蓝桥杯-卡片换位
@toc
1、题目描述
你玩过华容道的游戏吗?
这是个类似的,但更简单的游戏。
看下面 3 x 2 的格子
±–±--±–+
| A | * | * |
±–±--±–+
| B | | * |
±–±--±–+
在其中放 5 张牌,其中 A 代表关羽,B 代表张飞,* 代表士兵。
还有个格子是空着的。
你可以把一张牌移动到相邻的空格中去(对角不算相邻)。
游戏的目标是:关羽和张飞交换位置,其它的牌随便在哪里都可以。
输入描述
输入两行 6 个字符表示当前的局面
输出描述
一个整数,表示最少多少步,才能把 A B 换位(其它牌位置随意)
输入输出样例
示例
输入
* A
**B
输出
17
运行限制
- 最大运行时间:1s
- 最大运行内存: 256M
2、解题思路
我们首先获取开始时候A、B和空格的位置,我们从空格所在的位置开始向四个方向扩展,这里由于给定了2行3列共6个位置,其实扩展的次数也不是特别多,不过每次扩展的时候都需要判断扩展节点是否越界。
使用队列实现,开始的时候将空格所在的位置入队列,然后向四周扩展。
每扩展到一个位置,我们需要将当前的空格节点与扩展节点所在位置上的数据进行互换,然后我们标记当前的地图,这里我用一个Node类存储当前的地图:包括当前空格所在位置 ,当前的字符串,当前总共移动了多少次。
class Node{
int curX; //当前空格所在位置
int curY;
String currStr; //当前的字符串(地图情景)
int curStep; //当前移动了多少步
public Node() {
}
public Node(int curX, int curY, String currStr, int curStep) {
this.curX = curX;
this.curY = curY;
this.currStr = currStr;
this.curStep = curStep;
}
}
这里我们将两行拼接在一起,当作一个字符串就行,至于怎样从现在的字符串还原出原来二维数组的坐标,那也很简单,假设当前的空格位置为
pos,我们将其还原成二维数组中的位置如下:
我们每移动一次,我们都要检查当前的地图是否已经走过了,如果相同,则这个方向不行,换个方向搜索。否则,我们用Set集合存储当前的地图,然后将扩展后这个新节点加入队列中继续搜索。
我们定义扩展的四个方向如下:
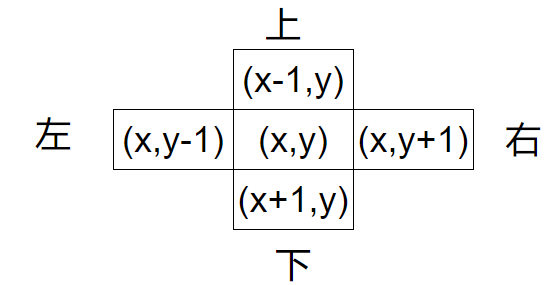
//定义方向
public static int[][] dirs={
{0,1}, //右
{1,0}, //下
{0,-1}, //左
{-1,0} //上
};
每次扩展到一个新的结点时候,我们都需要判断A和B是否已经换过位置了,如果换过位置,则搜索结束。
3、完整代码(AC)
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class Main1 {
//定义方向
public static int[][] dirs={
{0,1}, //右
{1,0}, //下
{0,-1}, //左
{-1,0} //上
};
public static String str1;
public static String str2;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
str1 = br.readLine();
str2 = br.readLine();
String str = str1.concat(str2);
bfs(str);
br.close();
}
public static void bfs(String str){
LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();//存放当前的一些数据(空格的位置、地图、步数)
HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>(); //判断当前的地图是否已经存在过了
//初始数据准备
int pos = str.indexOf(' ');//找到空格位置
//pos/3为原先二维中的行坐标,pos%3是列坐标
Node node = new Node(pos / 3, pos % 3, str, 0);
//标记A和B的位置
int posA = str.indexOf('A');
int posB = str.indexOf('B');
queue.offer(node); //入队
set.add(node.currStr);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
Node curr = queue.poll();
for (int[] dir : dirs) { //开始向四个方向扩展
int x = curr.curX + dir[0];
int y = curr.curY + dir[1];
if(x<0||x>1||y<0||y>2){ //判断是否越界
continue;
}
String tempStr = curr.currStr;
//空格和相邻位置交换,产生新的地图 (两个位置互换)
char[] tempChar = tempStr.toCharArray();
tempChar[curr.curX*3+curr.curY]=tempStr.charAt(x*3+y);
tempChar[x*3+y]=tempStr.charAt(curr.curX*3+curr.curY);
String s=new String(tempChar);
//当前最新生成的数据
Node tmp = new Node(x,y, s, curr.curStep + 1);
if(s.charAt(posA)=='B'&&s.charAt(posB)=='A'){
System.out.println(tmp.curStep);
return;
}
//判断这个地图是否重复
if(!set.contains(tmp.currStr)){
set.add(tmp.currStr);
queue.offer(tmp);
}
}
}
}
}
class Node{
int curX; //当前空格所在位置
int curY;
String currStr; //当前的字符串(地图情景)
int curStep; //当前移动了多少步
public Node() {
}
public Node(int curX, int curY, String currStr, int curStep) {
this.curX = curX;
this.curY = curY;
this.currStr = currStr;
this.curStep = curStep;
}
}
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)