2025-12-18:电网维护。用go语言,有 c 个电站,编号从 1 到 c。它们之间通过 n 条无向电缆相连,connect
2025-12-18:电网维护。用go语言,有 c 个电站,编号从 1 到 c。它们之间通过 n 条无向电缆相连,connections 数组中每个元素 [u, v] 表示电站 u 和 v 之间有连接。通过这些连接能够互相到达的一组电站构成一个“电网”(连通分量)。
起初所有电站都是在线(正常工作)的。随后会有一系列操作,记录在 queries 数组中,每条操作有两种形式:
-
[1, x](请求维护):要求对电站 x 进行维护检查。若 x 当前在线,则由 x 自行完成;若 x 已离线,则在与 x 同一连通分量内选择编号最小且目前在线的电站来完成检查;如果该连通分量中没有任何在线电站,则返回 -1。
-
[2, x](下线):将电站 x 设为离线状态(不可用)。
需要按 queries 中的顺序处理操作,并将所有类型为 [1, x] 的查询的返回结果汇总成一个数组输出。注意:电缆连接关系在整个过程中不变,节点即便离线也仍属于原来的连通分量,下线操作不会改变连通结构。
1 <= c <= 100000。
0 <= n == connections.length <= min(100000, c * (c - 1) / 2)。
connections[i].length == 2。
1 <= ui, vi <= c。
ui != vi。
1 <= queries.length <= 2 * 100000。
queries[i].length == 2。
queries[i][0] 为 1 或 2。
1 <= queries[i][1] <= c。
输入: c = 5, connections = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,5]], queries = [[1,3],[2,1],[1,1],[2,2],[1,2]]。
输出: [3,2,3]。
解释:

最初,所有电站 {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} 都在线,并组成一个电网。
查询 [1,3]:电站 3 在线,因此维护检查由电站 3 自行解决。
查询 [2,1]:电站 1 离线。剩余在线电站为 {2, 3, 4, 5}。
查询 [1,1]:电站 1 离线,因此检查由电网中编号最小的在线电站解决,即电站 2。
查询 [2,2]:电站 2 离线。剩余在线电站为 {3, 4, 5}。
查询 [1,2]:电站 2 离线,因此检查由电网中编号最小的在线电站解决,即电站 3。
题目来自力扣3607。
🔄 步骤一:构建初始图结构
首先根据输入的电缆连接关系 connections 构建一个无向图。使用邻接表来存储这个图,其中 graph[i] 是一个切片,保存了所有与电站 i 直接相连的电站编号。同时,初始化一个 vertices 切片,用于记录每个电站的详细信息,包括其所属的电网(连通分量)ID以及是否处于离线状态。初始时,所有电站的 powerGridId 设为 -1(表示未分配),offline 设为 false(表示在线)。
🔍 步骤二:识别连通分量并建立优先队列
接下来,需要找出图中所有的连通分量(即“电网”)。代码采用深度优先搜索(DFS)的方式进行遍历:
- 从第一个未分配电网ID的电站开始,进行DFS遍历,访问所有能到达的电站。
- 在遍历一个连通分量的过程中,为其中每一个电站分配相同的电网ID。
- 关键操作:为每个连通分量创建一个最小堆(优先队列)。在DFS遍历时,将当前访问的电站编号插入到该连通分量对应的堆中。由于堆是最小堆,堆顶元素始终是该连通分量中编号最小的电站。这一步是为后续高效查找最小在线电站做准备。
⚙️ 步骤三:处理查询操作
然后,按顺序处理查询数组 queries 中的每一个操作:
-
下线操作 (
op == 2):- 动作很简单:找到电站
x,将其offline标志设置为true。 - 注意,电站
x虽然离线了,但它仍然属于原来的连通分量,图的连接结构没有改变。代码中并没有在此时从堆中删除x,这是一种延迟删除策略。
- 动作很简单:找到电站
-
请求维护操作 (
op == 1):- 首先检查电站
x的当前状态。如果x在线,那么结果就是x本身。 - 如果
x已离线,则需要从其所属的连通分量对应的最小堆中找出编号最小的在线电站。 - 延迟删除的清理:由于下线操作没有直接删除堆中的元素,堆顶可能是一个已经离线的电站。因此,需要不断检查堆顶元素:
- 如果堆顶电站已离线,就将其从堆中弹出 (
heap.Pop)。 - 重复这个过程,直到堆顶是一个在线电站,或者堆为空。
- 如果堆顶电站已离线,就将其从堆中弹出 (
- 如果堆不为空,那么当前的堆顶元素就是该连通分量中编号最小的在线电站,将其作为结果。如果堆为空,说明这个连通分量里没有在线电站了,返回 -1。
- 首先检查电站
⏱️ 复杂度分析
-
总的时间复杂度:
- 构建图:O(c + n),其中 c 是电站数量,n 是电缆数量。
- DFS遍历:同样是 O(c + n),每个节点和边只访问一次。
- 处理查询:这是最复杂的部分。每个下线操作 (op==2) 是 O(1) 时间。每个维护请求操作 (op==1) 的时间成本则取决于需要弹出多少个已离线的堆顶元素。在最坏情况下,可能每次操作都需要 O(log c) 时间(堆操作)。然而,由于每个电站最多被弹出一次,所有查询中弹出操作的总次数是 O© 次。因此,处理 q 个查询的总时间复杂度可以近似为 O((c + q) log c)。
-
总的额外空间复杂度:
- 图结构
graph需要 O(c + n) 的空间。 vertices数组需要 O© 的空间。- 各个连通分量的最小堆总共存储了 c 个电站编号,所以也是 O© 的空间。
- 综合来看,总的额外空间复杂度为 O(c + n)。
- 图结构
Go完整代码如下:
package main
import (
"container/heap"
"fmt"
)
func processQueries(c int, connections [][]int, queries [][]int) []int {
graph := make([][]int, c+1)
vertices := make([]Vertex, c+1)
for i := 0; i <= c; i++ {
graph[i] = make([]int, 0)
vertices[i] = Vertex{vertexId: i, powerGridId: -1}
}
for _, conn := range connections {
u, v := conn[0], conn[1]
graph[u] = append(graph[u], v)
graph[v] = append(graph[v], u)
}
powerGrids := make([]*IntHeap, 0)
for i, powerGridId := 1, 0; i <= c; i++ {
v := &vertices[i]
if v.powerGridId == -1 {
powerGrid := &IntHeap{}
heap.Init(powerGrid)
traverse(v, powerGridId, powerGrid, graph, vertices)
powerGrids = append(powerGrids, powerGrid)
powerGridId++
}
}
ans := make([]int, 0)
for _, q := range queries {
op, x := q[0], q[1]
if op == 1 {
if !vertices[x].offline {
ans = append(ans, x)
} else {
powerGrid := powerGrids[vertices[x].powerGridId]
for powerGrid.Len() > 0 && vertices[(*powerGrid)[0]].offline {
heap.Pop(powerGrid)
}
if powerGrid.Len() > 0 {
ans = append(ans, (*powerGrid)[0])
} else {
ans = append(ans, -1)
}
}
} else if op == 2 {
vertices[x].offline = true
}
}
return ans
}
func traverse(u *Vertex, powerGridId int, powerGrid *IntHeap, graph [][]int, vertices []Vertex) {
u.powerGridId = powerGridId
heap.Push(powerGrid, u.vertexId)
for _, vid := range graph[u.vertexId] {
v := &vertices[vid]
if v.powerGridId == -1 {
traverse(v, powerGridId, powerGrid, graph, vertices)
}
}
}
type Vertex struct {
vertexId int
offline bool
powerGridId int
}
type IntHeap []int
func (h IntHeap) Len() int { return len(h) }
func (h IntHeap) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i] < h[j] }
func (h IntHeap) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *IntHeap) Push(x interface{}) {
*h = append(*h, x.(int))
}
func (h *IntHeap) Pop() interface{} {
old := *h
n := len(old)
x := old[n-1]
*h = old[0 : n-1]
return x
}
func main() {
c := 5
connections := [][]int{{1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 4}, {4, 5}}
queries := [][]int{{1, 3}, {2, 1}, {1, 1}, {2, 2}, {1, 2}}
result := processQueries(c, connections, queries)
fmt.Println(result)
}
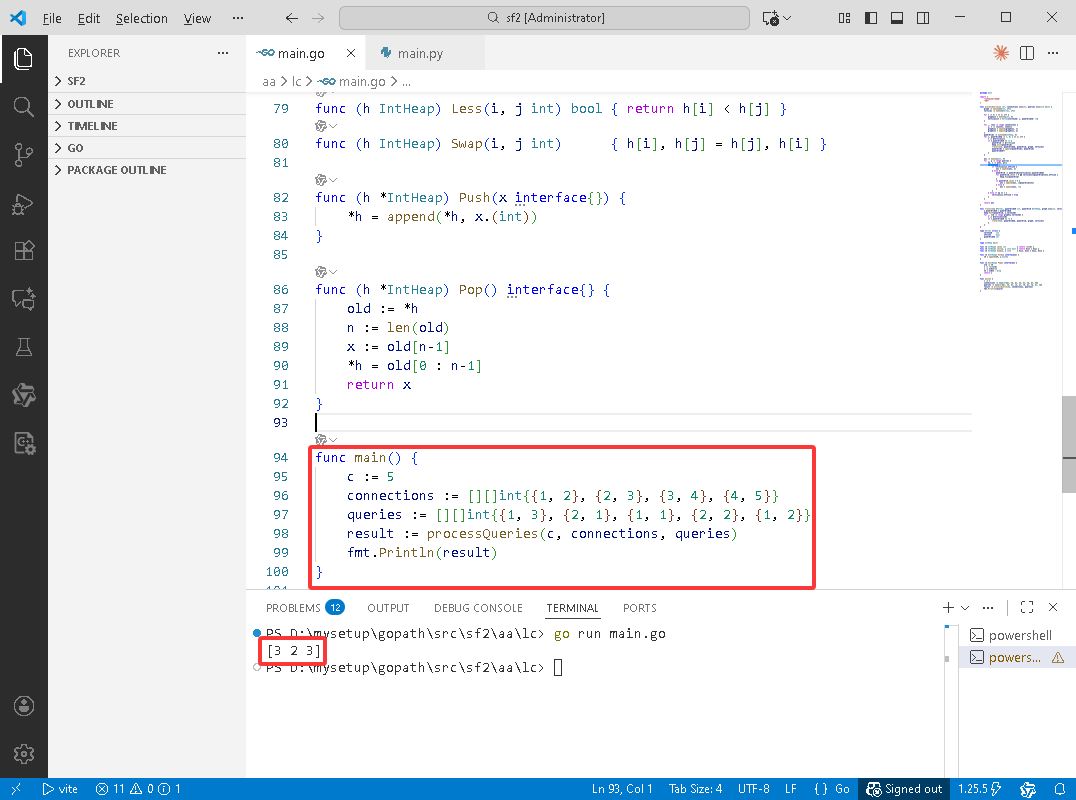
Python完整代码如下:
# -*-coding:utf-8-*-
import heapq
from typing import List
def processQueries(c: int, connections: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
# 构建邻接表
graph = [[] for _ in range(c + 1)]
# 顶点信息
vertices = [{'vertex_id': i, 'offline': False, 'power_grid_id': -1} for i in range(c + 1)]
for u, v in connections:
graph[u].append(v)
graph[v].append(u)
# 初始化电网列表
power_grids = []
power_grid_id = 0
# DFS遍历连通分量
def dfs(u: int, pg_id: int, pg_heap: List[int]):
vertices[u]['power_grid_id'] = pg_id
heapq.heappush(pg_heap, u)
for v in graph[u]:
if vertices[v]['power_grid_id'] == -1:
dfs(v, pg_id, pg_heap)
# 遍历所有顶点,找到所有连通分量
for i in range(1, c + 1):
if vertices[i]['power_grid_id'] == -1:
power_grid = []
dfs(i, power_grid_id, power_grid)
power_grids.append(power_grid)
power_grid_id += 1
ans = []
for op, x in queries:
if op == 1: # 查询操作
if not vertices[x]['offline']:
ans.append(x)
else:
pg = power_grids[vertices[x]['power_grid_id']]
# 弹出所有离线的顶点
while pg and vertices[pg[0]]['offline']:
heapq.heappop(pg)
if pg:
ans.append(pg[0])
else:
ans.append(-1)
elif op == 2: # 离线操作
vertices[x]['offline'] = True
return ans
# 测试用例
if __name__ == "__main__":
c = 5
connections = [[1, 2], [2, 3], [3, 4], [4, 5]]
queries = [[1, 3], [2, 1], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1, 2]]
result = processQueries(c, connections, queries)
print(result) # 输出结果
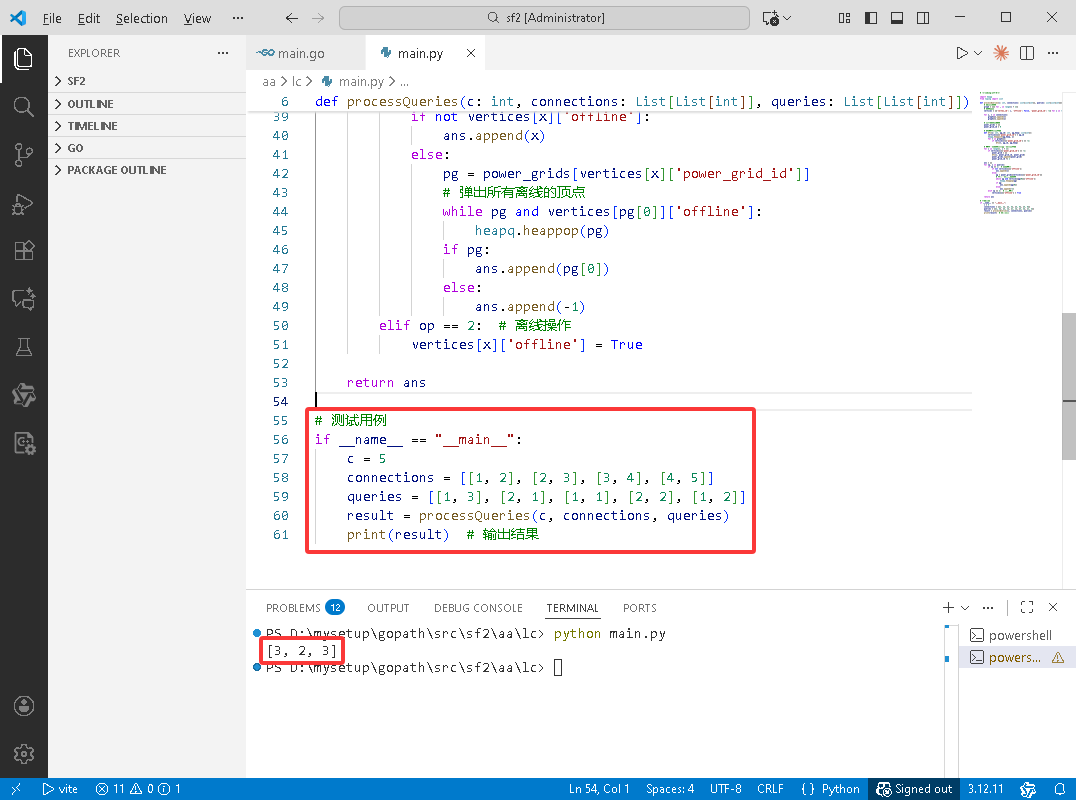
C++完整代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
// 顶点结构体
struct Vertex {
int vertexId;
bool offline;
int powerGridId;
Vertex(int id = 0) : vertexId(id), offline(false), powerGridId(-1) {}
};
void traverse(Vertex* u, int powerGridId, priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>>& powerGrid,
vector<vector<int>>& graph, vector<Vertex>& vertices) {
u->powerGridId = powerGridId;
powerGrid.push(u->vertexId);
for (int vid : graph[u->vertexId]) {
Vertex& v = vertices[vid];
if (v.powerGridId == -1) {
traverse(&v, powerGridId, powerGrid, graph, vertices);
}
}
}
vector<int> processQueries(int c, vector<vector<int>>& connections, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {
// 构建邻接表
vector<vector<int>> graph(c + 1);
vector<Vertex> vertices(c + 1);
for (int i = 0; i <= c; i++) {
vertices[i] = Vertex(i);
}
for (auto& conn : connections) {
int u = conn[0], v = conn[1];
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
// 存储所有电网(每个电网是一个最小堆)
vector<priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>>> powerGrids;
int powerGridId = 0;
// 遍历所有顶点,找到连通分量
for (int i = 1; i <= c; i++) {
Vertex& v = vertices[i];
if (v.powerGridId == -1) {
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> powerGrid;
traverse(&v, powerGridId, powerGrid, graph, vertices);
powerGrids.push_back(powerGrid);
powerGridId++;
}
}
vector<int> ans;
for (auto& q : queries) {
int op = q[0], x = q[1];
if (op == 1) { // 查询操作
if (!vertices[x].offline) {
ans.push_back(x);
} else {
// 获取顶点所在的电网
auto& powerGrid = powerGrids[vertices[x].powerGridId];
// 弹出所有离线的顶点
while (!powerGrid.empty() && vertices[powerGrid.top()].offline) {
powerGrid.pop();
}
if (!powerGrid.empty()) {
ans.push_back(powerGrid.top());
} else {
ans.push_back(-1);
}
}
} else if (op == 2) { // 离线操作
vertices[x].offline = true;
}
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
int c = 5;
vector<vector<int>> connections = {{1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 4}, {4, 5}};
vector<vector<int>> queries = {{1, 3}, {2, 1}, {1, 1}, {2, 2}, {1, 2}};
vector<int> result = processQueries(c, connections, queries);
cout << "[";
for (size_t i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
cout << result[i];
if (i < result.size() - 1) {
cout << ", ";
}
}
cout << "]" << endl;
return 0;
}
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)