Java重点 | Map集合的子类
【摘要】 本文将对Map的子类进行详细的介绍,通过代码实战举例,深入浅出的讲解,让你对 Map集合的子类的掌握更加深刻。
LinkedHashMap集合
java.util.LinkedHashMap<K, V>entends HashMap<K.,V> Map 接口的哈希表和链接列表实现,具有可预知的迭代顺序。
底层原理:哈希表+链表(记录元素的顺序)
举例
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("a","a");
map.put("b","b");
map.put("c","c");
map.put("a","d");
System.out.println(map); //{a=d, b=b, c=c} key不允许重复,无序
LinkedHashMap<String,String> linked = new LinkedHashMap<>();
linked.put("a","a");
linked.put("b","b");
linked.put("c","c");
linked.put("a","d");
System.out.println(linked);// key 不允许重复,有序{a=d, b=b, c=c}
}
Hashtable集合
java.util.Hashtable<K,V>集合 implements Map<K,V>接口
HashMap:底层是一个哈希表,是一个线程不安全的集合,是多线程的集合,速度快。
Hashtable:底层也是一个哈希表,是一个线程安全的集合,是单线程集合,速度慢 。
HashMap集合(之前学的所有的集合):可以存储null值,null键 。
Hashtable集合,不能存储nul值,null键。
Hashtable和Vector集合一样,在idk1.2版本之后被更先进的集合(HashMap,ArrayList)取代了。Hashtable的子类Properties依然活跃在历史舞台 Properties集合是一个唯一和IO流相结合的集合
举例
public class Hashtable集合 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,String> map =new HashMap<>();
map.put(null,"a");
map.put("a",null);
map.put(null,null);
System.out.println(map); //{null=null, a=null}
Hashtable<String,String> tab = new Hashtable<>();
tab.put(null,"a");//NullPointerException 空指针异常
tab.put("a",null);//NullPointerException 空指针异常
tab.put(null,null);//NullPointerException 空指针异常
}
}
Properties属性类
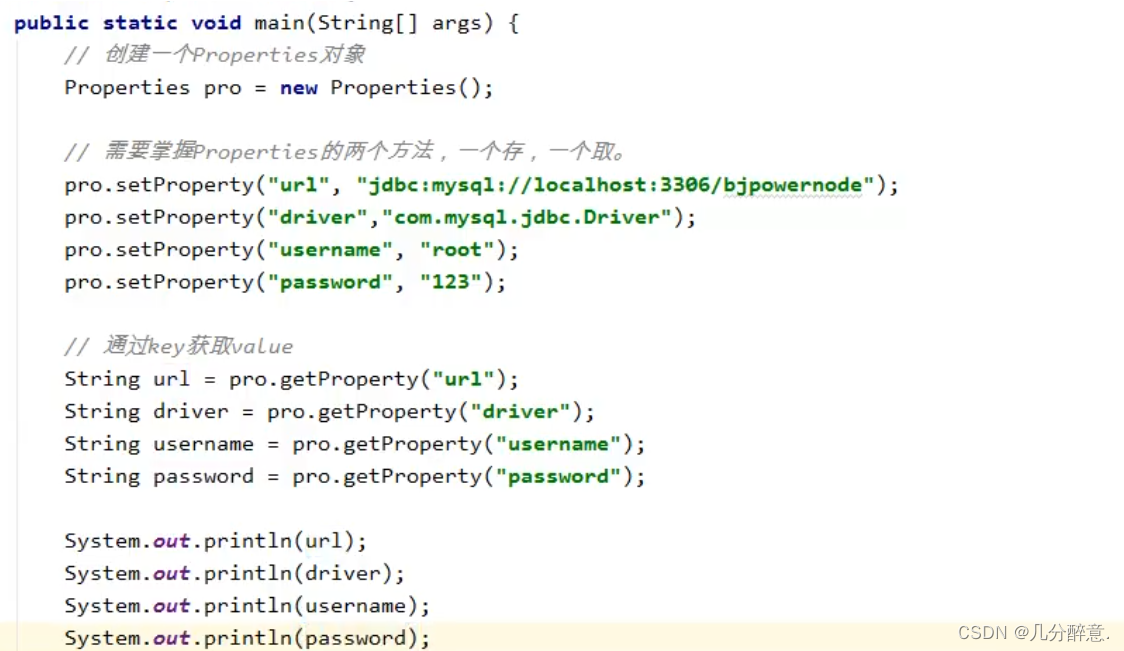
目前只需要掌播Properties属性类对象的相关方法即可。
Properties是一个Map集合,继承Hashtable,Properties的key和value都是string类型。 Properties被称为属性类对象。 Properties是线程安全的。
练习
计算一个字符串中每个字符出现的次数

示例
/*
练习:计算一个字符串中每个字符出现的次数
分析:
1.使用Scanner获取用户输入的字符串
2.创建Map集合,key是字符串中的字符,value是字符个数
3.遍历字符串,获取每一个字符
4.使用获取到的字符,去Map集合判断key是否存在
key存在:
通过字符串(key),获取value(字符个数)
value++
put(key,value)
key不存在:
put(key,1)
5.遍历Map集合,输出结果
*/
public class 计算一个字符串中每个字符出现的次数 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.使用Scanner获取用户输入的字符串
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");
String next = sc.next(); //获取字符串
//2.创建Map集合,key是字符串中的字符,value是字符个数
HashMap<Character,Integer> map =new HashMap<>();
//3.遍历字符串,获取每一个字符
for (Character c:next.toCharArray()){
//4.使用获取到的字符,去Map集合判断key是否存在
if (map.containsKey(c)){
//key已经存在,通过字符串(key),获取value(字符个数),让字符个数加一
Integer value = map.get(c);
value++;//让它加一
map.put(c,value);//把新的覆盖上去
}else {
//key不存在:put(key,1)
map.put(c,1); //集合中没这个key,让他存进集合,初始值为1
}
}
// 不遍历 直接输出也ok
System.out.println(map);
//5.遍历Map集合,输出结果
for (Character key:map.keySet()){
Integer value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+"="+value);
}
}
}
斗地主案例
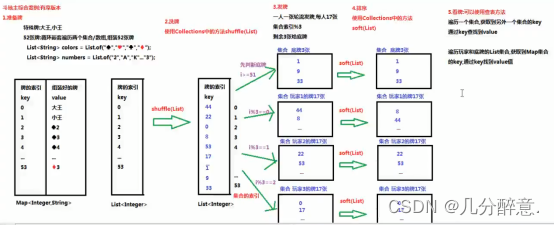
/*
斗地主综合案例:有序版本
1.准备牌
2.洗牌
3.发牌
4.排序
5.看牌
*/
public class 斗地主案例 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.准备牌
//创建一个Map集合,存储牌的索引和组装好的牌
HashMap<Integer,String> poker = new HashMap<>();
//创建一个List集合,存储牌的索引
ArrayList<Integer> pokerIndex = new ArrayList<>();
//定义两个集合,存储花色和牌的序号
List<String> colors = List.of("♠", "♥", "♣", "♦");
List<String> numbers = List.of("2", "A", "K", "Q", "J", "10", "9", "8", "7", "6", "5", "4", "3");
//把大王和小王存储到集合中
//定义一个牌的索引
int index=0;
poker.put(index,"大王");
pokerIndex.add(index);
index++;
poker.put(index,"小王");
pokerIndex.add(index);
index++;
//循环嵌套遍历两个集合,组装52张牌,存储到集合中
for (String nu:numbers){
for (String co:colors){
poker.put(index, nu + co);
pokerIndex.add(index);
index++;
}
}
// System.out.println(poker);
// System.out.println(pokerIndex);
//2.洗牌
Collections.shuffle(pokerIndex);
// System.out.println(pokerIndex);
//3.发牌
//定义四个集合,存储玩家牌的索引和底牌的索引
ArrayList<Integer> dipai = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> wanjia1 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> wanjia2 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> wanjia3 = new ArrayList<>();
//遍历存储牌索引的List集合,获取每一个牌的索引
for (int i = 0; i < pokerIndex.size(); i++) {
Integer s = pokerIndex.get(i);
//先判断底牌
if (i>=51){
dipai.add(s);
}else if (i%3==0){
wanjia1.add(s);
}else if (i%3==1){
wanjia2.add(s);
}else if (i%3==2){
wanjia3.add(s);
}
}
//4.排序
Collections.sort(dipai);
Collections.sort(wanjia1);
Collections.sort(wanjia2);
Collections.sort(wanjia3);
// System.out.println(wanjia1);
//5.看牌
lookPoker("飞飞",poker,wanjia1);
lookPoker("东海",poker,wanjia2);
lookPoker("彬彬",poker,wanjia3);
lookPoker("底牌",poker,dipai);
}
/*
5.看牌 定义一个看牌的方法,提高代码的复用性
参数:
String name:玩家名称
HashMap<Integer,String> poker:存储牌的扑克集合
ArrayList<Integer> list: 存储玩家和底牌的List集合
查表法:
遍历玩家或底牌集合,获取牌的索引
使用牌的索引,去Map集合找到对应的牌
*/
public static void lookPoker(String name,HashMap<Integer,String> poker,ArrayList<Integer> list){
//输出玩家名称不换行
System.out.print(name+": ");
//遍历玩家或底牌集合,获取牌的索引
for (Integer integer : list) {
//使用牌的索引,去Map集合找到对应的牌
String value = poker.get(integer);
System.out.print(value+" ");
}
System.out.println();//打印完每一个玩家的牌换行
}
}
JDK9对集合添加的优化_of方法


【声明】本内容来自华为云开发者社区博主,不代表华为云及华为云开发者社区的观点和立场。转载时必须标注文章的来源(华为云社区)、文章链接、文章作者等基本信息,否则作者和本社区有权追究责任。如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)