【愚公系列】《AIGC辅助软件开发》007-面向软件开发的提示工程:写Prompt就是逐步明确需求的过程
🏆 作者简介,愚公搬代码
🏆《头衔》:华为云特约编辑,华为云云享专家,华为开发者专家,华为产品云测专家,CSDN博客专家,CSDN商业化专家,阿里云专家博主,阿里云签约作者,腾讯云优秀博主,腾讯云内容共创官,掘金优秀博主,亚马逊技领云博主,51CTO博客专家等。
🏆《近期荣誉》:2022年度博客之星TOP2,2023年度博客之星TOP2,2022年华为云十佳博主,2023年华为云十佳博主等。
🏆《博客内容》:.NET、Java、Python、Go、Node、前端、IOS、Android、鸿蒙、Linux、物联网、网络安全、大数据、人工智能、U3D游戏、小程序等相关领域知识。
🏆🎉欢迎 👍点赞✍评论⭐收藏
🚀前言
在软件开发的过程中,需求的明确性和准确性是项目成功的关键。而随着人工智能技术的不断进步,提示工程(Prompt Engineering)作为一种新兴的方法论,正在为开发者提供一种更高效的需求表达方式。通过精确的Prompt设计,开发者能够与AI模型进行有效的互动,从而更好地实现功能需求和业务目标。
本文将深入探讨面向软件开发的提示工程,重点分析如何通过撰写有效的Prompt来逐步明确需求。我们将讨论Prompt的构成要素、最佳实践以及在实际开发中的应用案例。通过这些内容,您将了解到如何利用提示工程提升需求沟通的效率,减少开发中的误解和返工。
无论您是刚入行的开发者,还是希望提升项目管理和需求分析能力的经验丰富的从业者,这篇文章都将为您提供实用的指导和深刻的见解。让我们一起探索提示工程的魅力,助力软件开发的每一步都更加精准和高效!
🚀一、写Prompt就是逐步明确需求的过程
如果你是程序员,那么在你写程序前应有一个明确的目标。这个目标可能是你的老板提的,可能是你的客户提的,也可能是你自己的想法。如果是别人的想法,你希望最好能写成明确的需求文档,正常逻辑和异常逻辑都能事先考虑清楚,而不是在写程序过程中反复沟通确认,甚至最后还要返工。你还希望尽早知道这个功能要服务的用户群体是谁,解决用户哪方面的痛点,想要达成怎样的业务效果,预期能带来多少收入。
🔎1.让 ChatGPT 一步一步写出你想要的页面
任务描述
假如你是公司的资深程序员,你的老板给你安排了一项任务:制作一个H5页面,展示公司采集的微博数据中当天讨论量最大的10条微博。
思路分析
-
数据处理
- 微博数据已经完成采集,并存储在数据库中。每条微博的讨论量数据接近实时更新。
- 首先,编写一个程序来计算讨论量排名前10的微博。
-
API开发
- 接下来,开发一个API,用于查询讨论量Top 10的微博列表。
-
前端开发
- 前端部分需要创建一个列表页,展示Top 10微博的标题和部分内容。
- 同时,还需开发一个内容详情页,展示微博的完整内容及相关信息。
然后把这件事交给ChatGPT,你可以试着这么问,看看它怎么说。
🦋1.1 明确需求
做一个H5页面,把公司采集的微博数据中当天讨论量最大10条微博展示出来,只需要给出实现思路就行不需要代码。

ChatGPT好像是猜到了你的想法,把你刚才心中所想的又复述了一遍,并且更有条理但这并不是你想要的答案。
你想要ChatGPT帮你写代码。这样就得细化一下需求,把任务拆分成前端代码和后台代码。
前端需要一个列表页,列表页长什么样?老板好像没有说。所以首先要跟老板确认,明确页面的风格、展示元素,以及内容详情页的细节。你现在不仅是程序员,还得是懂业务懂老板想法并且会写代码的产品经理,需求文档就需要由你来写了。
比起写需求文档,你可能更愿意写代码。能不能不写文档,而是让ChatGPT来完成?ChatGPT见多识广,应该看过微博热搜列表页。于是你又提了一个Prompt:
🦋1.2 简单需求
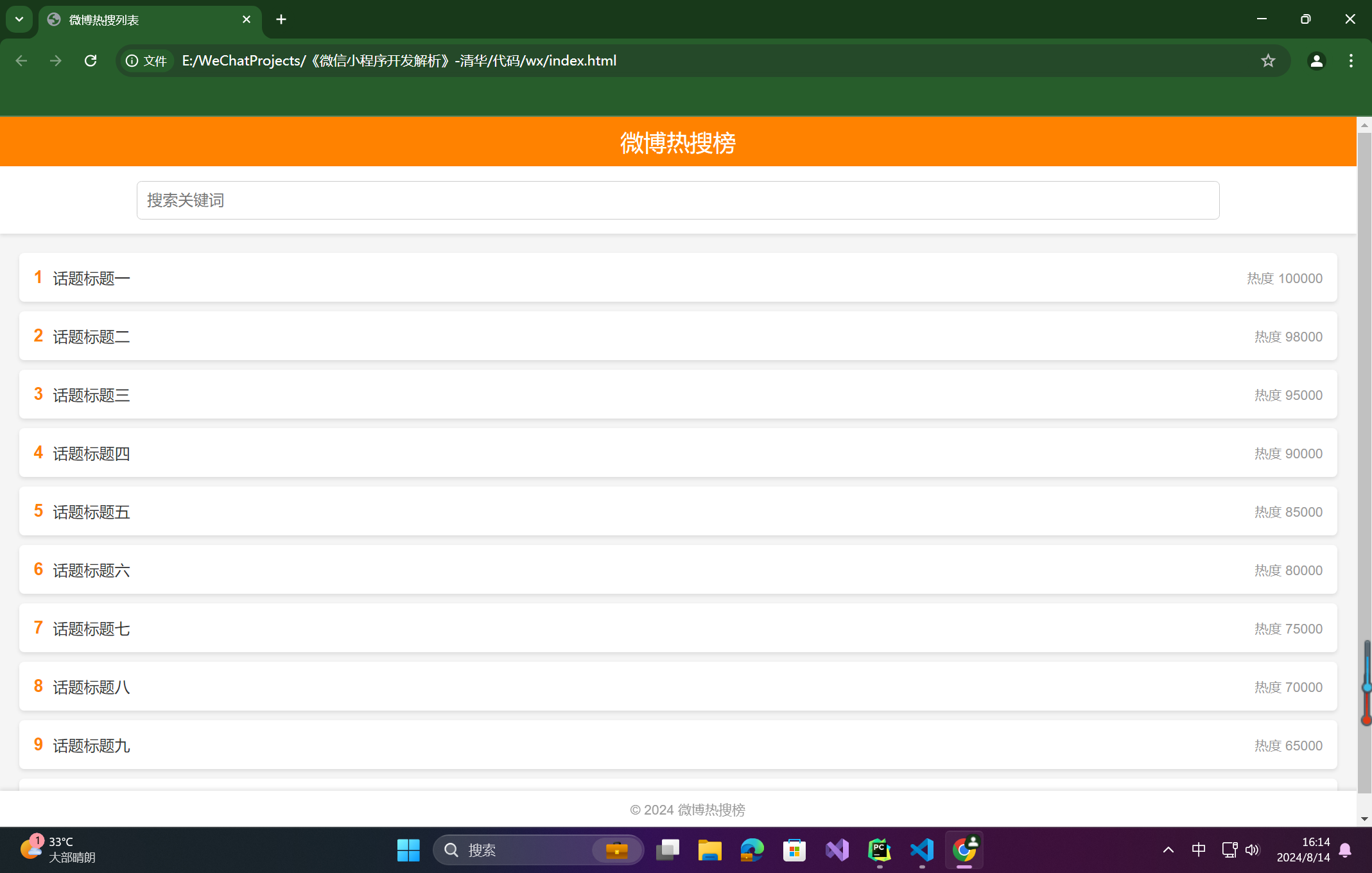
仿照微博热搜列表页,写一个HTML页面。

运行下面代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>微博热搜列表</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
background-color: #f5f5f5;
}
.header {
background-color: #ff8200;
color: white;
padding: 10px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 24px;
}
.search-bar {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
padding: 15px;
background-color: #ffffff;
box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
.search-bar input {
width: 80%;
padding: 10px;
font-size: 16px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.hot-search-list {
margin: 20px;
padding: 0;
list-style-type: none;
}
.hot-search-item {
background-color: #ffffff;
margin-bottom: 10px;
padding: 15px;
border-radius: 5px;
box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
}
.hot-search-item .rank {
font-size: 18px;
font-weight: bold;
color: #ff8200;
margin-right: 10px;
}
.hot-search-item .title {
flex-grow: 1;
font-size: 16px;
color: #333;
}
.hot-search-item .heat {
font-size: 14px;
color: #999;
}
.footer {
text-align: center;
padding: 10px;
background-color: #fff;
color: #999;
font-size: 14px;
position: fixed;
bottom: 0;
width: 100%;
box-shadow: 0 -2px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="header">微博热搜榜</div>
<div class="search-bar">
<input type="text" placeholder="搜索关键词">
</div>
<ul class="hot-search-list">
<li class="hot-search-item">
<div class="rank">1</div>
<div class="title">话题标题一</div>
<div class="heat">热度 100000</div>
</li>
<li class="hot-search-item">
<div class="rank">2</div>
<div class="title">话题标题二</div>
<div class="heat">热度 98000</div>
</li>
<li class="hot-search-item">
<div class="rank">3</div>
<div class="title">话题标题三</div>
<div class="heat">热度 95000</div>
</li>
<li class="hot-search-item">
<div class="rank">4</div>
<div class="title">话题标题四</div>
<div class="heat">热度 90000</div>
</li>
<li class="hot-search-item">
<div class="rank">5</div>
<div class="title">话题标题五</div>
<div class="heat">热度 85000</div>
</li>
<li class="hot-search-item">
<div class="rank">6</div>
<div class="title">话题标题六</div>
<div class="heat">热度 80000</div>
</li>
<li class="hot-search-item">
<div class="rank">7</div>
<div class="title">话题标题七</div>
<div class="heat">热度 75000</div>
</li>
<li class="hot-search-item">
<div class="rank">8</div>
<div class="title">话题标题八</div>
<div class="heat">热度 70000</div>
</li>
<li class="hot-search-item">
<div class="rank">9</div>
<div class="title">话题标题九</div>
<div class="heat">热度 65000</div>
</li>
<li class="hot-search-item">
<div class="rank">10</div>
<div class="title">话题标题十</div>
<div class="heat">热度 60000</div>
</li>
</ul>
<div class="footer">© 2024 微博热搜榜</div>
</body>
</html>
🦋1.3 细化需求
明确一下ChatGPT的角色,再细化下它的具体任务,就像产品经理写需求那样,最好把页面都有哪些元素都描述清楚。
现在你是一个程序员,你要写一段完整可运行的HTML+CSS+JavaScript代码。这段代码要实现一个功能,这个功能是一个微博标题列表页,每一条是一个标题,标题后面带上一个数字,这个数字表示这条微博的评论数,并实现分页和搜索功能。页面风格请参考微博热搜列表页。
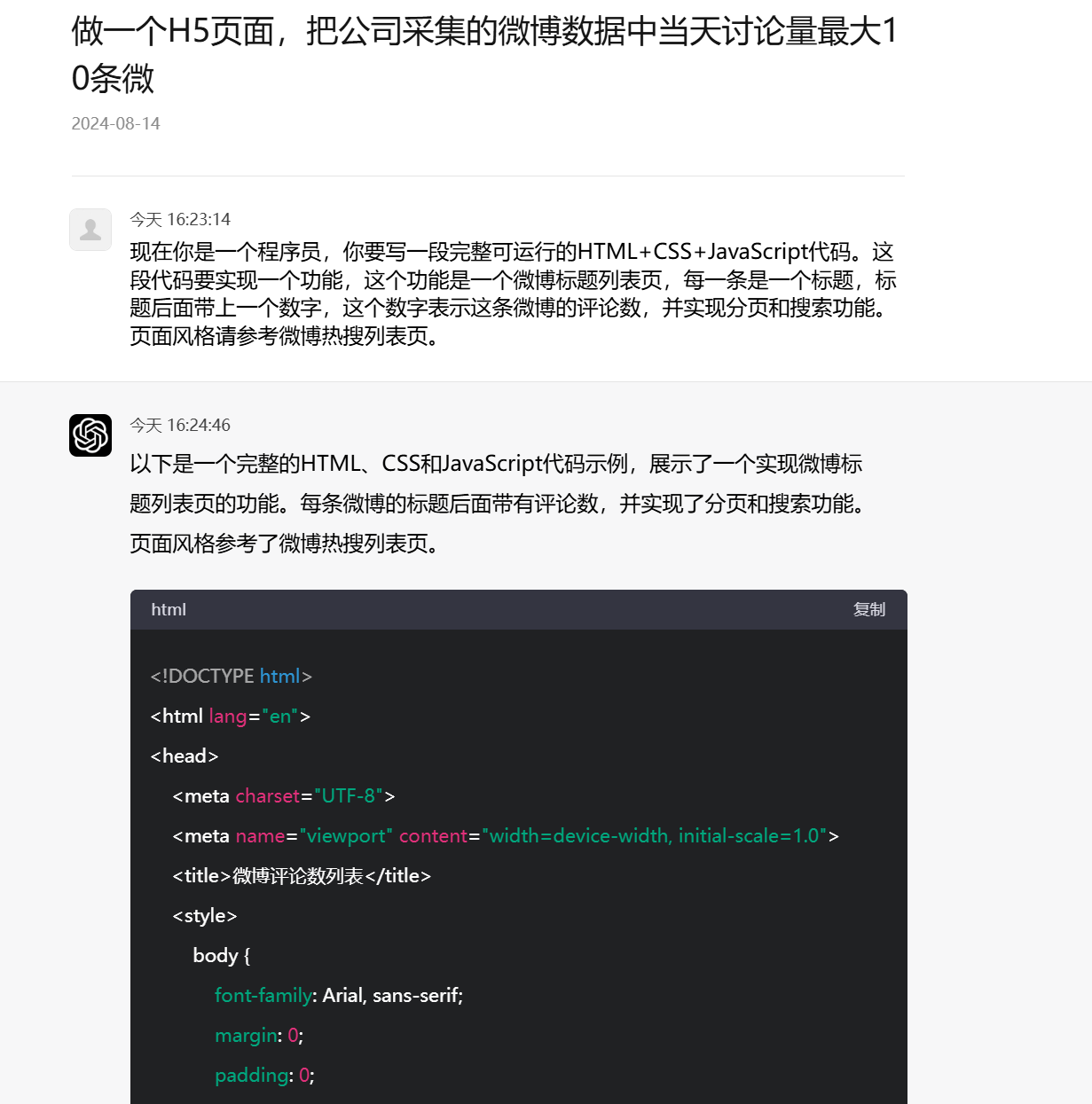
运行下面代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>微博评论数列表</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
background-color: #f5f5f5;
}
.header {
background-color: #ff8200;
color: white;
padding: 10px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 24px;
}
.search-container {
margin: 20px;
text-align: center;
}
.search-box {
padding: 10px;
width: 80%;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 5px;
font-size: 16px;
}
.list-container {
margin: 20px;
padding: 0;
list-style-type: none;
}
.list-item {
background-color: #ffffff;
margin-bottom: 10px;
padding: 15px;
border-radius: 5px;
box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
font-size: 16px;
color: #333;
}
.pagination {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
margin: 20px;
}
.pagination button {
background-color: #ff8200;
color: white;
border: none;
padding: 10px 15px;
margin: 0 5px;
cursor: pointer;
border-radius: 5px;
font-size: 16px;
}
.pagination button:disabled {
background-color: #ccc;
cursor: not-allowed;
}
.footer {
text-align: center;
padding: 10px;
background-color: #fff;
color: #999;
font-size: 14px;
position: fixed;
bottom: 0;
width: 100%;
box-shadow: 0 -2px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="header">微博评论数列表</div>
<div class="search-container">
<input type="text" id="search-box" class="search-box" placeholder="搜索微博标题..." oninput="searchWeibo()">
</div>
<ul class="list-container" id="weibo-list">
<!-- 微博列表将由JavaScript动态生成 -->
</ul>
<div class="pagination">
<button id="prev-btn" onclick="prevPage()">上一页</button>
<button id="next-btn" onclick="nextPage()">下一页</button>
</div>
<div class="footer">© 2024 微博评论数列表</div>
<script>
// 模拟的微博数据
const weiboData = [
{ title: "微博标题一", comments: 120 },
{ title: "微博标题二", comments: 98 },
{ title: "微博标题三", comments: 150 },
{ title: "微博标题四", comments: 76 },
{ title: "微博标题五", comments: 200 },
{ title: "微博标题六", comments: 85 },
{ title: "微博标题七", comments: 130 },
{ title: "微博标题八", comments: 60 },
{ title: "微博标题九", comments: 45 },
{ title: "微博标题十", comments: 110 },
{ title: "微博标题十一", comments: 120 },
{ title: "微博标题十二", comments: 98 },
{ title: "微博标题十三", comments: 150 },
{ title: "微博标题十四", comments: 76 },
{ title: "微博标题十五", comments: 200 },
{ title: "微博标题十六", comments: 85 },
{ title: "微博标题十七", comments: 130 },
{ title: "微博标题十八", comments: 60 },
{ title: "微博标题十九", comments: 45 },
{ title: "微博标题二十", comments: 110 }
];
let filteredData = weiboData;
const itemsPerPage = 5;
let currentPage = 1;
function renderList() {
const weiboList = document.getElementById('weibo-list');
weiboList.innerHTML = ''; // 清空现有内容
const start = (currentPage - 1) * itemsPerPage;
const end = start + itemsPerPage;
const currentItems = filteredData.slice(start, end);
currentItems.forEach((weibo, index) => {
const listItem = document.createElement('li');
listItem.className = 'list-item';
listItem.innerHTML = `<span>${weibo.title}</span><span>评论数:${weibo.comments}</span>`;
weiboList.appendChild(listItem);
});
// 更新按钮状态
document.getElementById('prev-btn').disabled = currentPage === 1;
document.getElementById('next-btn').disabled = end >= filteredData.length;
}
function nextPage() {
if (currentPage * itemsPerPage < filteredData.length) {
currentPage++;
renderList();
}
}
function prevPage() {
if (currentPage > 1) {
currentPage--;
renderList();
}
}
function searchWeibo() {
const query = document.getElementById('search-box').value.toLowerCase();
filteredData = weiboData.filter(weibo => weibo.title.toLowerCase().includes(query));
currentPage = 1; // 重置为第一页
renderList();
}
// 初始渲染
renderList();
</script>
</body>
</html>
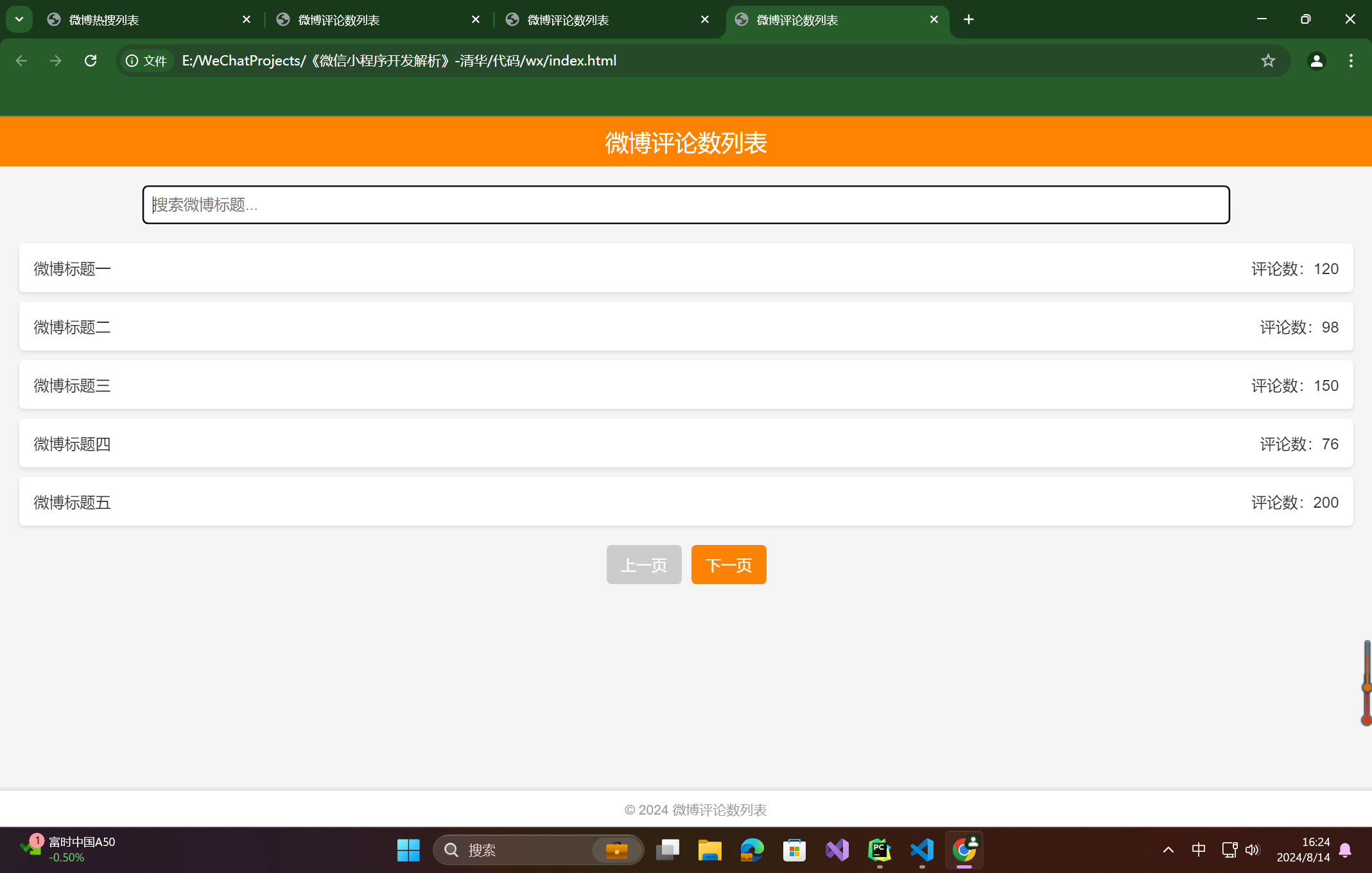
这样看来,只要不断明确细化需求,ChatGPT输出的结果就能无限逼近你的目标。
不过,你可能也发现了,把需求描述清晰也不是那么容易,即便是一个现成的简单页面也会遗漏掉很多的细节。但是经过一轮轮的迭代和反馈后,你不仅能快速发现自己的疏漏还能快速验证很多想法。
通过对比第一版的 Prompt 和最后一版的 Prompt,我们就能看出差异。所以,什么是清晰明确的Prompt?就是充满细节描述的 Prompt。
🔎2.让 ChatGPT 为你设计后台架构方案
有了前端页面,接下来还有后台。后台需要按互动量对微博排序的程序,以及一个查询列表可供页面调用的接口。
按互动量排序,这么大的数据量,是实时排,还是按天排?参考微博热搜是每分钟排次。假设待排序的微博有1亿条,让ChatGPT帮忙分析一下,这种数据量级用什么方案能足要求。
你现在是后台架构师,请帮我设计一个后台技术方案,包括使用的算法、需要的服务器CPU 和内存资源,以及程序源代码,能满足以下功能:
1.对于数据库中的所有微博,希望按互动量字段从大到小取出前10条
2.前10条微博,需要每分钟更新一次。
3.微博总数量有1亿条,存储在分布式数据库中。
4.每条记录包括4个字段:微博 ID、微博标题、微博详情 URL、互动量。

得到代码:
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from pyspark.sql.functions import col
import redis
# 创建SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder \
.appName("TopKWeibo") \
.getOrCreate()
# 连接到分布式数据库 (Cassandra, HBase, etc.)
# 假设数据表为 "weibo_table"
weibo_df = spark.read.format("cassandra").options(table="weibo_table", keyspace="weibo").load()
# 排序并取出前10条微博
top10_weibo = weibo_df.orderBy(col("interaction").desc()).limit(10).collect()
# 连接到Redis
redis_client = redis.StrictRedis(host='redis_host', port=6379, db=0)
# 更新Redis中的Top-10数据
for index, weibo in enumerate(top10_weibo):
weibo_data = {
"id": weibo.id,
"title": weibo.title,
"url": weibo.url,
"interaction": weibo.interaction
}
redis_client.hmset(f"weibo_top10:{index+1}", weibo_data)
# 关闭SparkSession
spark.stop()
ChatGPT不仅给出了方案,还编写了代码。把结果缓存在Redis中,这样可以提升系统并发查询的能力。
🔎3.让 ChatGPT 完成后台接口
请写一个RESTGUI API,负责给前端页面调用,查询互动量前10的微博。从上面我们设计的 Redis 中查询出互动量前10的微博。其中有几个字段要返回给前端页面:微博标题、微博内容 URL、微博互动量。
得到代码:
from flask import Flask, jsonify
import redis
app = Flask(__name__)
# 连接到Redis
redis_client = redis.StrictRedis(host='redis_host', port=6379, db=0, decode_responses=True)
@app.route('/api/top10_weibo', methods=['GET'])
def get_top10_weibo():
top10_weibo = []
# 从Redis中获取前10条微博数据
for i in range(1, 11):
weibo_key = f"weibo_top10:{i}"
weibo_data = redis_client.hgetall(weibo_key)
if weibo_data:
# 将数据添加到列表中
top10_weibo.append({
"title": weibo_data.get("title"),
"url": weibo_data.get("url"),
"interaction": int(weibo_data.get("interaction"))
})
# 返回JSON格式的响应
return jsonify(top10_weibo)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5000)
这样,前端、后台都齐全了。剩下的自己做些微调,就能交付1.0版本了。怎么样,ChatGPT是不是特别“靠谱”,事事有回应,件件有着落,哪怕到了晚上也能陪你随时加班。
当然在这个过程中,并不是你发一条简单的命令就能得到理想的结果。ChatGPT虽然懂的多,但大概率不能一次就明白你的需求。在与它的交互过程中,你会发现哪些需求点还需要明确,哪些背景还需要交代,哪些数据和案例还需要补充。最终,你打磨后的Prompt是份完整的需求文档,而 ChatGPT按照你的需求一步一步地把任务给完成了。
另外,在这个过程中,你从一个干活的角色转变成了设计解决方案的角色。这种身份和视角的转变,会产生积极的效果。
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)