw):
-
d = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
-
bounds = [3, 0, image.width, image.height]
-
-
camera = world.robot.camera
-
text_to_display = "Example Mode: " + example_mode + "\n\n"
-
text_to_display += "Fixed Camera Settings (Calibrated for this Robot):\n\n"
-
text_to_display += 'focal_length: %s\n' % camera.config.focal_length
-
text_to_display += 'center: %s\n' % camera.config.center
-
text_to_display += 'fov: <%.3f, %.3f> degrees\n' % (camera.config.fov_x.degrees,
-
camera.config.fov_y.degrees)
-
text_to_display += "\n"
-
text_to_display += "Valid exposure and gain ranges:\n\n"
-
text_to_display += 'exposure: %s..%s\n' % (camera.config.min_exposure_time_ms,
-
camera.config.max_exposure_time_ms)
-
text_to_display += 'gain: %.3f..%.3f\n' % (camera.config.min_gain,
-
camera.config.max_gain)
-
text_to_display += "\n"
-
text_to_display += "Current settings:\n\n"
-
text_to_display += 'Auto Exposure Enabled: %s\n' % camera.is_auto_exposure_enabled
-
text_to_display += 'Exposure: %s ms\n' % camera.exposure_ms
-
text_to_display += 'Gain: %.3f\n' % camera.gain
-
color_mode_str = "Color" if camera.color_image_enabled else "Grayscale"
-
text_to_display += 'Color Mode: %s\n' % color_mode_str
-
-
text = cozmo.annotate.ImageText(text_to_display,
-
position=cozmo.annotate.TOP_LEFT,
-
line_spacing=2,
-
color="white",
-
outline_color="black", full_outline=True)
-
text.render(d, bounds)
-
-
-
def demo_camera_exposure(robot: cozmo.robot.Robot):
-
global example_mode
-
-
# Ensure camera is in auto exposure mode and demonstrate auto exposure for 5 seconds
-
camera = robot.camera
-
camera.enable_auto_exposure()
-
example_mode = "Auto Exposure"
-
time.sleep(5)
-
-
# Demonstrate manual exposure, linearly increasing the exposure time, while
-
# keeping the gain fixed at a medium value.
-
example_mode = "Manual Exposure - Increasing Exposure, Fixed Gain"
-
fixed_gain = (camera.config.min_gain + camera.config.max_gain) * 0.5
-
for exposure in range(camera.config.min_exposure_time_ms, camera.config.max_exposure_time_ms+1, 1):
-
camera.set_manual_exposure(exposure, fixed_gain)
-
time.sleep(0.1)
-
-
# Demonstrate manual exposure, linearly increasing the gain, while keeping
-
# the exposure fixed at a relatively low value.
-
example_mode = "Manual Exposure - Increasing Gain, Fixed Exposure"
-
fixed_exposure_ms = 10
-
for gain in np.arange(camera.config.min_gain, camera.config.max_gain, 0.05):
-
camera.set_manual_exposure(fixed_exposure_ms, gain)
-
time.sleep(0.1)
-
-
# Switch back to auto exposure, demo for a final 5 seconds and then return
-
camera.enable_auto_exposure()
-
example_mode = "Mode: Auto Exposure"
-
time.sleep(5)
-
-
-
def cozmo_program(robot: cozmo.robot.Robot):
-
robot.world.image_annotator.add_annotator('camera_info', camera_info)
-
-
# Demo with default grayscale camera images
-
robot.camera.color_image_enabled = False
-
demo_camera_exposure(robot)
-
-
# Demo with color camera images
-
robot.camera.color_image_enabled = True
-
demo_camera_exposure(robot)
-
-
-
cozmo.robot.Robot.drive_off_charger_on_connect = False # Cozmo can stay on his charger for this example
-
cozmo.run_program(cozmo_program, use_viewer=True, force_viewer_on_top=True)
Fin
文章来源: zhangrelay.blog.csdn.net,作者:zhangrelay,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:zhangrelay.blog.csdn.net/article/details/86621319
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)