2025-03-15:判断矩形的两个角落是否可达。用go语言,给定两个正整数 xCorner 和 yCorner,以及一个二维整
2025-03-15:判断矩形的两个角落是否可达。用go语言,给定两个正整数 xCorner 和 yCorner,以及一个二维整数数组 circles,表示若干个圆的信息。判断是否存在一条从矩形的左下角到右上角的路径,这条路径完全在矩形内部,不会触碰或经过任何圆的内部和边界,只在起点和终点与矩形接触。如果存在这样的路径返回true,否则返回false。
3 <= xCorner, yCorner <= 1000000000。
1 <= circles.length <= 1000。
circles[i].length == 3。
1 <= xi, yi, ri <= 1000000000。
输入:X = 3, Y = 4, circles = [[2,1,1]]。
输出:true。
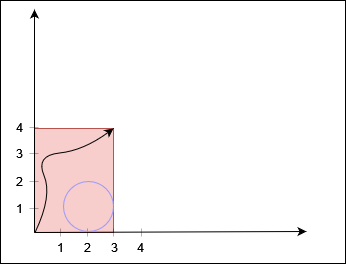
黑色曲线表示一条从 (0, 0) 到 (3, 4) 的路径。
题目来自leetcode3235。
大体步骤如下:
1.定义一个函数 canReachCorner,用于判断矩形的两个角落是否可达。
2.初始化一个记录圆是否被访问过的布尔数组 visited,长度为圆的数量。
3.定义深度优先搜索函数 dfs,用于遍历圆并判断是否存在可达路径。
4.实现函数 pointInCircle,用于判断点是否在圆内部。
5.实现函数 circleIntersectsTopLeftOfRectangle,用于判断圆是否与矩形左上角相交。
6.实现函数 circleIntersectsBottomRightOfRectangle,用于判断圆是否与矩形右下角相交。
7.实现函数 circlesIntersectInRectangle,用于判断两个圆是否在矩形内相交。
8.实现函数 abs,用于求取整数的绝对值。
9.在 main 函数中,给定矩形边界和圆的信息,调用 canReachCorner 函数判断路径是否可达,并输出结果。
总的时间复杂度分析:
-
遍历圆的过程中,需要对每个圆进行判断和搜索,因此最坏情况下时间复杂度为 O(N^2),其中 N 为圆的数量。
-
在判断点是否在圆内、判断圆与矩形相交等操作中,时间复杂度为 O(1)。
-
因此总的时间复杂度为 O(N^2),其中 N 为圆的数量。
总的额外空间复杂度分析:
- 程序中额外使用了 visited 数组来记录圆是否被访问过,其大小与圆的数量成正比,因此额外空间复杂度为 O(N),其中 N 为圆的数量。
Go完整代码如下:
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
func canReachCorner(xCorner int, yCorner int, circles [][]int) bool {
visited := make([]bool, len(circles))
var dfs func(i int) bool
dfs = func(i int) bool {
x1, y1, r1 := circles[i][0], circles[i][1], circles[i][2]
if circleIntersectsBottomRightOfRectangle(x1, y1, r1, xCorner, yCorner) {
return true
}
visited[i] = true
for j := 0; j < len(circles); j++ {
if !visited[j] && circlesIntersectInRectangle(x1, y1, r1, circles[j][0], circles[j][1], circles[j][2], xCorner, yCorner) && dfs(j) {
return true
}
}
return false
}
for i := range circles {
x, y, r := circles[i][0], circles[i][1], circles[i][2]
if pointInCircle(0, 0, x, y, r) || pointInCircle(xCorner, yCorner, x, y, r) {
return false
}
if !visited[i] && circleIntersectsTopLeftOfRectangle(x, y, r, xCorner, yCorner) && dfs(i) {
return false
}
}
return true
}
func pointInCircle(px, py, x, y, r int) bool {
return (x-px)*(x-px)+(y-py)*(y-py) <= r*r
}
func circleIntersectsTopLeftOfRectangle(x, y, r, xCorner, yCorner int) bool {
return (abs(x) <= r && 0 <= y && y <= yCorner) ||
(0 <= x && x <= xCorner && abs(y-yCorner) <= r) ||
pointInCircle(x, y, 0, yCorner, r)
}
func circleIntersectsBottomRightOfRectangle(x, y, r, xCorner, yCorner int) bool {
return (abs(y) <= r && 0 <= x && x <= xCorner) ||
(0 <= y && y <= yCorner && abs(x-xCorner) <= r) ||
pointInCircle(x, y, xCorner, 0, r)
}
func circlesIntersectInRectangle(x1, y1, r1, x2, y2, r2, xCorner, yCorner int) bool {
return (x1-x2)*(x1-x2)+(y1-y2)*(y1-y2) <= (r1+r2)*(r1+r2) &&
x1*r2+x2*r1 < (r1+r2)*xCorner &&
y1*r2+y2*r1 < (r1+r2)*yCorner
}
func abs(x int) int {
if x < 0 {
return -x
}
return x
}
func main() {
X := 3
Y := 4
circles := [][]int{{2, 1, 1}}
result := canReachCorner(X, Y, circles)
fmt.Println(result)
}
Python完整代码如下:
# -*-coding:utf-8-*-
def can_reach_corner(x_corner, y_corner, circles):
visited = [False] * len(circles)
def dfs(i):
x1, y1, r1 = circles[i][0], circles[i][1], circles[i][2]
if circle_intersects_bottom_right_of_rectangle(x1, y1, r1, x_corner, y_corner):
return True
visited[i] = True
for j in range(len(circles)):
if not visited[j] and circles_intersect_in_rectangle(x1, y1, r1, circles[j][0], circles[j][1], circles[j][2], x_corner, y_corner) and dfs(j):
return True
return False
for i in range(len(circles)):
x, y, r = circles[i][0], circles[i][1], circles[i][2]
if point_in_circle(0, 0, x, y, r) or point_in_circle(x_corner, y_corner, x, y, r):
return False
if not visited[i] and circle_intersects_top_left_of_rectangle(x, y, r, x_corner, y_corner) and dfs(i):
return False
return True
def point_in_circle(px, py, x, y, r):
return (x-px)*(x-px) + (y-py)*(y-py) <= r*r
def circle_intersects_top_left_of_rectangle(x, y, r, x_corner, y_corner):
return (abs(x) <= r and 0 <= y <= y_corner) or \
(0 <= x <= x_corner and abs(y-y_corner) <= r) or \
point_in_circle(x, y, 0, y_corner, r)
def circle_intersects_bottom_right_of_rectangle(x, y, r, x_corner, y_corner):
return (abs(y) <= r and 0 <= x <= x_corner) or \
(0 <= y <= y_corner and abs(x-x_corner) <= r) or \
point_in_circle(x, y, x_corner, 0, r)
def circles_intersect_in_rectangle(x1, y1, r1, x2, y2, r2, x_corner, y_corner):
return (x1-x2)*(x1-x2) + (y1-y2)*(y1-y2) <= (r1+r2)*(r1+r2) and \
x1*r2 + x2*r1 < (r1+r2)*x_corner and \
y1*r2 + y2*r1 < (r1+r2)*y_corner
def abs_val(x):
return -x if x < 0 else x
def main():
x = 3
y = 4
circles = [[2, 1, 1]]
result = can_reach_corner(x, y, circles)
print(result)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)