【愚公系列】2023年12月 HarmonyOS教学课程 062-ArkTS语言基础类库(XML)
🏆 作者简介,愚公搬代码
🏆《头衔》:华为云特约编辑,华为云云享专家,华为开发者专家,华为产品云测专家,CSDN博客专家,CSDN商业化专家,阿里云专家博主,阿里云签约作者,腾讯云优秀博主,腾讯云内容共创官,掘金优秀博主,51CTO博客专家等。
🏆《近期荣誉》:2023年华为云十佳博主,2022年CSDN博客之星TOP2,2022年华为云十佳博主等。
🏆《博客内容》:.NET、Java、Python、Go、Node、前端、IOS、Android、鸿蒙、Linux、物联网、网络安全、大数据、人工智能、U3D游戏、小程序等相关领域知识。
🏆🎉欢迎 👍点赞✍评论⭐收藏
🚀前言
数据传输的数据格式有以下几种常见的格式:
-
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation):JSON是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,可读性高且易于解析。它使用键值对的方式表示数据,并且支持多层嵌套。
-
XML(eXtensible Markup Language):XML是一种标记语言,可用于存储和传输结构化数据。它使用标签来定义数据和数据之间的关系。
-
Form Data(表单数据):表单数据是一种常见的数据传输格式,通过HTTP请求中的表单提交进行数据传输,数据以键值对的形式存在。
完整的XML相关知识点可以看这篇文章:https://blog.csdn.net/aa2528877987/article/details/122660175
本文主要讲解HarmonyOS中XML生成、解析、转换。
🚀一、XML
🔎1.概述
XML是可扩展标记语言(eXtensible Markup Language)的缩写。它是一种用于表示和传输结构化数据的标记语言。XML使用自定义的标签来标记数据的各个部分,并使用起始标签和结束标签将数据包裹起来。这种结构化的格式使得数据可以被解析和处理,从而更好地进行数据交换和存储。
与HTML类似,XML也使用尖括号(< >)来定义标签。但与HTML不同,XML标签是自定义的,可以根据需要创建新的标签。XML还支持属性,可以在标签中添加额外的信息。XML数据可以通过解析器解析为可用的对象,如树状结构或文档对象模型(DOM),从而进行进一步的处理和操作。
XML被广泛应用于数据存储、数据交换和Web服务等领域。它是一种通用的、可扩展的标记语言,可以适应不同的数据结构和应用需求。
🔎2.组成
XML文档是由元素、属性和内容组成的。以下是它们的详细解释:
- 元素(element):XML文档的基本构建块,也是文档的结构和数据的组织单元。元素由开始标签和结束标签组成,两者之间包含了元素的内容。例如:
<book>
<title>XML for Beginners</title>
<author>John Doe</author>
</book>
<book>、<title>和<author>都是元素。
- 属性(attribute):元素的附加信息,以名称-值对的形式出现在开始标签中。属性提供有关元素的额外信息。例如:
<book category="fiction">
<title>XML for Beginners</title>
<author>John Doe</author>
</book>
category是book元素的属性,其值为fiction。
- 内容(content):元素中的文本或其他元素。在元素的开始标签和结束标签之间可以包含文本或其他元素。例如:
<book>
<title>XML for Beginners</title>
<author>John Doe</author>
</book>
<title>XML for Beginners</title>和<author>John Doe</author>是book元素的内容。
🔎3.文档结构定义形式
🦋3.1 XML Schema
在XML中使用XML Schema定义结构的方式是使用一个独立的XML Schema文件,该文件定义了你希望XML文档符合的结构规范。
首先,创建一个XML Schema文件,例如"example.xsd"。在该文件中定义你的元素、属性和数据类型。以下是一个示例XML Schema文件的基本结构:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<!-- 在这里定义你的元素、属性和数据类型 -->
</xs:schema>
接下来,在你的XML文档中引用该XML Schema文件,以使XML文档与定义的结构匹配。为此,在XML文档的根元素上添加一个xmlns:xsi属性和xsi:schemaLocation属性。xmlns:xsi属性指定XML命名空间xsi的定义,xsi:schemaLocation属性指定XML Schema文件的位置。
下面是一个示例XML文档的基本结构,引用了上述的XML Schema文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<rootElement xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.example.com example.xsd">
<!-- 在这里编写你的XML文档 -->
</rootElement>
xmlns:xsi属性定义了xsi命名空间,并指定了其定义的位置。xsi:schemaLocation属性指定了XML Schema文件的位置,其中"http://www.example.com"是XML命名空间的URI,"example.xsd"是XML Schema文件的位置。
该XML文档的结构和内容应符合在XML Schema文件中定义的规范。如果XML文档与XML Schema不匹配,解析器将会报告错误。
🦋3.2 DTD
DTD(Document Type Definition)是一种用来定义XML文档结构的语言,它可以定义元素、属性和实体的规则和约束。
<!DOCTYPE bookstore [
<!ELEMENT bookstore (book+)>
<!ELEMENT book (title, author, price)>
<!ELEMENT title (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT author (#PCDATA)>
<!ELEMENT price (#PCDATA)>
<!ATTLIST book id ID #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST book category CDATA #REQUIRED>
]>
<bookstore>
<book category="Children">
<title>Harry Potter</title>
<author>J.K. Rowling</author>
<price>29.99</price>
</book>
<book category="Fiction">
<title>The Catcher in the Rye</title>
<author>J.D. Salinger</author>
<price>19.99</price>
</book>
</bookstore>
通过<!DOCTYPE>声明引用了DTD定义,然后使用<!ELEMENT>定义了元素的结构,<!ATTLIST>定义了元素的属性。
<!ELEMENT bookstore (book+)>定义了bookstore元素必须包含一个或多个book元素。<!ELEMENT book (title, author, price)>定义了book元素包含title、author和price三个子元素。<!ELEMENT title (#PCDATA)>定义了title元素只能包含文本内容。<!ELEMENT author (#PCDATA)>定义了author元素只能包含文本内容。<!ELEMENT price (#PCDATA)>定义了price元素只能包含文本内容。<!ATTLIST book id ID #IMPLIED>定义了book元素有一个可选的id属性,类型为ID。<!ATTLIST book category CDATA #REQUIRED>定义了book元素必须有一个category属性,类型为CDATA。
🔎4.生成
import xml from '@ohos.xml';
import util from '@ohos.util';
// 1.基于Arraybuffer构造XmlSerializer对象
// @ts-ignore
let arrayBuffer = new ArrayBuffer(2048); // 创建一个2048字节的缓冲区
// @ts-ignore
let thatSer = new xml.XmlSerializer(arrayBuffer); // 基于Arraybuffer构造XmlSerializer对象
// 2.基于DataView构造XmlSerializer对象
// @ts-ignore
let arrayBuffer = new ArrayBuffer(2048); // 创建一个2048字节的缓冲区
let dataView = new DataView(arrayBuffer); // 使用DataView对象操作ArrayBuffer对象
// @ts-ignore
let thatSer = new xml.XmlSerializer(dataView); // 基于DataView构造XmlSerializer对象
thatSer.setDeclaration(); // 写入xml的声明
thatSer.startElement('bookstore'); // 写入元素开始标记
thatSer.startElement('book'); // 嵌套元素开始标记
thatSer.setAttributes('category', 'COOKING'); // 写入属性及属性值
thatSer.startElement('title');
thatSer.setAttributes('lang', 'en');
thatSer.setText('Everyday'); // 写入标签值
thatSer.endElement(); // 写入结束标记
thatSer.startElement('author');
thatSer.setText('Giada');
thatSer.endElement();
thatSer.startElement('year');
thatSer.setText('2005');
thatSer.endElement();
thatSer.endElement();
thatSer.endElement();
let view = new Uint8Array(arrayBuffer); // 使用Uint8Array读取arrayBuffer的数据
let textDecoder = util.TextDecoder.create(); // 调用util模块的TextDecoder类
let res = textDecoder.decodeWithStream(view); // 对view解码
console.info(res);
得到结果
<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"utf-8\"?>
<bookstore>\r\n
<book category=\"COOKING\">\r\n
<title lang=\"en\">Everyday</title>\r\n
<author>Giada</author>\r\n
<year>2005</year>\r\n
</book>\r\n
</bookstore>
🔎5.解析
🦋5.1 解析XML标签和标签值
import xml from '@ohos.xml';
import util from '@ohos.util'; // 需要使用util模块函数对文件编码
let strXml =
'<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>' +
'<note importance="high" logged="true">' +
'<title>Play</title>' +
'<lens>Work</lens>' +
'</note>';
let textEncoder = new util.TextEncoder();
let arrBuffer = textEncoder.encodeInto(strXml); // 对数据编码,防止包含中文字符乱码
// 1.基于ArrayBuffer构造XmlPullParser对象
let that = new xml.XmlPullParser(arrBuffer.buffer, 'UTF-8');
// // 2.基于DataView构造XmlPullParser对象
// let dataView = new DataView(arrBuffer.buffer);
// let that = new xml.XmlPullParser(dataView, 'UTF-8');
let str = '';
function func(name, value){
str = name + value;
console.info(str);
return true; //true:继续解析 false:停止解析
}
let options = {supportDoctype:true, ignoreNameSpace:true, tagValueCallbackFunction:func};
that.parse(options);
得到结果
note
title
Play
title
lens
Work
lens
note
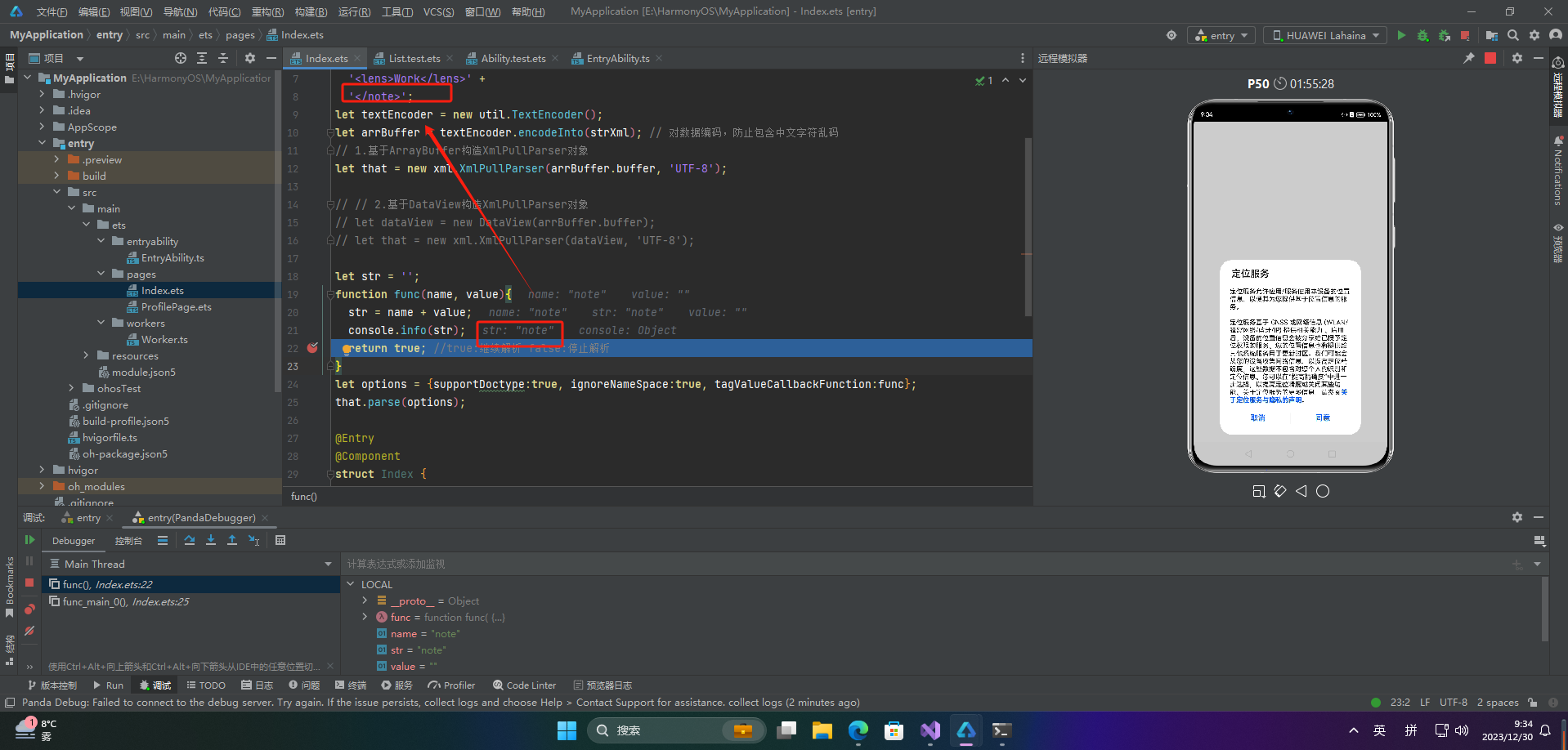
🦋5.2 解析XML属性和属性值
import xml from '@ohos.xml';
import util from '@ohos.util'; // 需要使用util模块函数对文件编码
let strXml =
'<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>' +
'<note importance="high" logged="true">' +
' <title>Play</title>' +
' <title>Happy</title>' +
' <lens>Work</lens>' +
'</note>';
let textEncoder = new util.TextEncoder();
let arrBuffer = textEncoder.encodeInto(strXml); // 对数据编码,防止包含中文字符乱码
let that = new xml.XmlPullParser(arrBuffer.buffer, 'UTF-8');
let str = '';
function func(name, value){
str += name + ' ' + value + ' ';
return true; // true:继续解析 false:停止解析
}
let options = {supportDoctype:true, ignoreNameSpace:true, attributeValueCallbackFunction:func};
that.parse(options);
console.info(str); // 一次打印出所有的属性及其值
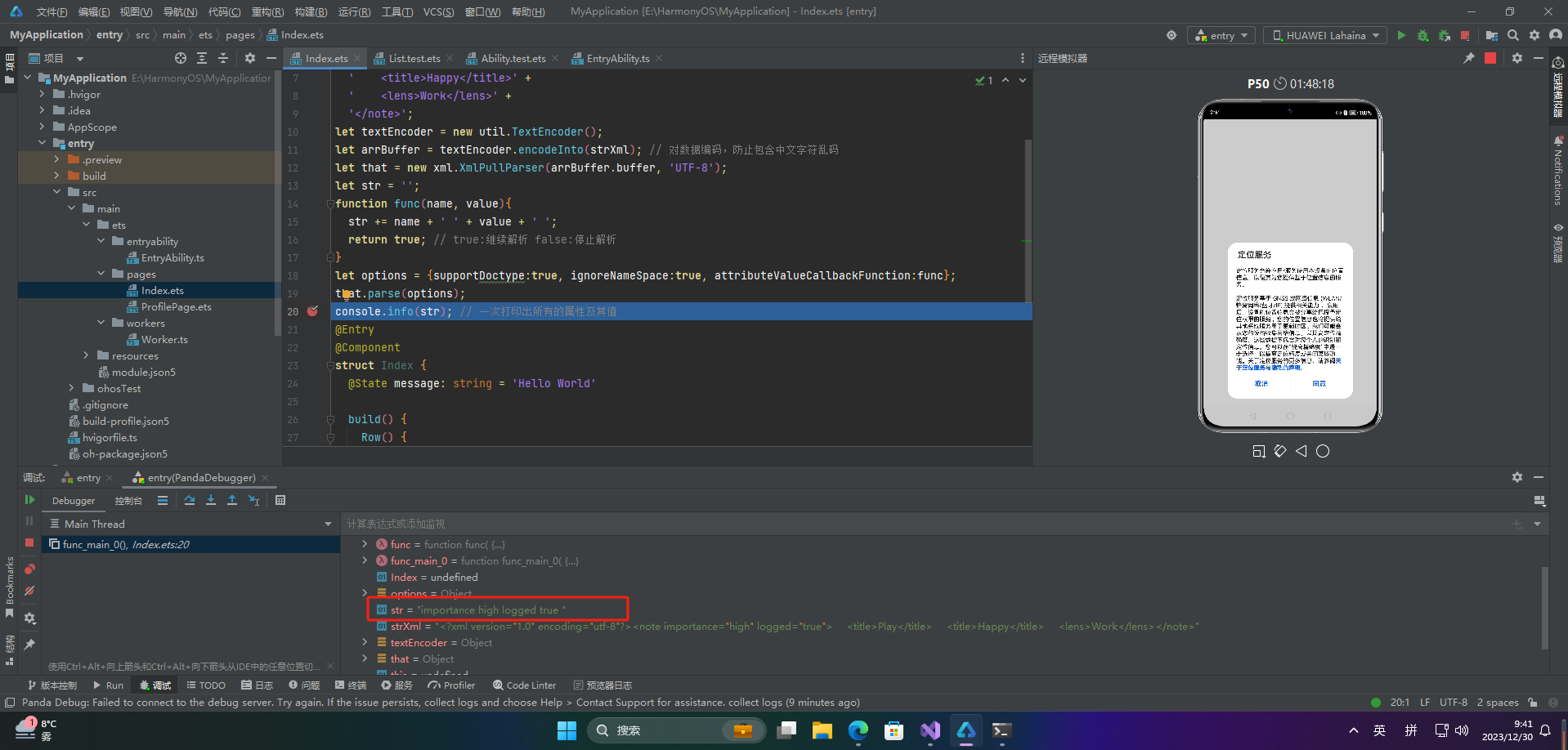
🦋5.3 解析XML事件类型和元素深度
import xml from '@ohos.xml';
import util from '@ohos.util'; // 需要使用util模块函数对文件编码
let strXml =
'<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>' +
'<note importance="high" logged="true">' +
'<title>Play</title>' +
'</note>';
let textEncoder = new util.TextEncoder();
let arrBuffer = textEncoder.encodeInto(strXml); // 对数据编码,防止包含中文字符乱码
let that = new xml.XmlPullParser(arrBuffer.buffer, 'UTF-8');
let str = '';
function func(name, value){
str = name + ' ' + value.getDepth(); // getDepth 获取元素的当前深度
console.info(str)
return true; //true:继续解析 false:停止解析
}
let options = {supportDoctype:true, ignoreNameSpace:true, tokenValueCallbackFunction:func};
that.parse(options);
console.info(str); // 一次打印出所有的属性及其值
得到结果
0 0 // 0:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 对应事件类型START_DOCUMENT值为0 0:起始深度为0
2 1 // 2:<note importance="high" logged="true"> 对应事件类型START_TAG值为2 1:深度为1
2 2 // 2:<title>对应事件类型START_TAG值为2 2:深度为2
4 2 // 4:Play对应事件类型TEXT值为4 2:深度为2
3 2 // 3:</title>对应事件类型END_TAG值为3 2:深度为2
3 1 // 3:</note>对应事件类型END_TAG值为3 1:深度为1(与<note对应>)
1 0 // 1:对应事件类型END_DOCUMENT值为1 0:深度为0
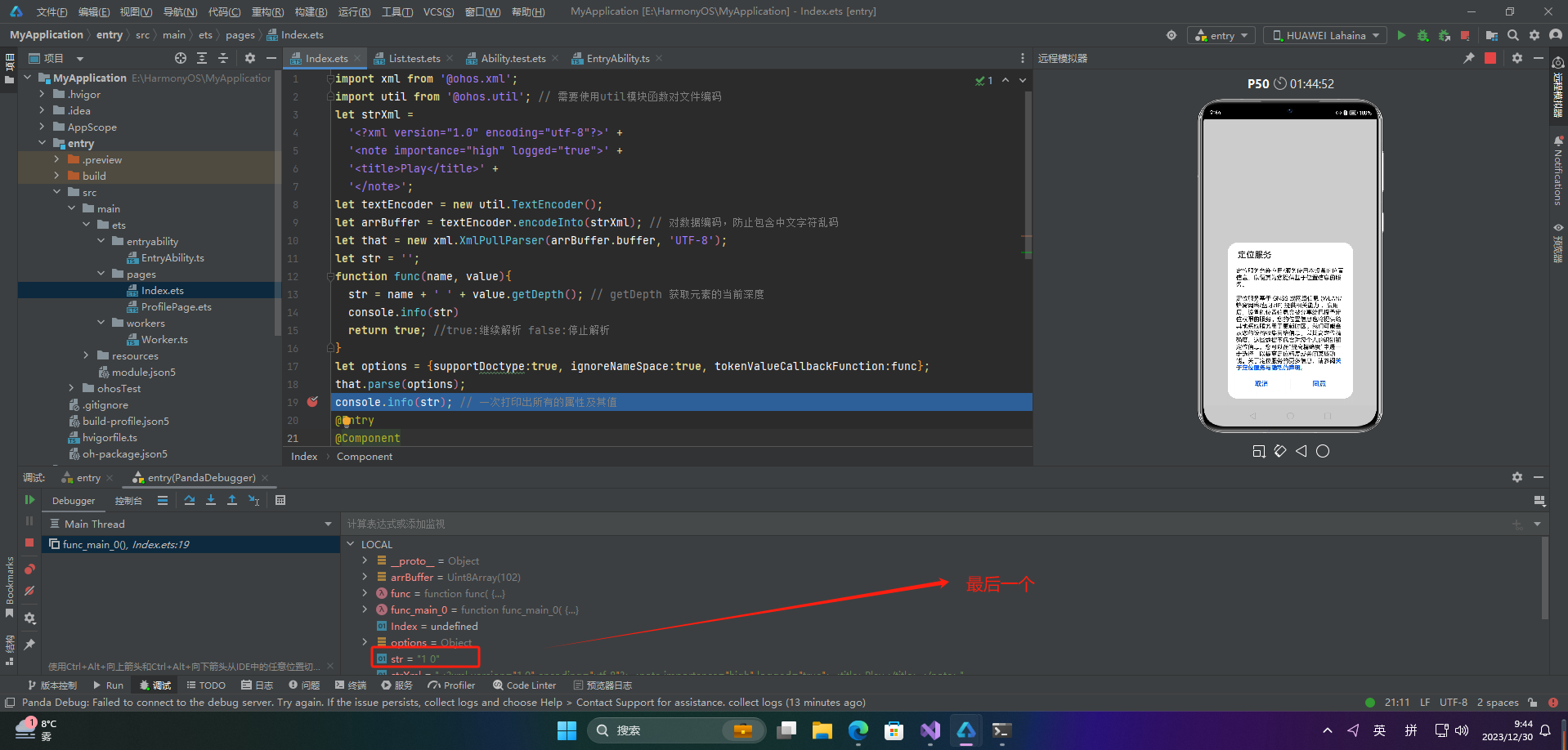
🦋5.4 场景示例
import xml from '@ohos.xml';
import util from '@ohos.util';
let strXml =
'<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>' +
'<book category="COOKING">' +
'<title lang="en">Everyday</title>' +
'<author>Giada</author>' +
'</book>';
let textEncoder = new util.TextEncoder();
let arrBuffer = textEncoder.encodeInto(strXml);
let that = new xml.XmlPullParser(arrBuffer.buffer, 'UTF-8');
let str = '';
function tagFunc(name, value) {
str = name + value;
console.info('tag-' + str);
return true;
}
function attFunc(name, value) {
str = name + ' ' + value;
console.info('attri-' + str);
return true;
}
function tokenFunc(name, value) {
str = name + ' ' + value.getDepth();
console.info('token-' + str);
return true;
}
let options = {
supportDocType: true,
ignoreNameSpace: true,
tagValueCallbackFunction: tagFunc,
attributeValueCallbackFunction: attFunc,
tokenValueCallbackFunction: tokenFunc
};
that.parse(options);
得到结果
tag-
token-0 0
tag-book
attri-category COOKING
token-2 1
tag-title
attri-lang en
token-2 2
tag-Everyday
token-4 2
tag-title
token-3 2
tag-author
token-2 2
tag-Giada
token-4 2
tag-author
token-3 2
tag-book
token-3 1
tag-
token-1 0
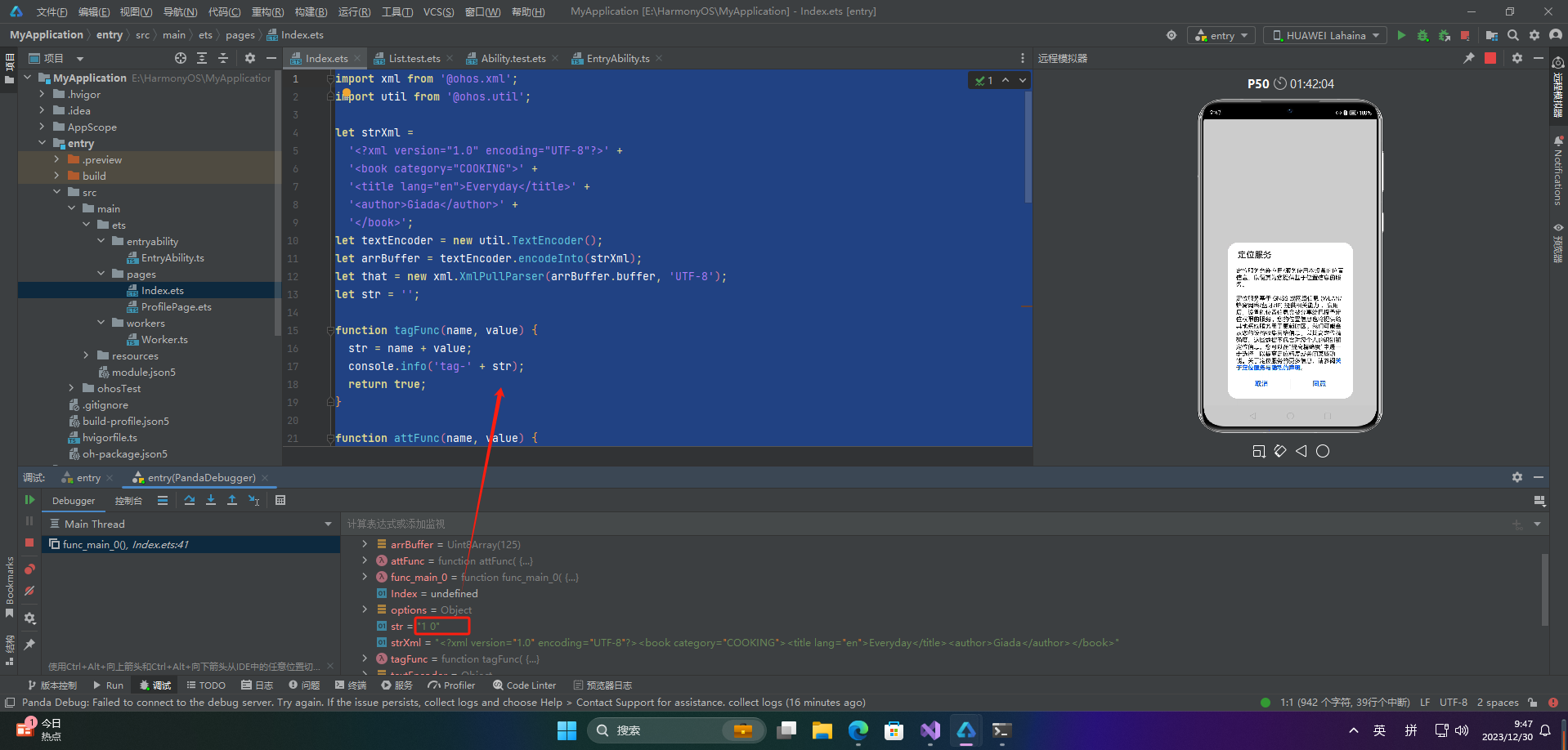
🔎6.转换
import convertxml from '@ohos.convertxml';
let xml =
'<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>' +
'<note importance="high" logged="true">' +
' <title>Happy</title>' +
' <todo>Work</todo>' +
' <todo>Play</todo>' +
'</note>';
let options = {
// trim: false 转换后是否删除文本前后的空格,否
// declarationKey: "_declaration" 转换后文件声明使用_declaration来标识
// instructionKey: "_instruction" 转换后指令使用_instruction标识
// attributesKey: "_attributes" 转换后属性使用_attributes标识
// textKey: "_text" 转换后标签值使用_text标识
// cdataKey: "_cdata" 转换后未解析数据使用_cdata标识
// docTypeKey: "_doctype" 转换后文档类型使用_doctype标识
// commentKey: "_comment" 转换后注释使用_comment标识
// parentKey: "_parent" 转换后父类使用_parent标识
// typeKey: "_type" 转换后元素类型使用_type标识
// nameKey: "_name" 转换后标签名称使用_name标识
// elementsKey: "_elements" 转换后元素使用_elements标识
trim: false, declarationKey: "_declaration",
instructionKey: "_instruction", attributesKey: "_attributes",
textKey: "_text", cdataKey: "_cdata", doctypeKey: "_doctype",
commentKey: "_comment", parentKey: "_parent", typeKey: "_type",
nameKey: "_name", elementsKey: "_elements"
}
let conv = new convertxml.ConvertXML();
let result = conv.convertToJSObject(xml, options);
let strRes = JSON.stringify(result); // 将js对象转换为json字符串,用于显式输出
console.info(strRes);
// 也可以直接处理转换后的JS对象,获取标签值
let title = result['_elements'][0]['_elements'][0]['_elements'][0]['_text']; // 解析<title>标签对应的值
let todo = result['_elements'][0]['_elements'][1]['_elements'][0]['_text']; // 解析<todo>标签对应的值
let todo2 = result['_elements'][0]['_elements'][2]['_elements'][0]['_text']; // 解析<todo>标签对应的值
console.info(title); // Happy
console.info(todo); // Work
console.info(todo2); // Play
🚀感谢:给读者的一封信
亲爱的读者,
我在这篇文章中投入了大量的心血和时间,希望为您提供有价值的内容。这篇文章包含了深入的研究和个人经验,我相信这些信息对您非常有帮助。
如果您觉得这篇文章对您有所帮助,我诚恳地请求您考虑赞赏1元钱的支持。这个金额不会对您的财务状况造成负担,但它会对我继续创作高质量的内容产生积极的影响。
我之所以写这篇文章,是因为我热爱分享有用的知识和见解。您的支持将帮助我继续这个使命,也鼓励我花更多的时间和精力创作更多有价值的内容。
如果您愿意支持我的创作,请扫描下面二维码,您的支持将不胜感激。同时,如果您有任何反馈或建议,也欢迎与我分享。

再次感谢您的阅读和支持!
最诚挚的问候, “愚公搬代码”
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)