用SpringBoot搭建个人博客01-----使用AOP统一处理Web请求日志
【摘要】 摘要
AOP 是面向切面的编程,就是在运行期通过动态代理的方式对代码进行增强处理,比较核心的概念有 切点,切面,通知,有关AOP的详情参考:。 本文要介绍的是在一个SpringBoot项目中如何统一的处理Web请求日志,基本思想还是采用AOP的方式,拦截请求,然后,写入日志。
相关依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org....
摘要
AOP 是面向切面的编程,就是在运行期通过动态代理的方式对代码进行增强处理,比较核心的概念有 切点,切面,通知,有关AOP的详情参考:。
本文要介绍的是在一个SpringBoot项目中如何统一的处理Web请求日志,基本思想还是采用AOP的方式,拦截请求,然后,写入日志。
相关依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency>
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId> </dependency>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
项目引入spring-boot-starter-web 依赖之后无需在引入相关的日志依赖,因为spring-boot-starter-web中已经集成了slf4j 的依赖。
引入spring-boot-starter-aop 依赖之后,AOP 的功能即是启动状态,无需在添加@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解。
定义系统日志注解
/**
* 系统日志注解
* Created by xiang.wei on 2018/10/17
*
* @author xiang.wei
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface SysLog { String value() default "";
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
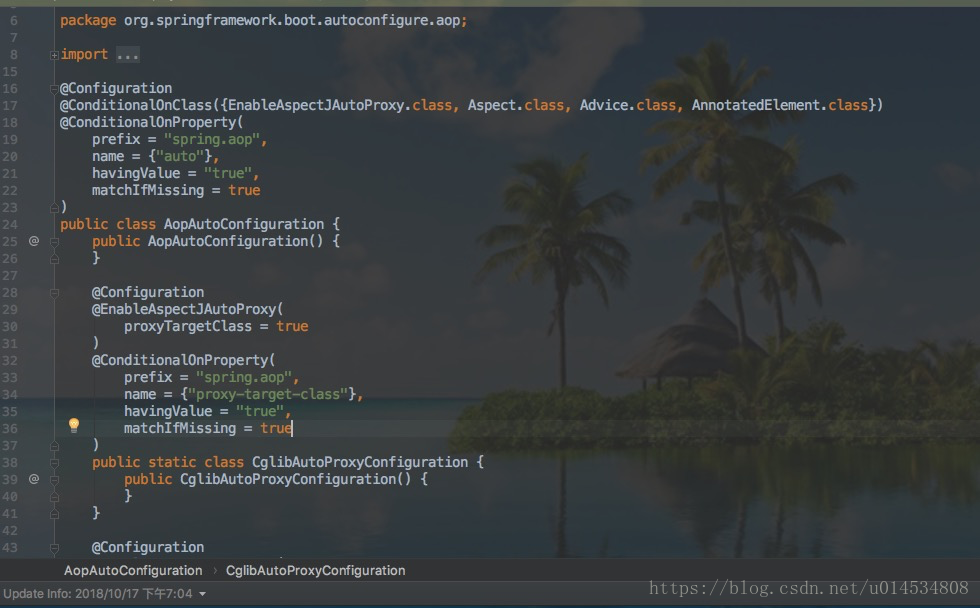
定义切面
@Aspect
@Component
public class SysLogAspect { private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SysLogAspect.class);
// @Autowired
// private MtoLogService mtoLogService; /** * 定义日志切点 */ @Pointcut("@annotation(com.jay.common.annotation.SysLog)") public void logPointCut() { } /** * 环绕通知 * @param point * @return */ @Around("logPointCut()") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Object proceed = point.proceed();
// 执行时长 long time = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime; saveSysLog(point, time); return proceed; } private void saveSysLog(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, long time) { MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature(); Method method = signature.getMethod(); MtoLog mtoLog = new MtoLog();
// 获取注解内容 SysLog annotation = method.getAnnotation(SysLog.class); if (annotation != null) { mtoLog.setOperation(annotation.value()); }
// 获取类名 String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName();
// 获取方法名 String methodName = method.getName(); mtoLog.setMethod(className + "." + methodName + "()");
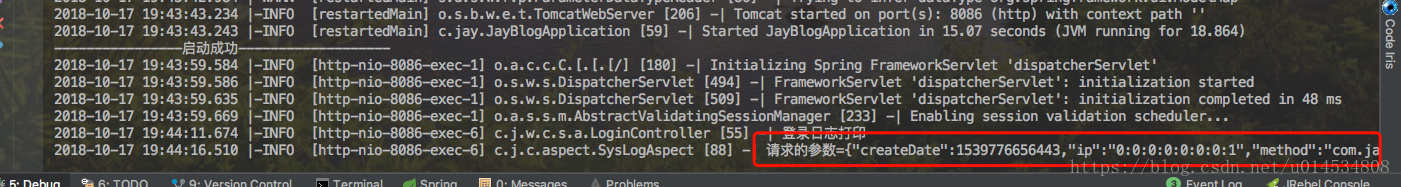
// 获取参数 Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs(); if (args != null) { String param = JSON.toJSONString(args[0]); mtoLog.setParams(param); } mtoLog.setTime(time); HttpServletRequest request = HttpContextUtils.getHttpServletRequest(); mtoLog.setIp(IpUtil.getIpAddr(request)); mtoLog.setCreateDate(new Date()); logger.info("请求的参数="+JSON.toJSONString(mtoLog));
// mtoLogService.insert(mtoLog); }
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
使用
@SysLog("登录接口") @RequestMapping(value = "/login", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String login(String username,String password, @RequestParam(value = "rememberMe", defaultValue = "0") int rememberMe, ModelMap model) {
。。。。
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
运行效果:
参考博客
http://blog.didispace.com/springbootaoplog/
代码地址
https://github.com/XWxiaowei/JayBlog/tree/v3-logback-validation
文章来源: feige.blog.csdn.net,作者:码农飞哥,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:feige.blog.csdn.net/article/details/83116265
【版权声明】本文为华为云社区用户转载文章,如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)