【SpringBoot】整合SpringCache轻松启用Redis缓存
【摘要】 SpringCache是Spring提供的一种缓存抽象机制,旨在通过简化缓存操作来提高系统性能和响应速度。可以将方法的返回值缓存起来,当下次调用方法时如果从缓存中查询到了数据,可以直接从缓存中获取结果,而无需再次执行方法体中的代码。
目录:
1.前言
Spring Cache是Spring提供的一种缓存抽象机制,旨在通过简化缓存操作来提高系统性能和响应速度。Spring Cache可以将方法的返回值缓存起来,当下次调用方法时如果从缓存中查询到了数据,可以直接从缓存中获取结果,而无需再次执行方法体中的代码。
2.常用注解
- @Cacheable:在方法执行前查看是否有缓存对应的数据,如果有直接返回数据,如果没有调用方法获取数据返回,并缓存起来;
- @CacheEvict:将一条或多条数据从缓存中删除;
- @CachePut:将方法的返回值放到缓存中;
- @EnableCaching:开启缓存注解功能;
- @Caching:组合多个缓存注解。
3.启用缓存
3.1.配置yaml文件
spring:
cache:
type: simple
simple:
time-to-live: 600s3.2.添加注解
在启动类上添加注解@EnableCaching:
@Slf4j
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class SpringBootstrap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootstrap.class, args);
}
}3.3.创建缓存
使用
@CachePut注解。当方法执行完后,如果缓存不存在则创建缓存;如果缓存存在则更新缓存。注解中的value属性可指定缓存的名称,key属性则可指定缓存的键,可使用SpEL表达式来获取key的值。
这里result表示方法的返回值UserInfo,从UserInfo中获取id属性。
@CachePut(value = "user", key = "#result.id")
public UserInfo create(UserCreateRequest request) {
// 将请求中的数据映射给实体类(相关方法自行创建)
User user = UserConverter.createByRequest(request);
boolean save = userService.save(user);
if (save) {
return UserConverter.toInfo(user);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("User.create.fail");
}
}3.4.更新缓存
同样使用
@CachePut注解。当方法执行完后,如果缓存不存在则创建缓存;如果缓存存在则更新缓存。
@CachePut(value = "user", key = "#result.id")
public UserInfo update(UserUpdateRequest request) {
// 将请求中的数据映映射给wrapper(相关方法自行创建)
Wrapper<User> wrapper = UserConverter.updateWrapperByRequest(request);
boolean update = userService.update(wrapper);
if (update) {
return UserConverter.toInfo(user);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("User.update.fail");
}
}3.5.查询缓存
使用
@Cacheable注解。在方法执行前,首先会查询缓存,如果缓存不存在,则根据方法的返回结果创建缓存;如果缓存存在,则直接返回数据,不执行方法。这里使用request表示方法的参数UserQueryRequest。
@Cacheable(value = "user", key = "#request.id")
public UserInfo query(UserQueryRequest request) {
User user = userService.getById(request.getId());
if (Objects.isNull(user)) {
throw new RuntimeException("User.not.exist");
}
return c2cInterestCategory;
}3.6.删除缓存
使用
@CacheEvict注解。当方法执行完后,会根据key删除对应的缓存。这里可以使用condition属性,当返回结果为true(删除成功)后,才去删除缓存。
@CacheEvict(value = "user", key = "#request.id", condition = "#result.equals(true)")
public Boolean delete(UserDeleteRequest request) {
return userService.removeById(request.getId());
}3.7.多重操作
使用
@Caching注解,通过使用不同的属性进行相应操作。
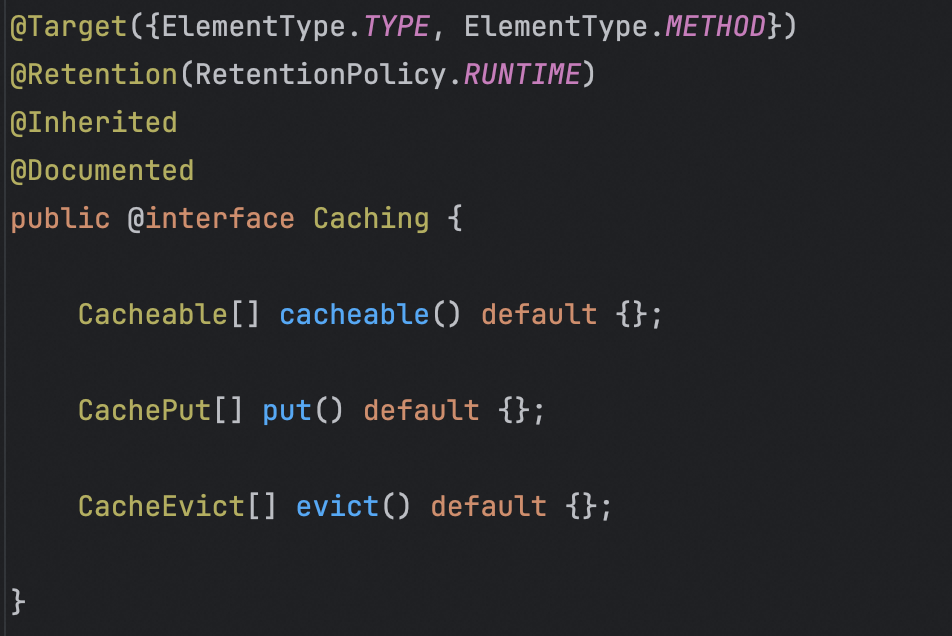
创建/更新多个缓存:
@Caching(
put = {
@CachePut(value = "userById", key = "#result.id"),
@CachePut(value = "userByPhone", key = "#request.phone")
}
)删除多个缓存:
@Caching(
evict = {
@CacheEvict(value = "userById", key = "#result.id"),
@CacheEvict(value = "userByPhone", key = "#request.phone")
}
)
【声明】本内容来自华为云开发者社区博主,不代表华为云及华为云开发者社区的观点和立场。转载时必须标注文章的来源(华为云社区)、文章链接、文章作者等基本信息,否则作者和本社区有权追究责任。如果您发现本社区中有涉嫌抄袭的内容,欢迎发送邮件进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,本社区将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容,举报邮箱:
cloudbbs@huaweicloud.com
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)