java-第3章 流程控制语句
实验内容:
1.判断整数的奇偶性。
2.输出所有的水仙花数。
3.猜数字游戏。
4.输入并统计学生成绩
实验步骤:
1. 从键盘上输入一个整数,判断其奇偶性并输出。
提示:从控制台输入数据的方法示例:
-
System.out.println("请输入一个整数:");
-
-
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
-
-
int num=scan.nextInt();
源代码:
-
package sy3;
-
-
import java.util.Scanner;
-
-
public class Sy_1 {
-
-
public static void main(String[] args){
-
-
System.out.println("请输入一个整数:");
-
-
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
-
-
int num = sc.nextInt();
-
-
if(num%2 == 0)
-
-
System.out.printf(num+"是偶数");
-
-
else{
-
-
System.out.printf(num+"是奇数");
-
-
}
-
-
}
-
-
}
运行结果截图:

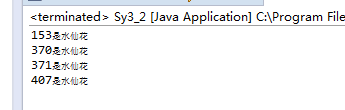
2. 输出所有的水仙花数。所谓水仙花数是指一个三位整数,其各位数字的立方和等于其自身,例如:153=13+53+33。要求在一行输出结果。
源代码:
-
package sy3;
-
-
public class Sy3_2 {
-
-
public static void main(String[] args){
-
-
int x=0,y=0,z=0;
-
-
for(int i=100;i<1000;i++) {
-
-
x = i/100;
-
-
y = (i%100)/10;
-
-
z = (i%100)%10;
-
-
if(i == x*x*x+y*y*y+z*z*z){
-
-
System.out.println(i+"是水仙花");
-
-
}
-
-
}
-
-
}
-
-
}
运行结果截图:
3.猜数字游戏:编写一个Java应用程序,实现下列功能:
(1)程序随机分配给客户一个1~100之间的整数.
(2)用户从控制台输入自己的猜测。
(3)程序在控制台返回提示信息,提示信息分别是“猜大了”、“猜小了”和“猜对了”。
(4)用户可根据提示信息再次输入猜测,直到提示信息是“恭喜你,猜对了!”。
源代码:
-
package sy3;
-
-
import java.util.Scanner;
-
-
public class Sy3_3 {
-
-
public static void main(String[] args){
-
-
System.out.println("请输入一个整数:");
-
-
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
-
-
int num = (int)(Math.random()*100)+1;
-
-
int guess = sc.nextInt();
-
-
System.out.println("请输入你的猜测:");
-
-
-
-
while(guess != num){
-
-
if(guess > num){
-
-
System.out.println("猜大了");
-
-
guess = sc.nextInt();
-
-
}
-
-
else if(guess < num){
-
-
System.out.println("猜小了");
-
-
guess = sc.nextInt();
-
-
}
-
-
}
-
-
System.out.println("恭喜你,猜对了");
-
-
}
-
-
}
-
-
运行结果截图:

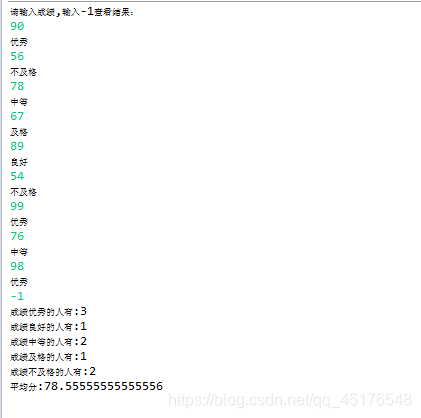
4.输入一批学生成绩,以-1作为结束标记。
(1)统计这批学生中不及格、及格、中等、良好、优秀的人数。
(2)求这批学生的平均分。
提示:从控制台输入成绩的方法示例:
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一批学生成绩,以-1作为结束标记:");
源代码:
-
package sy3;
-
-
-
-
import java.util.Scanner;
-
-
-
-
public class Sy3_4 {
-
-
public static void main(String[] args){
-
-
int score=0,a=0,b=0,c=0,d=0,e=0,sum=0;
-
-
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
-
-
System.out.println("请输入成绩,输入-1查看结果:");
-
-
score = sc.nextInt();
-
-
-
-
-
-
while(score != -1){
-
-
if(score>=90){
-
-
System.out.println("优秀");
-
-
a++;
-
-
}
-
-
else if(score>=80){
-
-
System.out.println("良好");
-
-
b++;
-
-
}
-
-
else if(score >= 70){
-
-
System.out.println("中等");
-
-
c++;
-
-
}
-
-
else if(score >= 60){
-
-
System.out.println("及格");
-
-
d++;
-
-
}
-
-
else{
-
-
System.out.println("不及格");
-
-
e++;
-
-
}
-
-
sum += score;
-
-
score = sc.nextInt();
-
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
System.out.println("成绩优秀的人有:"+a);
-
-
System.out.println("成绩良好的人有:"+b);
-
-
System.out.println("成绩中等的人有:"+c);
-
-
System.out.println("成绩及格的人有:"+d);
-
-
System.out.println("成绩不及格的人有:"+e);
-
-
-
-
-
-
double average = sum*1.0/(a+b+c+d+e);
-
-
System.out.printf("平均分:" + average);
-
-
-
-
}
-
-
-
-
}
运行结果截图:
实验小结
通过本章的学习,了解了几种常用的循环语句,条件语句。
条件语句:if条件句有三种形式
1:if(表达式){方法体}
2:if(表达式){方法体} else {方法体}
3:if(表达式){方法体} else if(表达式){方法体} else{方法体}
了解了循环语句:
包括while循环语句,do…while循环语句和for循环其中while(布尔表达式)和 do…while(布尔表达式)类似,while是先判断后执行,do…while是先执行一次然后再判断条件。如果布尔表达式结果为真,那么两个循环语句结果相同,若布尔表达式的第一次结果为假,do…while会先执行一次,而while则不会继续执行。
for循环格式:for(变量初始化;条件判断;步进){循环语句},只进行一步初始化,然后进行条件判断,为真后执行for中的循环语句,执行后进行步进,然后继续进行条件判断,直到结果为假,跳出循环
文章来源: beishan.blog.csdn.net,作者:北山啦,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:beishan.blog.csdn.net/article/details/112262310
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)