【Vue3】学习watch监视(上)
🍋介绍
在Vue3中,watch 函数是一个非常强大且常用的功能,用于监视数据的变化并执行相应的操作。本文将深入探讨Vue3中的watch监视功能,包括基本用法、高级用法以及与Vue2中watch的比较。
- 特点:
Vue3中的watch只能监视以下四种数据:
ref定义的数据。reactive定义的数据。- 函数返回一个值(
getter函数)。- 一个包含上述内容的数组。
🍋情况一:监视【ref】定义的基本数据类型
首先我们准备好需要的代码
<template>
<div class="person">
<h2>求和:{{ sum }}</h2>
<button @click="changeSum">Sum+1</button>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup name="Person11">
import {ref} from 'vue'
let sum = ref(0)
function changeSum (){
sum.value +=1
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.person {
background-color: skyblue;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px;
border-radius: 10px;
padding: 20px;
}
button {
margin: 0 5px;
}
</style>
接下来我们将watch导入一下
import {ref,watch} from 'vue'
接下来我们定义监视
watch(sum, (newValue,oldValue)=>{
console.log(newValue,oldValue)
})
运行结果如下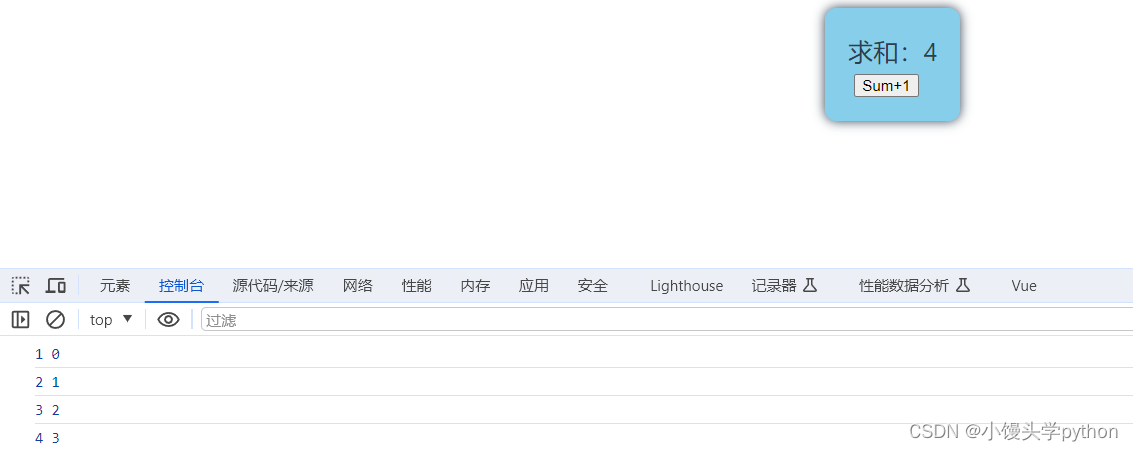
如果我们想要停止监视呢
const stopWatch = watch(sum, (newValue,oldValue)=>{
console.log(newValue,oldValue)
if(newValue >= 5)
{
stopWatch()
}
})
运行结果如下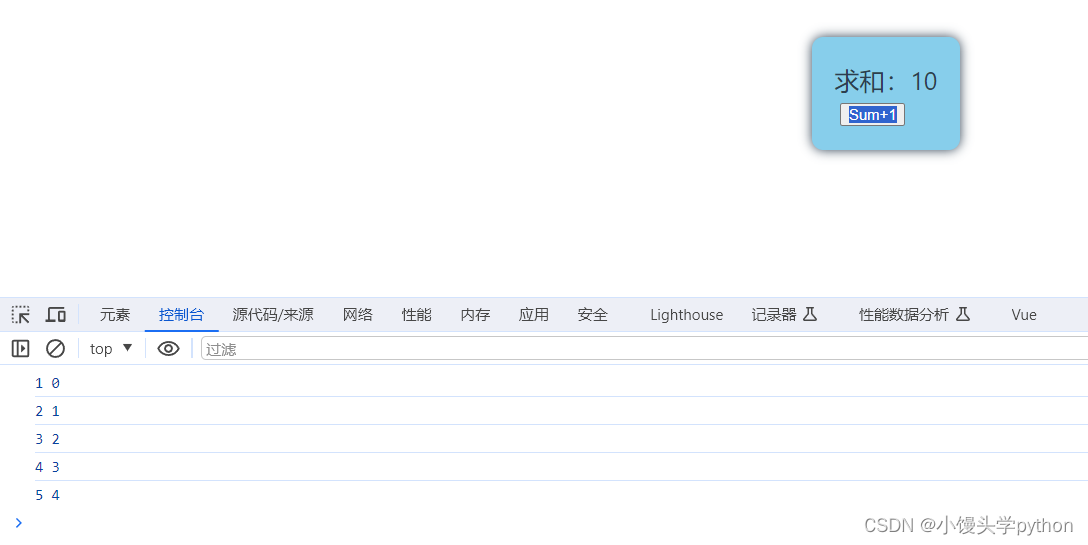
注意:
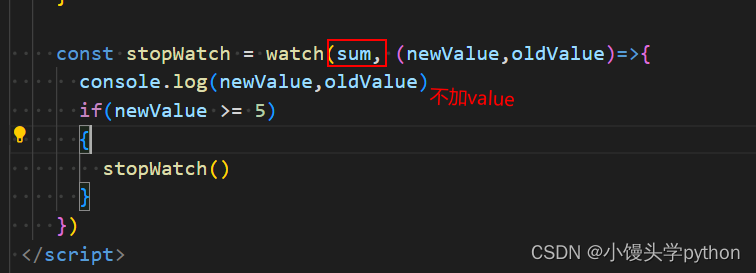
🍋情况二:监视【ref】定义的对象类型数据
监视ref定义的【对象类型】数据:直接写数据名,监视的是对象的【地址值】,若想监视对象内部的数据,要手动开启深度监视。
注意:
若修改的是
ref定义的对象中的属性,newValue和oldValue都是新值,因为它们是同一个对象。若修改整个
ref定义的对象,newValue是新值,oldValue是旧值,因为不是同一个对象了。
准备代码数据如下
<template>
<div class="person">
<h2>姓名:{{ person.name }}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{ person.age }}</h2>
<button @click="changeName">修改名字</button>
<button @click="changeAge">修改年龄</button>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup name="Person11">
import {ref,watch} from 'vue'
let person = ref({
name:"馒头",
age:22
})
function changeName(){
person.value.name += '*'
}
function changeAge(){
person.value.age += 1
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.person {
background-color: skyblue;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px;
border-radius: 10px;
padding: 20px;
}
button {
margin: 0 5px;
}
</style>
接下来为了测试更明显,我们将watch写出来,并添加一个button,用来修改Person整体而并非是其中的数据
<template>
<div class="person">
<h2>姓名:{{ person.name }}</h2>
<h2>年龄:{{ person.age }}</h2>
<button @click="changeName">修改名字</button>
<button @click="changeAge">修改年龄</button>
<button @click="changePerson">修改人</button>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup name="Person11">
import {ref,watch} from 'vue'
let person = ref({
name:"馒头",
age:22
})
function changeName(){
person.value.name += '*'
}
function changeAge(){
person.value.age += 1
}
function changePerson(){
person.value = {name:'小馒头',age:23}
}
watch(person,(newValue,oldValue)=>{
console.log(newValue,oldValue)
})
</script>
<style scoped>
.person {
background-color: skyblue;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px;
border-radius: 10px;
padding: 20px;
}
button {
margin: 0 5px;
}
</style>
当我们点击修改名字和修改年龄的时候是没有触发监视的,但是当点击修改Person的时候,就会触发了,这其实是监视对象的地址如下图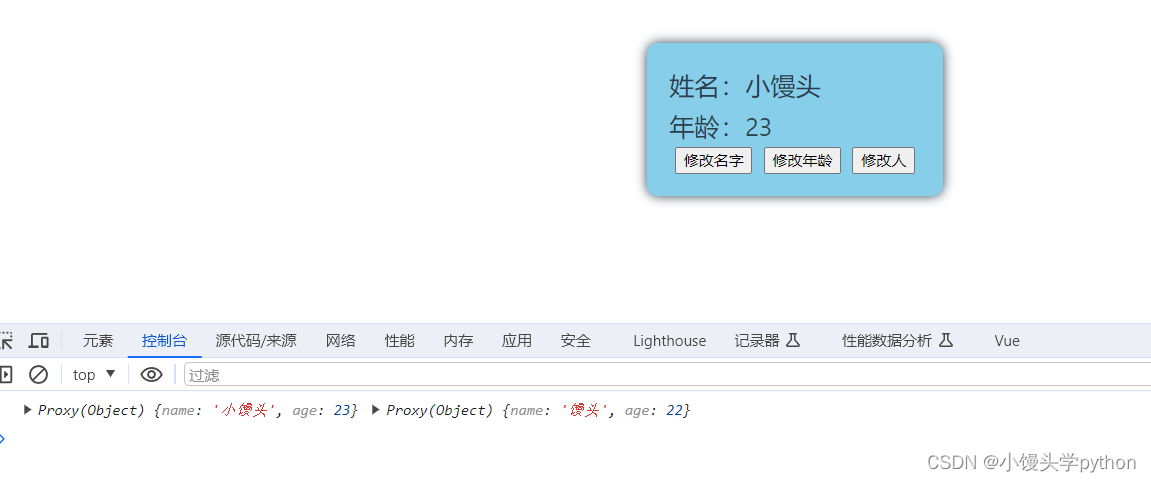
如果我们想监视对象内部的数据,那么我们需要开启深度监视,这样我们就会都监视了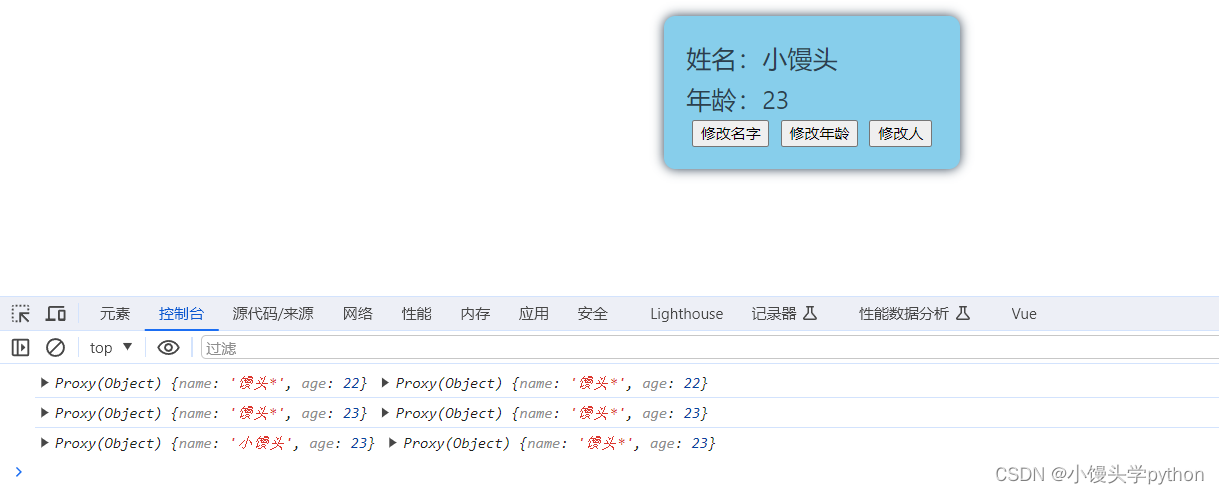
扩展:如果你希望在监听器被设置时立即执行一次回调函数,你可以将 immediate 设置为 true。
{ immediate: true }
🍋与Vue2中watch的比较
在Vue2中,watch的使用方式与Vue3有些许不同。Vue2中的watch是一个选项,可以在watch对象中直接定义需要监视的数据和回调函数。而在Vue3中,watch函数更加灵活,可以在任何地方使用,并支持监视多个数据和深层次的数据。
总的来说,Vue3中的watch函数提供了更加灵活和强大的功能,能够更好地满足复杂项目的需求。
🍋总结
通过本文的介绍,我们了解了Vue3中的watch监视功能的基本用法、高级用法以及与Vue2中watch的比较。watch函数是Vue3响应式系统的核心功能之一,能够帮助我们更好地监视数据的变化,并在数据变化时执行相应的操作。下一节接着介绍其他情况~~~
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者



评论(0)