Verilog初级教程(8)Verilog中的assign语句
写在前面
本系列相关博文链接:
Verilog初级教程(7)Verilog模块例化以及悬空端口的处理
Verilog初级教程(5)Verilog中的多维数组和存储器
Verilog初级教程(2)Verilog HDL的初级语法
FPGA/ASIC初学者应该学习Verilog还是VHDL?
-
个人微信公众号: FPGA LAB
-
注:学习交流使用!
正文
wire类型的信号需要连续赋值。例如,考虑一根电线用于连接面包板上的元件。只要将+5V电池施加在电线的一端,连接在电线另一端的元件就会得到所需的电压。

在Verilog中,这个概念是通过赋值语句(assign)来实现的,在赋值语句中,任何线或其他类似线的数据类型都可以用一个值来连续驱动,这个值可以是常数,也可以是一组信号组成的表达式。
赋值语法
赋值语法以关键字assign开头,后面是信号名,可以是单个信号,也可以是不同信号网的连接。驱动强度和延迟是可选的,主要用于数据流建模,而不是综合到实际硬件中。右侧的表达式或信号被分配给左侧的网或网的表达式。
语法结构如下:
assign <net_expression> = [drive_strength] [delay] <expression of different signals or constant value>
- 1
延迟值对于指定门的延迟很有用,并用于模拟实际硬件中的时序行为,因为该值决定了何时应该用评估值分配网。
使用 assign 语句时, 需要遵循一些规则:
- LHS(左值) 应该始终是wire类型的标量或向量网络, 或者标量或矢量网络的串联, 而绝对不能是reg类型的标量或矢量寄存器。
- RHS 可以包含标量或向量寄存器以及函数调用。
- 只要 RHS 上的任何操作数的值发生变化, LHS 就会使用新值进行更新。
- assign 语句也称为连续赋值, 并且始终处于活动状态
例如:

综合后的RTL图:
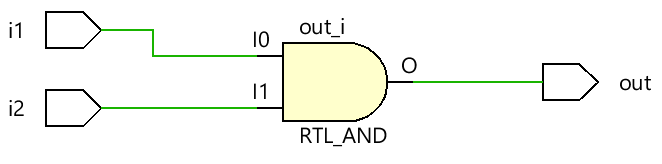
reg类型变量赋值
reg类型的变量不能使用assign进行连续赋值,这是因为reg类型的变量可以存储数据,并且不需要连续驱动。我们只能在initial以及always块内对reg类型变量进行赋值。
隐性连续赋值
当使用assign给wire类型的网络赋值时,称为显示连续赋值,如果在定义的时候就对其连续赋值,称为隐形连续赋值。
wire [1:0] a;
assign a = x & y; // Explicit assignment
wire [1:0] a = x & y; // Implicit assignment
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
隐形连续赋值在Verilog中是被允许的。
组合逻辑设计
assign语句常用于组合逻辑设计,如下的电路图:
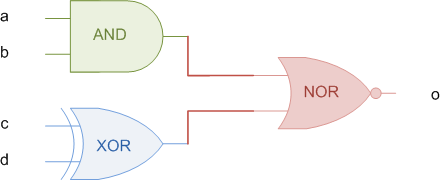
使用Verilog描述为:
// This module takes four inputs and performs a boolean
// operation and assigns output to o. The combinational
// logic is realized using assign statement.
module combo ( input a, b, c, d, output o); assign o = ~((a & b) | c ^ d);
endmodule
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
其RTL硬件原理图为:

行为仿真:

举例说明
半加器设计
Verilog描述为:
module ha ( input a, b, output sum, cout); assign sum = a ^ b;
assign cout = a & b;
endmodule
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
对应的RTL原理图为:

tb文件:
module tb;
// Declare testbench variables
reg a, b;
wire sum, cout;
integer i; // Instantiate the design and connect design inputs/outputs with
ha u0 ( .a(a), .b(b), .sum(sum), .cout(cout)); initial begin // At the beginning of time, initialize all inputs of the design // to a known value, in this case we have chosen it to be 0. a <= 0; b <= 0; // Use a $monitor task to print any change in the signal to // simulation console $monitor("a=%0b b=%0b sum=%0b cout=%0b", a, b, sum, cout); // Because there are only 2 inputs, there can be 4 different input combinations // So use an iterator "i" to increment from 0 to 4 and assign the value // to testbench variables so that it drives the design inputs for (i = 0; i < 4; i = i + 1) begin {a, b} = i; #10; end
end
endmodule
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
仿真结果:
ncsim> run
a=0 b=0 sum=0 cout=0
a=0 b=1 sum=1 cout=0
a=1 b=0 sum=1 cout=0
a=1 b=1 sum=0 cout=1
ncsim: *W,RNQUIE: Simulation is complete.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6

更多的例子不在话下。
参考资料
交个朋友
-
个人微信公众号:FPGA LAB
-
知乎:李锐博恩
文章来源: reborn.blog.csdn.net,作者:李锐博恩,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:reborn.blog.csdn.net/article/details/106985139
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)