2025-12-08:所有人渡河所需的最短时间。用go语言,有 n 个人在起点营地,要借一只船把所有人运到对岸。船的最大载人数为
2025-12-08:所有人渡河所需的最短时间。用go语言,有 n 个人在起点营地,要借一只船把所有人运到对岸。船的最大载人数为 k。渡河所需时间会受到环境的影响,这种影响按长度为 m 的循环序列变化,每个阶段 j 对时间有一个倍率 mul[j]:
-
当倍率大于 1 时,实际耗时比基准更长;小于 1 时,耗时变短。基准情况下(倍率为 1)第 i 号人的独自划船时间为 time[i] 分钟。
-
一次由一组人 g 一起出发时,这次过河的耗时等于组内成员的最大 time 值乘以当前阶段的倍率 mul[当前阶段]。
-
若这次渡河耗时为 d 分钟,则阶段指针向前移动 floor(d) 步,随后对 m 取模(即新阶段 = (当前阶段 + floor(d)) mod m)。
-
除非所有人都已到达对岸,否则必须派回一人把船送回起点。返回者只能单独返回,耗时等于该人的 time 值乘以返回时所在阶段的倍率;返回耗时同样使阶段指针前进 floor(return_time) 步并取模。
-
目标是计算把所有人都运到对岸所需的最短总时间;如果无法完成,则返回 -1。
1 <= n == time.length <= 12。
1 <= k <= 5。
1 <= m <= 5。
1 <= time[i] <= 100。
m == mul.length。
0.5 <= mul[i] <= 2.0。
输入: n = 1, k = 1, m = 2, time = [5], mul = [1.0,1.3]。
输出: 5.00000。
解释:
第 0 个人从阶段 0 出发,渡河时间 = 5 × 1.00 = 5.00 分钟。
所有人已经到达目的地,因此总时间为 5.00 分钟。
题目来自力扣3594。
🚢 问题解决步骤
1. 预处理阶段:计算所有可能组合的最大时间
- 目的:由于船一次最多载k人,需要预先计算所有可能的人员组合(子集)过河所需的最大时间。
- 方法:
- 使用状态压缩,用一个n位的二进制数(掩码)表示人员的在岸状态(1表示未过河,0表示已过河)。
- 初始化一个大小为
2^n的数组maxTime,通过动态规划计算每个子集的最大time[i]值。 - 对于人员数量超过k的子集,将其
maxTime设为无穷大(math.MaxInt),表示无效组合。
- 作用:后续决策中快速获取任意有效组合的基准时间。
2. 初始化阶段:设置数据结构与初始状态
- 数据结构:
- 距离数组
dis:三维数组dis[stage][mask][direction],记录在特定阶段stage、剩余人员掩码mask、船的方向direction(0在起点侧,1在对岸侧)下的最短已知时间。初始值为无穷大。 - 优先队列(最小堆):用于Dijkstra算法,按总时间从小到大处理状态。
- 距离数组
- 初始状态:
- 船在起点侧(
direction=0),所有n个人都未过河(mask为全1,即(1<<n)-1),阶段为0,已用时间为0。 - 将该状态加入堆中。
- 船在起点侧(
3. 核心循环:Dijkstra算法处理状态
- 循环条件:优先队列不为空时,不断取出当前耗时最短的状态进行处理。
- 状态检查:
- 如果当前状态的剩余人员掩码
left为0,表示所有人已过河,返回当前时间作为答案。 - 如果当前时间已大于
dis中记录的时间,跳过该状态(已存在更优解)。
- 如果当前状态的剩余人员掩码
- 状态转移:
- 当船在起点侧(direction=0):
- 枚举所有未过河人员的有效子集
sub(人员数≤k),计算该组合过河时间:cost = maxTime[sub] * mul[当前阶段]。 - 新阶段索引更新:
新阶段 = (当前阶段 + floor(cost)) % m。 - 新掩码更新:剩余人员掩码更新为
left ^ sub(移除过河人员)。 - 船方向变为1(对岸侧)。
- 新状态加入堆。
- 枚举所有未过河人员的有效子集
- 当船在对岸侧(direction=1):
- 必须派一人返回起点。枚举所有已过河人员(即掩码中为0的位,通过
u-1^left获取),每次只选一人(单元素子集)。 - 计算返回时间:
cost = time[返回者] * mul[当前阶段]。 - 新阶段索引更新同上。
- 新掩码更新:剩余人员掩码更新为
left ^ lb(添加返回者)。 - 船方向变为0(起点侧)。
- 新状态加入堆。
- 必须派一人返回起点。枚举所有已过河人员(即掩码中为0的位,通过
- 当船在起点侧(direction=0):
4. 终止条件
- 成功:当从堆中取出的状态掩码为0(无人剩余)时,返回该状态的时间。
- 失败:如果堆耗尽仍未找到解,返回-1。
⏱️ 复杂度分析
总的时间复杂度
- 预处理
maxTime:需要计算所有2^n个子集,时间复杂度为 O(2^n)。 - 状态总数:由
dis数组维度决定,共有m × 2^n × 2个可能状态(阶段数m,掩码数2^n,方向2种)。 - 每个状态的处理:
- 当船在起点侧:最多需要枚举
2^n个子集(实际是剩余人员的子集,但最坏情况接近2^n)。 - 当船在对岸侧:最多需要枚举n种返回选择。
- 当船在起点侧:最多需要枚举
- 使用优先队列(堆)的Dijkstra算法,每个状态插入和取出操作是O(log S),其中S是状态总数。
- 综合时间复杂度:约为 O(m × 2^(2n) × n × log(m × 2^n))。由于n≤12,k≤5,m≤5,该复杂度在可接受范围内。
总的额外空间复杂度
maxTime数组:大小为2^n。dis数组:大小为m × 2^n × 2。- 优先队列:最坏情况下可能存储所有状态,即
O(m × 2^n)。 - 综合空间复杂度:O(m × 2^n)。
💎 总结
该解决方案通过状态压缩将人员组合表示为二进制掩码,结合Dijkstra算法在状态空间中进行最优路径搜索,并考虑了阶段变化的倍增影响。算法系统地探索所有可能的渡河方案,确保找到用时最短的解决方案。其复杂度虽然指数级增长,但在题目约束下(n≤12)是可行的。
Go完整代码如下:
package main
import (
"container/heap"
"fmt"
"math"
"math/bits"
)
func minTime(n, k, m int, time []int, mul []float64) float64 {
u := 1 << n
// 计算每个 time 子集的最大值
maxTime := make([]int, u)
for i, t := range time {
highBit := 1 << i
for mask, mx := range maxTime[:highBit] {
maxTime[highBit|mask] = max(mx, t)
}
}
// 把 maxTime 中的大小大于 k 的集合改为 inf
for i := range maxTime {
if bits.OnesCount(uint(i)) > k {
maxTime[i] = math.MaxInt
}
}
dis := make([][][2]float64, m)
for i := range dis {
dis[i] = make([][2]float64, u)
for j := range dis[i] {
dis[i][j] = [2]float64{math.MaxFloat64, math.MaxFloat64}
}
}
h := hp{}
push := func(d float64, stage, mask int, direction uint8) {
if d < dis[stage][mask][direction] {
dis[stage][mask][direction] = d
heap.Push(&h, tuple{d, stage, mask, direction})
}
}
push(0, 0, u-1, 0) // 起点
for len(h) > 0 {
top := heap.Pop(&h).(tuple)
d := top.dis
stage := top.stage
left := top.mask // 剩余没有过河的人
direction := top.direction
if left == 0 { // 所有人都过河了
return d
}
if d > dis[stage][left][direction] {
continue
}
if direction == 0 {
// 枚举 sub 这群人坐一艘船
for sub := left; sub > 0; sub = (sub - 1) & left {
if maxTime[sub] != math.MaxInt {
cost := float64(maxTime[sub]) * mul[stage]
push(d+cost, (stage+int(cost))%m, left^sub, 1)
}
}
} else {
// 枚举回来的人
for s, lb := u-1^left, 0; s > 0; s ^= lb {
lb = s & -s
cost := float64(maxTime[lb]) * mul[stage]
push(d+cost, (stage+int(cost))%m, left^lb, 0)
}
}
}
return -1
}
type tuple struct {
dis float64
stage, mask int
direction uint8 // 状态机:0 未过河,1 已过河
}
type hp []tuple
func (h hp) Len() int { return len(h) }
func (h hp) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i].dis < h[j].dis }
func (h hp) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *hp) Push(v any) { *h = append(*h, v.(tuple)) }
func (h *hp) Pop() (v any) { a := *h; *h, v = a[:len(a)-1], a[len(a)-1]; return }
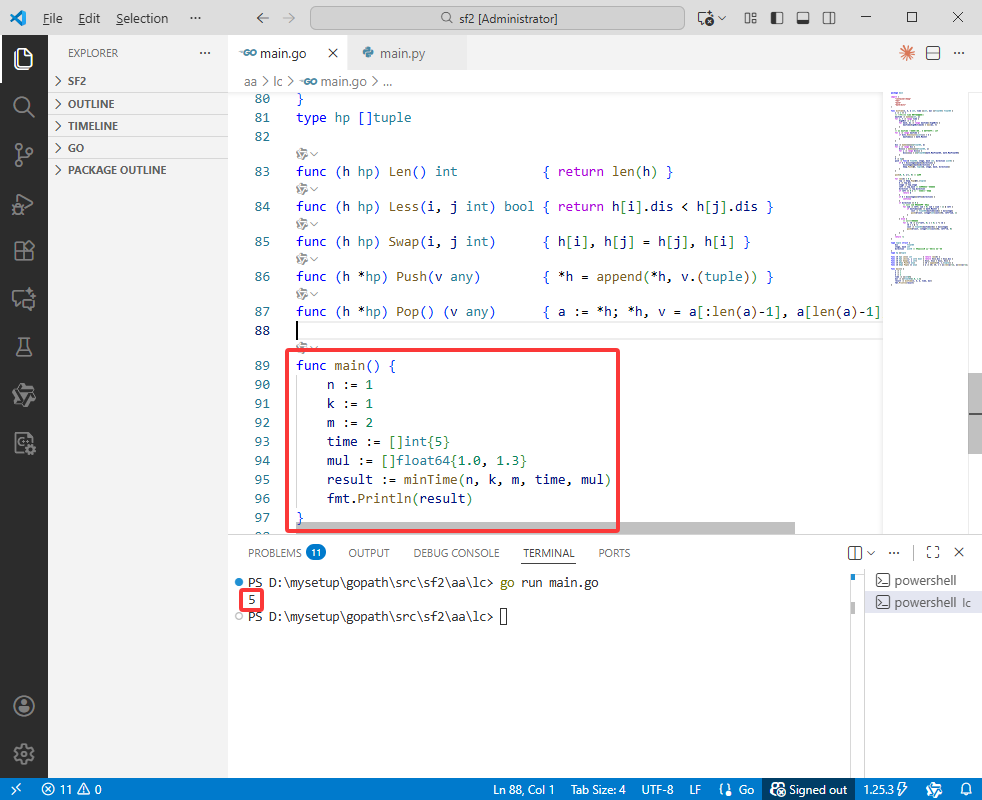
func main() {
n := 1
k := 1
m := 2
time := []int{5}
mul := []float64{1.0, 1.3}
result := minTime(n, k, m, time, mul)
fmt.Println(result)
}
Python完整代码如下:
# -*-coding:utf-8-*-
import heapq
import math
from typing import List
def minTime(n: int, k: int, m: int, time: List[int], mul: List[float]) -> float:
u = 1 << n
# 计算每个子集的最大时间
max_time = [0] * u
for i, t in enumerate(time):
high_bit = 1 << i
for mask in range(high_bit):
max_time[high_bit | mask] = max(max_time[mask], t)
# 将人数超过 k 的集合设为无穷大
for i in range(u):
if bin(i).count('1') > k:
max_time[i] = math.inf
# 初始化距离数组
INF = float('inf')
dist = [[[INF, INF] for _ in range(u)] for _ in range(m)]
# 优先队列 (时间, 阶段, 剩余人员掩码, 方向)
# 方向: 0-从左到右(未过河), 1-从右到左(已过河)
pq = []
def push(d: float, stage: int, mask: int, direction: int):
if d < dist[stage][mask][direction]:
dist[stage][mask][direction] = d
heapq.heappush(pq, (d, stage, mask, direction))
# 起点: 阶段0,所有人都未过河(掩码全为1),方向0(从左到右)
push(0.0, 0, u - 1, 0)
while pq:
d, stage, left, direction = heapq.heappop(pq)
# 所有人都过河了
if left == 0:
return d
# 如果当前距离大于记录的距离,跳过
if d > dist[stage][left][direction]:
continue
if direction == 0: # 从左到右,送人过河
sub = left
while sub > 0:
if max_time[sub] != math.inf:
cost = max_time[sub] * mul[stage]
new_stage = (stage + int(cost)) % m
push(d + cost, new_stage, left ^ sub, 1)
sub = (sub - 1) & left
else: # 从右到左,返回接人
s = (u - 1) ^ left # 已过河的人员
while s > 0:
lb = s & -s # 最低位1
if max_time[lb] != math.inf:
cost = max_time[lb] * mul[stage]
new_stage = (stage + int(cost)) % m
push(d + cost, new_stage, left ^ lb, 0)
s ^= lb
return -1.0
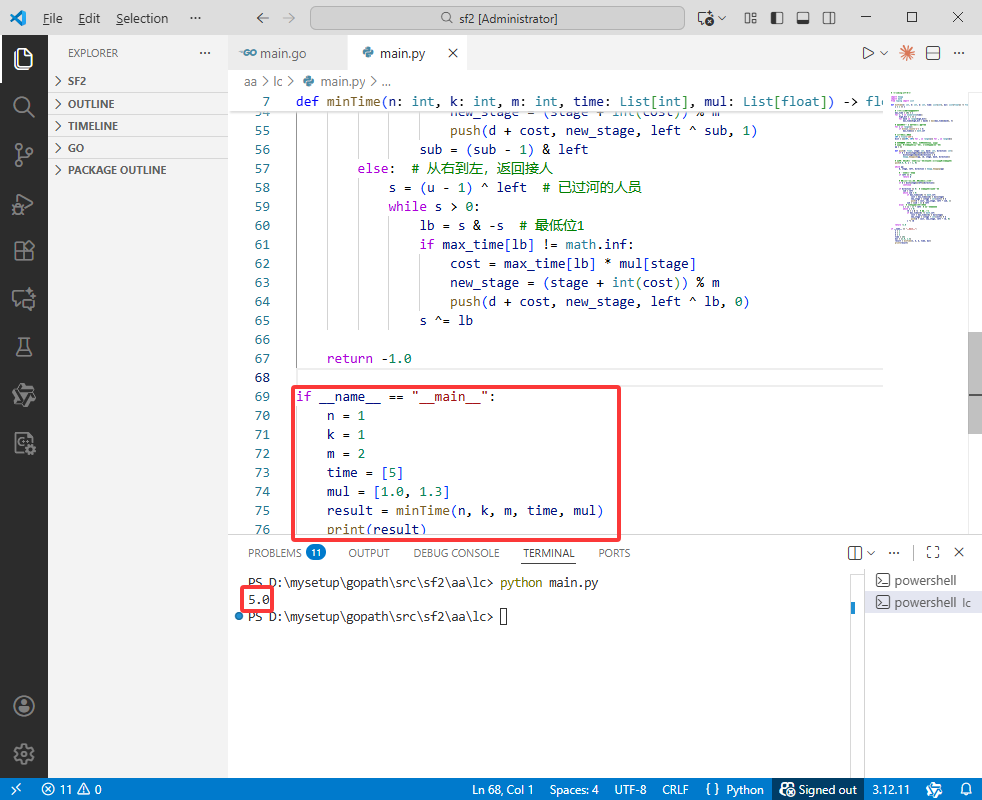
if __name__ == "__main__":
n = 1
k = 1
m = 2
time = [5]
mul = [1.0, 1.3]
result = minTime(n, k, m, time, mul)
print(result)
C++完整代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <bitset>
#include <cstring>
#include <limits>
using namespace std;
struct Tuple {
double dis;
int stage;
int mask;
int direction; // 0-从左到右(未过河), 1-从右到左(已过河)
Tuple(double d, int s, int m, int dir) : dis(d), stage(s), mask(m), direction(dir) {}
bool operator<(const Tuple& other) const {
return dis > other.dis; // 最小堆
}
};
double minTime(int n, int k, int m, vector<int>& time, vector<double>& mul) {
int u = 1 << n;
// 计算每个子集的最大时间
vector<int> maxTime(u, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int highBit = 1 << i;
int t = time[i];
for (int mask = 0; mask < highBit; mask++) {
maxTime[highBit | mask] = max(maxTime[mask], t);
}
}
// 将人数超过 k 的集合设为无穷大
const int INF_INT = numeric_limits<int>::max();
for (int i = 0; i < u; i++) {
if (bitset<32>(i).count() > k) {
maxTime[i] = INF_INT;
}
}
// 初始化距离数组
const double INF = numeric_limits<double>::max();
vector<vector<vector<double>>> dist(m,
vector<vector<double>>(u, vector<double>(2, INF)));
// 优先队列
priority_queue<Tuple> pq;
auto push = [&](double d, int stage, int mask, int direction) {
if (d < dist[stage][mask][direction]) {
dist[stage][mask][direction] = d;
pq.push(Tuple(d, stage, mask, direction));
}
};
// 起点:阶段0,所有人都未过河(掩码全为1),方向0(从左到右)
push(0.0, 0, u - 1, 0);
while (!pq.empty()) {
Tuple top = pq.top();
pq.pop();
double d = top.dis;
int stage = top.stage;
int left = top.mask;
int direction = top.direction;
// 所有人都过河了
if (left == 0) {
return d;
}
// 如果当前距离大于记录的距离,跳过
if (d > dist[stage][left][direction]) {
continue;
}
if (direction == 0) { // 从左到右,送人过河
int sub = left;
while (sub > 0) {
if (maxTime[sub] != INF_INT) {
double cost = maxTime[sub] * mul[stage];
int newStage = (stage + static_cast<int>(cost)) % m;
push(d + cost, newStage, left ^ sub, 1);
}
sub = (sub - 1) & left;
}
} else { // 从右到左,返回接人
int s = (u - 1) ^ left; // 已过河的人员
while (s > 0) {
int lb = s & -s; // 最低位1
if (maxTime[lb] != INF_INT) {
double cost = maxTime[lb] * mul[stage];
int newStage = (stage + static_cast<int>(cost)) % m;
push(d + cost, newStage, left ^ lb, 0);
}
s ^= lb;
}
}
}
return -1.0;
}
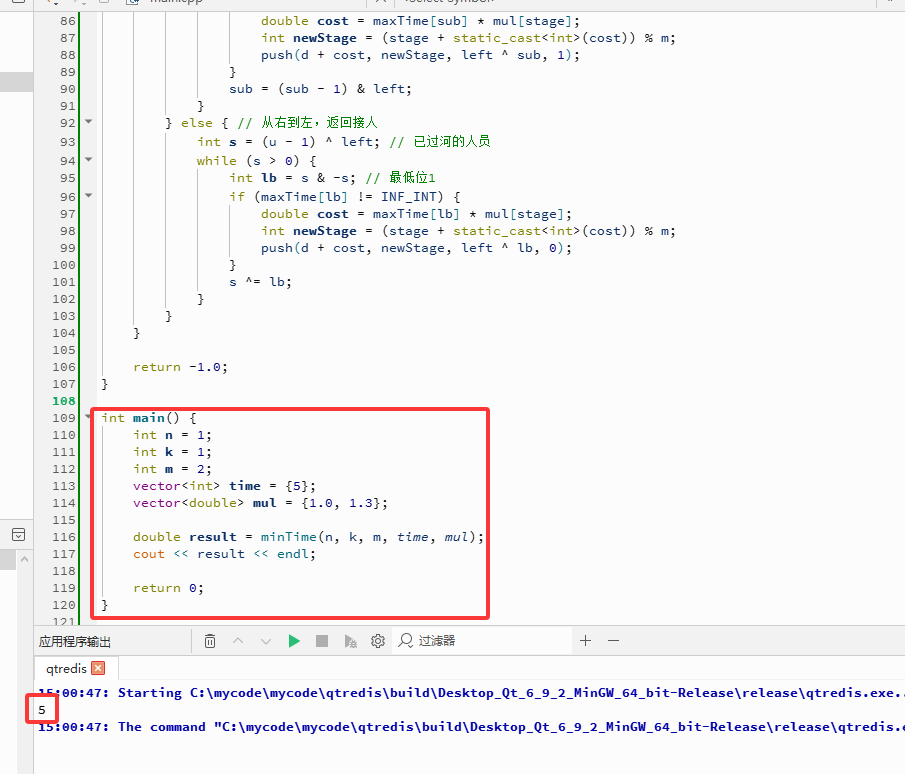
int main() {
int n = 1;
int k = 1;
int m = 2;
vector<int> time = {5};
vector<double> mul = {1.0, 1.3};
double result = minTime(n, k, m, time, mul);
cout << result << endl;
return 0;
}
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)