Springboot之---强大的Servlet(一)
If I have seen further, it is by standing on the shoulders of giants
如果我比别人看得更远,那是因为我站在巨人的肩膀上
如今回头看下Servlet不仅如此强大,还具有很强烈的参考意义,能在现如今流行的大部分框架中找到它的影子。下面文章不止与探索Servlet,可能在其中穿插其他的关联知识点,旨在能从此次的学习中获取更多的知识点参考资料总结,转化为自己的理解输出,在文中我尽量以截图+复制全限定类名的方式记录,以便感兴趣的再次查找。
Springboot与Servlet
在springboot中内嵌了Tomcat容器,而Tomcat又是Servlet的容器,Springboot就与Servlet产生了紧密的联系。
在分析各个类时,注意下每个类所在的包是如何在tomcat与boot之间跨越的~
生命周期
1、初始化
2、处理请求
3、销毁
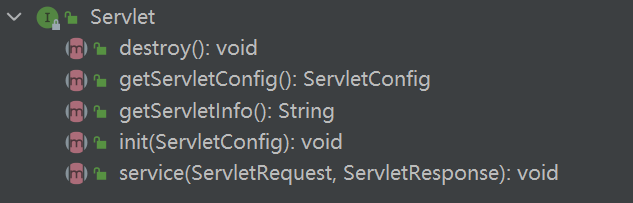
应用上下文ServletContext
应用上下文即可看做:一次请求到达,到响应结束的过程中间的catlog,即阅读中结合上下文语境,是一个广义定义。
为什么说到上下文呢?来看下ServletContext的实现,第一个经典实现既是ApplicationContext我们不止在一次源码和应用中见到它,另外加载器目前有两种选择:ContextLoaderListener和ContextLoaderServlet。其功能是完全相同。会在下文进行介绍
/**
* Standard implementation of <code>ServletContext</code> that represents
* a web application's execution environment. An instance of this class is
* associated with each instance of <code>StandardContext</code>.
* 代表web应用程序的执行环境。这个类的一个实例是
*与StandardContext的每个实例关联。
* @author Craig R. McClanahan
* @author Remy Maucherat
*/
public class ApplicationContext implements ServletContext {
protected static final boolean STRICT_SERVLET_COMPLIANCE;///翻译为是否严格遵守
protected static final boolean GET_RESOURCE_REQUIRE_SLASH;//获取资源是否需要斜线。
static {
STRICT_SERVLET_COMPLIANCE = Globals.STRICT_SERVLET_COMPLIANCE;
String requireSlash = System.getProperty("org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationContext.GET_RESOURCE_REQUIRE_SLASH");
if (requireSlash == null) {
GET_RESOURCE_REQUIRE_SLASH = STRICT_SERVLET_COMPLIANCE;
} else {
GET_RESOURCE_REQUIRE_SLASH = Boolean.parseBoolean(requireSlash);
}
}
注:特别重要上述配置为tomcat中第一个开关配置,决定多个属性的值。来自于下面的Globals.STRICT_SERVLET_COMPLIANCE;默认为false
验证:
public static final boolean STRICT_SERVLET_COMPLIANCE =Boolean.parseBoolean(System.getProperty("org.apache.catalina.STRICT_SERVLET_COMPLIANCE", "false"));
和官网截图
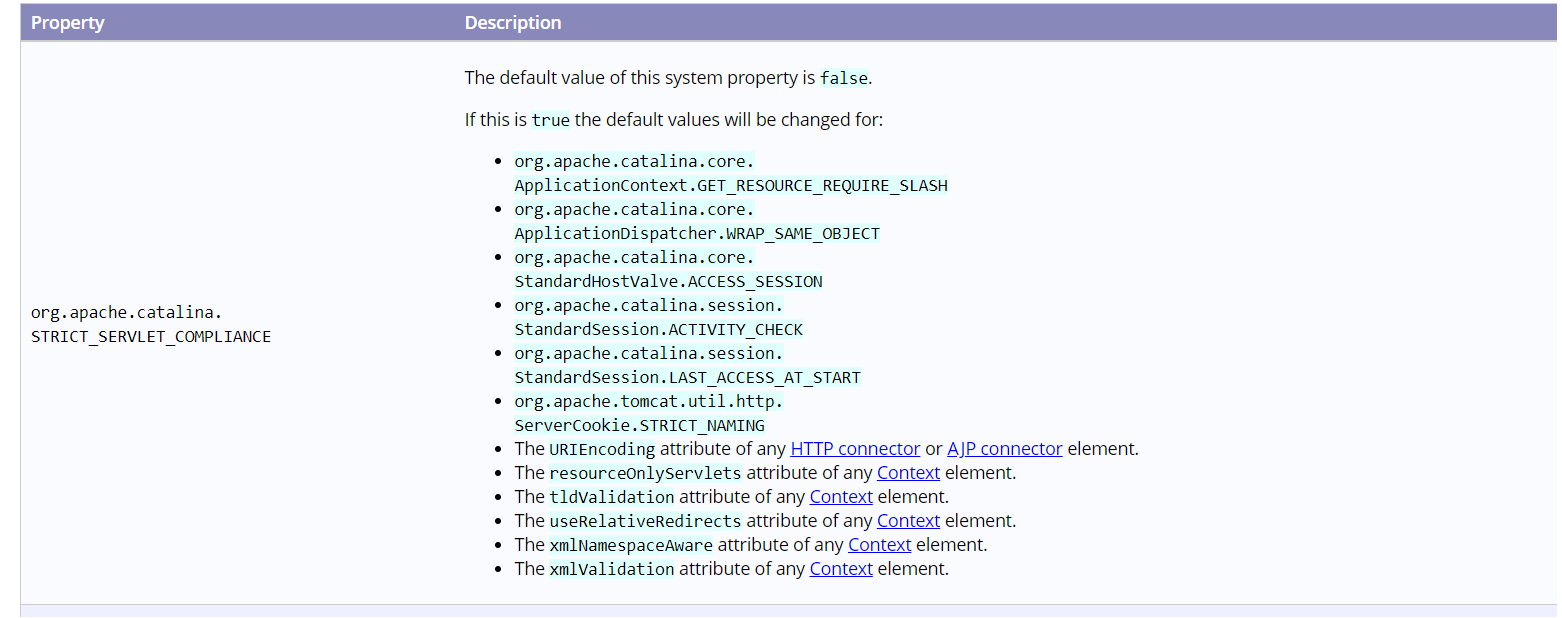
问题:会因为tomcat的版本配置不同改变此值,在8.5.57当中会改变为true,当controller中配置多个映射路径会出现访问不到的问题
此处参考博文:https://blog.csdn.net/xing930408/article/details/111225064
Tomcat文档:https://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-8.5-doc/config/systemprops.html
而GET_RESOURCE_REQUIRE_SLASH直接赋值为STRICT_SERVLET_COMPLIANCE
SpringBoot ApplicationContext
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver
都在说ApplicationContext衍生了BeanFactory那么对此都扩展了那些功能?ApplicationContext定了高级容器的基本规范,其实他也不是直接继承BeanFactory基础容器,可以看到ApplicationContext的直接父接口对BeanFactory进行很多拓展其中就包括:
1.事件的注册和发布
2.消息解析
3.资源解析
4.Bean工厂层级管理
5.监听器
6.容器环境
通过以上拓展,我们基本可以知道高级IOC容器有哪些特点,这也是学习整个ApplicationContext容器重点了解的部分
再比较ApplicationContext和ConfigurableApplicationContext定义的方法以及下图层级关系,ConfigurableApplicationContext是ApplicationContext的子接口,也就包含了ApplicationContext。通过方法可以知道,ConfigurableApplicationContext重在对各种属性的配置,而ApplicationContext接口主要各种属性的get方法。
Spring这种将get和set分开到两个接口的设计增大了属性设置和获取的灵活性,将两者分开也更加清晰。在以后的解决方案设计中,可以参考,将配置信息和获取信息分开,两者互不干扰,在保证重要的基础属性不变的情况,可以按需进行拓展。其实Spring的框架设计中应用了大量的装饰者模式,这也是高拓展点的需要
该类提供了高级IOC规范
其中有几个注意点:
从ListableBeanFactory接口继承来的:用于访问应用组件的工厂方法
从ResourceLoader接口继承来的:用通用的方式加载文件资源
从ApplicationEventPublisher接口继承来的:注册和发布事件
从MessageSource接口继承来的:处理消息,支持国际化
从父应用上下文定义的在子上下文中将始终保持优先
https://www.javaguides.net/2019/10/how-to-get-application-context-in-spring-boot.html
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,
MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
/**
* 返回一个唯一的应用上下文id+
* @return the unique id of the context, or {@code null} if none
*/
@Nullable
String getId();
/**
* 返回已经部署的该应用上下文的名称.
* @return a name for the deployed application, or the empty String by default
*/
String getApplicationName();
/**
* 返回此上下文友好的名称---这有什么用呢?
* @return a display name for this context (never {@code null})
*/
String getDisplayName();
/**
* 返回该上下文第一次被加载的时间戳
* @return the timestamp (ms) when this context was first loaded
*/
long getStartupDate();
/**
*返回父应用上下文, 如果没有父上下文,该上下文就是在上下文层次的根
* @return the parent context, or {@code null} if there is no parent
*/
@Nullable
ApplicationContext getParent();
AutowireCapableBeanFactory getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
}
这其中对AutowireCapableBeanFactory getAutowireCapableBeanFactory()方法有疑惑,然后网上百度了一下。Spring提供了一种机制,能够为第三方框架赋能,让Spring去管理的Bean去装配和填充那些没有被SpringIOC管理的bean。也就是Spring提供了使用第三方框架的能力,能够做到无缝的将第三方框架整合到Spring中来进行使用,Junit与Quartz借用了这种机制为自己赋能。
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「还你一梦」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/ligel136738/article/details/113533132
AutowireCapableBeanFactory
package org.springframework.beans.factory.config;
import java.util.Set;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.TypeConverter;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
public interface AutowireCapableBeanFactory extends BeanFactory {
int AUTOWIRE_NO = 0;
int AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME = 1;
int AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE = 2;
int AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR = 3;
@Deprecated
int AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT = 4;
String ORIGINAL_INSTANCE_SUFFIX = ".ORIGINAL";
<T> T createBean(Class<T> beanClass) throws BeansException;
void autowireBean(Object existingBean) throws BeansException;
Object configureBean(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
Object createBean(Class<?> beanClass, int autowireMode, boolean dependencyCheck) throws BeansException;
Object autowire(Class<?> beanClass, int autowireMode, boolean dependencyCheck) throws BeansException;
void autowireBeanProperties(Object existingBean, int autowireMode, boolean dependencyCheck)
throws BeansException;
void applyBeanPropertyValues(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
Object initializeBean(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException;
Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException;
void destroyBean(Object existingBean);
<T> NamedBeanHolder<T> resolveNamedBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
@Nullable
Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String requestingBeanName) throws BeansException;
@Nullable
Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String requestingBeanName,
@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException;
}
在ApplacationContext中并没有实现此工厂接口,如上文可见,是在初始化Spring管理Bean之外的实例时直接调用getAutowireCapableBeanFactory方法
AutowireCapableBeanFactory定义了5种装配策略:
不自动注入:AUTOWIRE_NO
使用BeanName策略注入:AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME
使用类型装配策略:AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE
使用构造器装配策略:AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR
自动装配策略:AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT
以AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory为例,其实现如下
@@Override
public void autowireBean(Object existingBean) {
//使用非单例bean定义,以避免将bean注册为依赖bean
// Use non-singleton bean definition, to avoid registering bean as dependent bean.
RootBeanDefinition bd = new RootBeanDefinition(ClassUtils.getUserClass(existingBean));
Bean的作用域
bd.setScope(BeanDefinition.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE);
检查给定类在给定上下文中是否是缓存安全的,
即它是由给定类加载器加载还是由其父级加载。类加载器
bd.allowCaching = ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(bd.getBeanClass(), getBeanClassLoader());
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(existingBean);
初始化BeanRapper并创建
initBeanWrapper(bw);
实际上该方法的逻辑主要是在populateBean中。这个方法是Spring中一个重要的方法。用于装配Bean。主要是通过反射获取到我们new出来的对象的属性及注解,若是注解时Autowired、Value、Inject时,进行Bean组装。此方法执行完毕,我们new出来的方法就可以通过注解注入的bean进行操作了
作者:小胖学编程
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/14dd69b5c516
来源:简书
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
populateBean(bd.getBeanClass().getName(), bd, bw);
}
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)