Sympy解决高等数学问题
Python中的Sympy解决高等数学问题

使用Python中的Sympy库解决高等数学中极限、导数、偏导数、定积分、不定积分、双重积分等问题
Sympy是一个Python的科学计算库,它旨在成为功能齐全的计算机代数系统。 SymPy 包括从基本符号算术到微积分,代数,离散数学和量子物理学的功能。 它可以在 LaTeX 中显示结果。

看到这图,是不是感觉快喘不过气了呢。Python来帮你解决。
from sympy import *
import sympy
- 1
- 2
输入“x= symbols(“x”)”命令定义一个符号
x = Symbol("x")
y = Symbol("y")
- 1
- 2
1. 实用技巧
1.1 符号函数
sympy提供了很多数学符号,总结如下
- 虚数单位
sympy.I
- 1
- 自然对数
sympy.E
- 1
- 无穷大
sympy.oo
- 1
- 圆周率
sympy.pi
- 1
- 求n次方根
sympy.root(8,3)
- 1
- 取对数
sympy.log(1024,2)
- 1
- 求阶乘
sympy.factorial(4)
- 1
- 三角函数
sympy.sin(sympy.pi)
sympy.tan(sympy.pi/4)
sympy.cos(sympy.pi/2)
- 1
- 2
- 3
1.2 展开表达式expand
f = (1+x)**3
expand(f)
- 1
- 2
x 3 + 3 x 2 + 3 x + 1 \displaystyle x^{3} + 3 x^{2} + 3 x + 1 x3+3x2+3x+1
1.3 泰勒展开公式series
ln(1+x).series(x,0,4)
- 1
x − x 2 2 + x 3 3 + O ( x 4 ) \displaystyle x - \frac{x^{2}}{2} + \frac{x^{3}}{3} + O\left(x^{4}\right) x−2x2+3x3+O(x4)
sin(x).series(x,0,8)
- 1
x − x 3 6 + x 5 120 − x 7 5040 + O ( x 8 ) \displaystyle x - \frac{x^{3}}{6} + \frac{x^{5}}{120} - \frac{x^{7}}{5040} + O\left(x^{8}\right) x−6x3+120x5−5040x7+O(x8)
cos(x).series(x,0,9)
- 1
1 − x 2 2 + x 4 24 − x 6 720 + x 8 40320 + O ( x 9 ) \displaystyle 1 - \frac{x^{2}}{2} + \frac{x^{4}}{24} - \frac{x^{6}}{720} + \frac{x^{8}}{40320} + O\left(x^{9}\right) 1−2x2+24x4−720x6+40320x8+O(x9)
(1/(1+x)).series(x,0,5)
- 1
1 − x + x 2 − x 3 + x 4 + O ( x 5 ) \displaystyle 1 - x + x^{2} - x^{3} + x^{4} + O\left(x^{5}\right) 1−x+x2−x3+x4+O(x5)
tan(x).series(x,0,4)
- 1
x + x 3 3 + O ( x 4 ) \displaystyle x + \frac{x^{3}}{3} + O\left(x^{4}\right) x+3x3+O(x4)
(1/(1-x)).series(x,0,4)
- 1
1 + x + x 2 + x 3 + O ( x 4 ) \displaystyle 1 + x + x^{2} + x^{3} + O\left(x^{4}\right) 1+x+x2+x3+O(x4)
(1/(1+x)).series(x,0,4)
- 1
1 − x + x 2 − x 3 + O ( x 4 ) \displaystyle 1 - x + x^{2} - x^{3} + O\left(x^{4}\right) 1−x+x2−x3+O(x4)
1.4 符号展开
a = Symbol("a")
b = Symbol("b")
#simplify( )普通的化简
simplify((x**3 + x**2 - x - 1)/(x**2 + 2*x + 1))
#trigsimp( )三角化简
trigsimp(sin(x)/cos(x))
#powsimp( )指数化简
powsimp(x**a*x**b)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
x a + b \displaystyle x^{a + b} xa+b
2. 求极限limit
limit(sin(x)/x,x,0)
- 1
1 \displaystyle 1 1
f2=(1+x)**(1/x)
- 1
f2
- 1
( x + 1 ) 1 x \displaystyle \left(x + 1\right)^{\frac{1}{x}} (x+1)x1
重要极限
f1=sin(x)/x
f2=(1+x)**(1/x)
f3=(1+1/x)**x
lim1=limit(f1,x,0)
lim2=limit(f2,x,0)
lim3=limit(f3,x,oo)
print(lim1,lim2,lim3)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
1 E E
- 1
dir可以表示极限的趋近方向
f4 = (1+exp(1/x))
f4
- 1
- 2
e 1 x + 1 \displaystyle e^{\frac{1}{x}} + 1 ex1+1
lim4 = limit(f4,x,0,dir="-")
lim4
- 1
- 2
1 \displaystyle 1 1
lim5 = limit(f4,x,0,dir="+")
lim5
- 1
- 2
∞ \displaystyle \infty ∞
3. 求导diff
diff(函数,自变量,求导次数)
3.1 一元函数
求导问题
diff(sin(2*x),x)
- 1
2 cos ( 2 x ) \displaystyle 2 \cos{\left(2 x \right)} 2cos(2x)
diff(ln(x),x)
- 1
1 x \displaystyle \frac{1}{x} x1
3.2 多元函数
求偏导问题
diff(sin(x*y),x,y)
- 1
− x y sin ( x y ) + cos ( x y ) \displaystyle - x y \sin{\left(x y \right)} + \cos{\left(x y \right)} −xysin(xy)+cos(xy)
4. 积分integrate
4.1 定积分
- 函数的定积分: integrate(函数,(变量,下限,上限))
- 函数的不定积分: integrate(函数,变量)
f = x**2 + 1
integrate(f,(x,-1.1))
- 1
- 2
− 1.54366666666667 \displaystyle -1.54366666666667 −1.54366666666667
integrate(exp(x),(x,-oo,0))
- 1
1 \displaystyle 1 1
4.2 不定积分
f = 1/(1+x*x)
integrate(f,x)
- 1
- 2
atan ( x ) \displaystyle \operatorname{atan}{\left(x \right)} atan(x)
4.3 双重积分
f = (4/3)*x + 2*y
integrate(f,(x,0,1),(y,-3,4))
- 1
- 2
11.6666666666667 \displaystyle 11.6666666666667 11.6666666666667
5. 求解方程组solve
#解方程组
#定义变量
f1=x+y-3
f2=x-y+5
solve([f1,f2],[x,y])
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
{x: -1, y: 4}
6. 计算求和式summation
计算求和式可以使用sympy.summation函数,其函数原型为sympy.summation(f, *symbols, **kwargs)
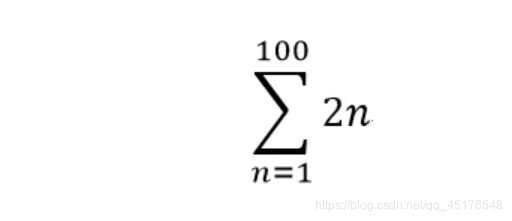
**
sympy.summation(2 * n,(n,1,100))
- 1
10100
到这里就结束了,如果对你有帮助,欢迎点赞关注评论,你的点赞对我很重要。在此也祝愿大家可以把数学学好

参考:
https://docs.sympy.org/latest/index.html
文章来源: blog.csdn.net,作者:北山啦,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:blog.csdn.net/qq_45176548/article/details/114828346
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)