《OpenCV3编程入门》第5章-学习笔记7--输入输出XML和YAML文件--详解代码示例
1.XML和YAML文件简介
XML(eXtensible Markup Lauguage)是一种元标记语言,所谓的“元标记”就是开发者可以根据自身需要定义自己的标记。XML是一种语义/结构化语言,它描述了文档的结构和语义
YAML(Ain’t a Markup Language)强调这种语言是以数据为中心的。YAML是一种可读性高,用来表示资料序列的格式
总之,YAML试图用一种比XML更敏捷的方式,完成XML所完成的任务
2.FileStorage 类操作文件的使用引导
我们一般使用如下过程来写入或读取数据到 XML 或 YAML 文件中
1.实例化一个FileStorage类的对象,用默认带参数的构造函数完成初始化。或者用FileStorage::open()成员函数辅助初始化
2.使用流操作<<进行文件写入操作,或者>>进行文件读取操作。类似c++中的文件输入输出流
3.使用FileStorage::release()函数折构掉FileStorage类对象,同时关闭文件。
2.1 【第一步】XML、YAML文件打开
(1)准备文件写操作
FileStorage是OpenCV中XML和YAML文件的存储类,封装了所有有关信息
构造函数为FileStorage::FileStorage ,有两个重载
-
FileStorage::FileStorage()
-
FileStorage::FileStorage(const string& source ,int flags,const string& encoding=string)
实际中如何使用?(xml和yaml文件操作一致,下面使用方法换后缀后即可通用)
第一种:
FileStorage fs("abc.xml", FileStorage::WRITE);
第二种:
-
FileStorage fs;
-
fs.open("abc.xml", FileStorage::WRITE);
(2)准备文件读操作
第一种:
FileStorage fs("abc.xml", FileStorage::READ);
第二种:
-
FileStorage fs;
-
fs.open("abc.xml", FileStorage::READ);
2.2 【第二步】进行读写操作
重定向符号: << >>
2.3 【第三步】vector(arrays)和maps的输入输出
vector 使用 [ ]
maps 使用 { }
-
fs << "string" <<"[";
-
fs <<"imgae1.jpg" <<"abs.jpg";
-
fs << "]";
-
-
//
-
fs <<"MAP";
-
fs <<"{"<<"gg"<<1;
-
fs <<"bb"<<2<<"}";
2.4 【第四步】文件关闭
fs.release(); //显式关闭文件
3 示例程序:XML和YAML文件的写入
-
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
-
#include <time.h>
-
using namespace cv;
-
-
int main() {
-
//初始化
-
//FileStorage fs("test.yaml", FileStorage::WRITE);
-
FileStorage fs("test.xml", FileStorage::WRITE);
-
//开始文件写入
-
fs << "frameCount" << 5;
-
time_t rawtime;
-
time(&rawtime);
-
fs << "calibrationDate" << asctime(localtime(&rawtime));
-
Mat cameraMattrix = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 1000, 0, 320, 0, 1000, 240, 0, 0, 1);
-
Mat distCoeffs = (Mat_<double>(5, 1) << 0.1, 0.01, -0.001, 0, 0);
-
fs << "cameraMatrix" << cameraMattrix << "distCoeffs" << distCoeffs;
-
fs << "features" << "[";
-
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
-
int x = rand() % 640;
-
int y = rand() % 480;
-
uchar lbp = rand() % 256;
-
-
fs << "{:" << "x" << x << "y" << y << "lbp" << "[:";
-
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++)
-
fs << ((lbp >> j) & 1);
-
fs << "]" << "}";
-
}
-
fs << "]";
-
fs.release();
-
-
std::cout << "文件读写完毕,请在工程目录下查看生成的文件!";
-
getchar();
-
-
return(0);
-
}
运行结果:
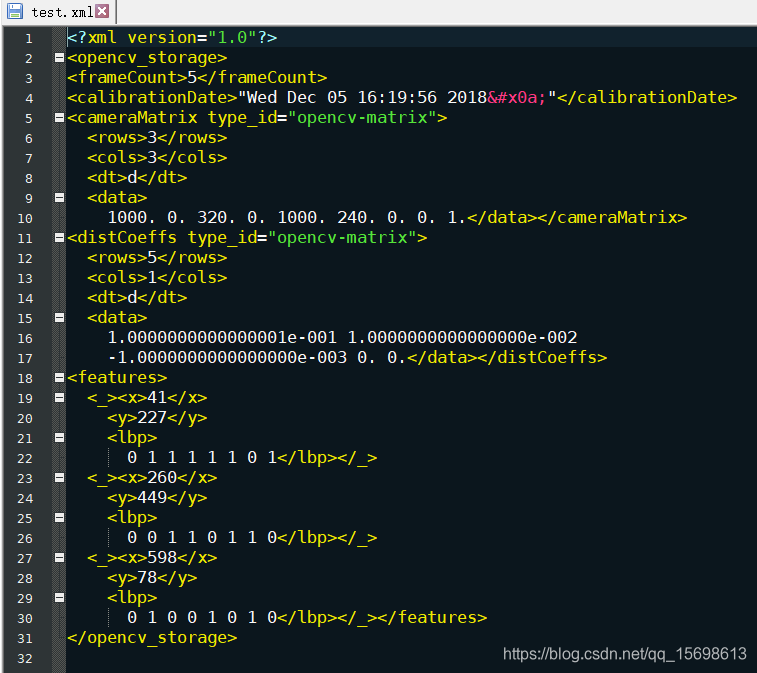
假如把:
FileStorage fs("test.xml", FileStorage::WRITE); 改为 FileStorage fs("test.yaml", FileStorage::WRITE);
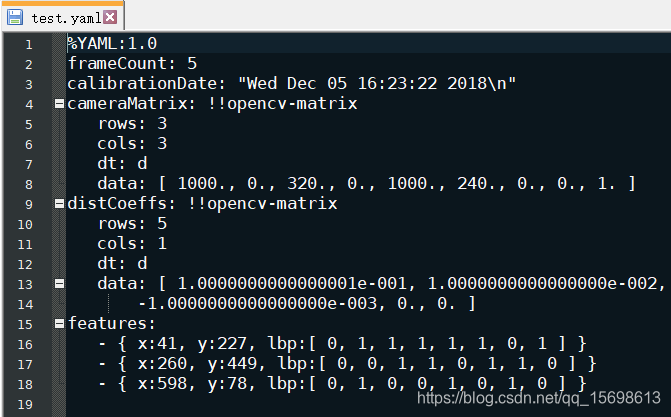
4. XML 和 YAML 文件的读取
-
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
-
#include <time.h>
-
using namespace cv;
-
using namespace std;
-
-
int main() {
-
//改变console字体颜色
-
system("color 6F");
-
-
//初始化
-
FileStorage fs2("test.yaml", FileStorage::READ);
-
-
//第一种方法,对FileNode操作
-
int frameCount = (int)fs2["frameCount"];
-
-
std::string date;
-
//第二种方法,使用FileNode运算符>>
-
fs2["calibrationDate"] >> date;
-
-
Mat cameraMatrix2, distCoeffs2;
-
fs2["cameraMatrix"] >> cameraMatrix2;
-
fs2["distCoeffs"] >> distCoeffs2;
-
-
cout << "frameCount:" << frameCount << endl
-
<< "calibration date:" << date << endl
-
<<"camera matrix:"<<cameraMatrix2<<endl
-
<< "distortion coeffs:" << distCoeffs2 << endl;
-
-
FileNode features = fs2["features"];
-
FileNodeIterator it = features.begin(), it_end = features.end();
-
int idx = 0;
-
vector<uchar> lbpval;
-
-
//使用FileNodeIterator遍历序列
-
for (; it != it_end; ++it, idx++) {
-
cout << "feature #" << idx << ":";
-
cout << "x=" << (int)(*it)["x"] << ",y=" << (int)(*it)["y"] << ",lbp:(";
-
//我们也可以使用filenode>>std::vector操作符来很容易的读取阵列
-
(*it)["lbp"] >> lbpval;
-
for (int i = 0; i < (int)lbpval.size(); i++)
-
cout << " " << (int)lbpval[i];
-
cout << ")" << endl;
-
}
-
fs2.release();
-
-
printf("\n文件读取完毕,输入任意键结束程序!");
-
getchar();
-
-
return(0);
-
}
工程目录准备:
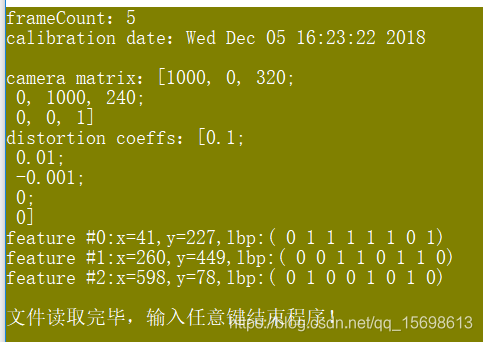
运行结果:
文章来源: kings.blog.csdn.net,作者:人工智能博士,版权归原作者所有,如需转载,请联系作者。
原文链接:kings.blog.csdn.net/article/details/84837657
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)