ModelBox开发指南-YOLOv7来了
ModelBox开发指南-YOLOv7来了
一个活泼的YOLOv7模型转换与技能开发指南。
YOLO系列新鲜出炉的目标检测器YOLOv7据说“surpasses all known object detectors in both speed and accuracy in the range from 5 FPS to 160 FPS ”:

其中,为边缘GPU设计的YOLOv7-Tiny在V100上达到了286FPS,本边缘AI爱好者立刻一个仰卧起坐,决定在ModelBox上测试一下。如果对ModelBox AI应用开发还不熟悉,请先阅读ModelBox 端云协同AI开发套件(RK3568)上手指南,或ModelBox 端云协同AI开发套件(博时特EC02)上手指南,或ModelBox 端云协同AI开发套件(Windows)上手指南。
直接使用工程
这个应用对应的ModelBox版本已经做成模板放在华为云OBS中,在Windows及开发套件中都可以用sdk中的solution工具下载,如果只是使用此工程不关注开发细节,则可以只阅读本章。接下来我们给出该应用在ModelBox中的完整开发过程(以开发套件为例):
1)下载模板
在sdk目录下执行./solution.py -l可看到当前公开的技能模板:
rock@rock-3a:~/███/modelbox$ ./solution.py -l
...
Solutions name:
mask_det_yolo3
...
surpass_detection_yolov7
结果中的surpass_detection_yolov7即为本应用模板,可使用如下命令下载模板:
rock@rock-3a:~/███/modelbox$ ./solution.py -s surpass_detection_yolov7
...
solution脚本的参数中,-l代表list,即列出当前已有的模板名称;-s代表solution-name,即下载对应名称的模板。下载下来的模板资源,将存放在ModelBox核心库的solution目录下。
2)创建工程
在ModelBox sdk目录下使用create.py创建surpass_detection_yolov7工程:
rock@rock-3a:~/███/modelbox$ ./create.py -t server -n surpass_detection_yolov7 -s surpass_detection_yolov7
sdk version is modelbox-xxx
success: create surpass_detection_yolov7 in ███/modelbox/workspace
create脚本的参数中,-t表示创建事务的类别,包括工程(server)、Python功能单元(Python)、推理功能单元(infer)等;-n代表name,即创建事务的名称;-s代表solution-name,表示将使用后面参数值代表的模板创建工程,而不是创建空的工程。
workspace目录下将创建出surpass_detection_yolov7工程,工程目录如下:
surpass_detection_yolov7
├─data
│ ├─car_test_video.mp4 // 测试视频
│ └─classes.txt // 类别标签
├─etc
│ └─flowunit // 功能单元目录
│ ├─surpass_pre // 检测预处理功能单元
│ │ ├─surpass_pre.py
│ │ └─surpass_pre.toml
│ └─surpass_post // 检测后处理功能单元
│ ├─surpass_post.py
│ └─surpass_post.toml
├─graph
│ └─surpass_detection_yolov7.toml // 默认技能流程图,使用测试视频运行
├─model
│ └─surpass
│ ├─surpass.toml // 推理单元配置文件
│ └─yolov7-tiny.onnx // 推理模型
└─build_project.sh
3)运行项目
进入项目目录后执行main脚本:
rock@rock-3a:~/███/modelbox/workspace/surpass_detection_yolov7$ ./bin/main.sh
...
运行结束后在hilens_data_dir目录下生成了result.mp4结果文件与性能评估结果文件夹mb_profile:
可以查看运行结果:
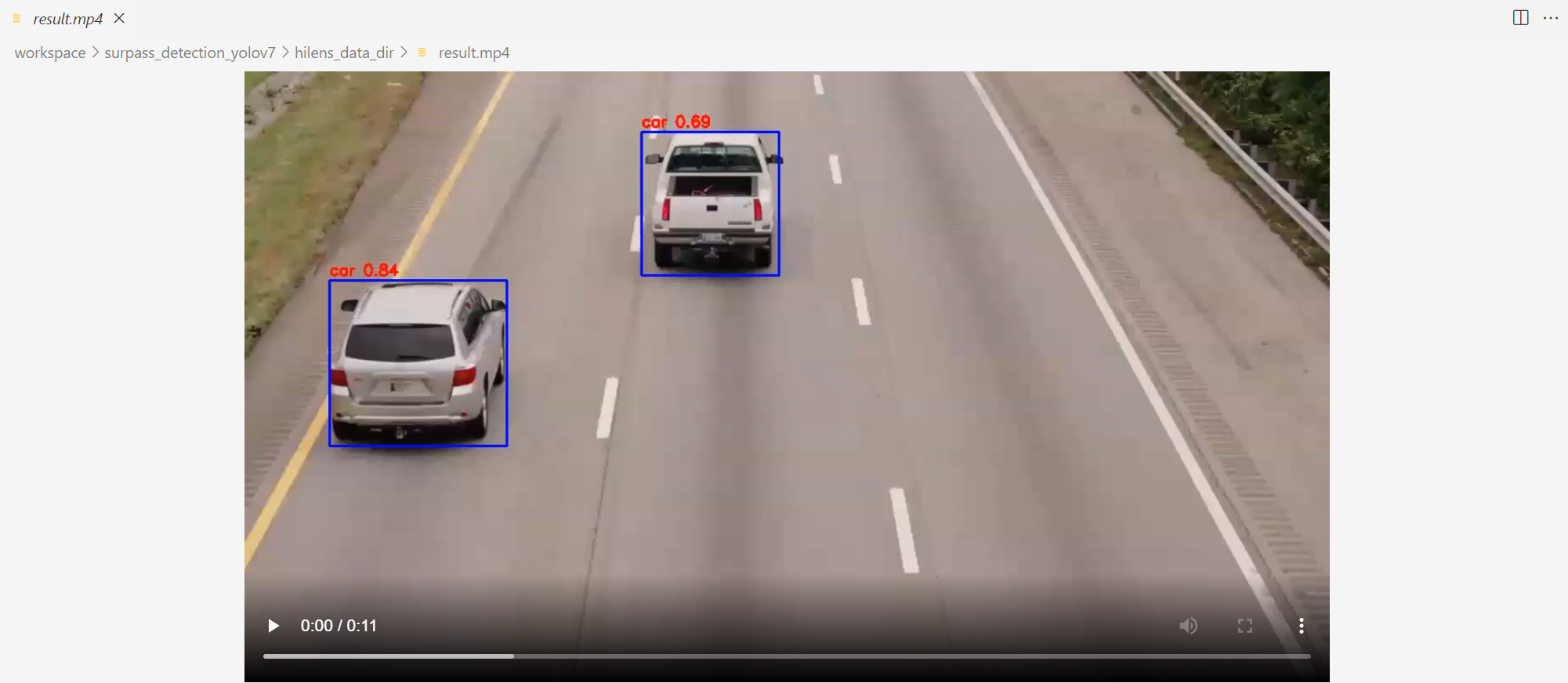
从零开发工程
如果你对项目开发过程感兴趣,可以通过本章进行进一步了解。
模型准备
众所周知,边缘技能开发第一步是模型转换。YOLOv7官方代码仓中很体贴的准备了Pytorch到onnx的模型导出脚本export.py,对于预训练模型为了与yolo系列模型保持后处理统一,我们在模型转换时稍微修改模型文件,修改models/yolo.py Detect类:
class Detect(nn.Module):
stride = None # strides computed during build
export = False # onnx export
end2end = False
include_nms = False
def __init__(self, nc=80, anchors=(), ch=()): # detection layer
super(Detect, self).__init__()
self.nc = nc # number of classes
self.no = nc + 5 # number of outputs per anchor
self.nl = len(anchors) # number of detection layers
self.na = len(anchors[0]) // 2 # number of anchors
self.grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init grid
a = torch.tensor(anchors).float().view(self.nl, -1, 2)
self.register_buffer('anchors', a) # shape(nl,na,2)
self.register_buffer('anchor_grid', a.clone().view(self.nl, 1, -1, 1, 1, 2)) # shape(nl,1,na,1,1,2)
self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, self.no * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv
def forward(self, x):
for i in range(self.nl):
x[i] = self.m[i](x[i])
return x
调用export.py脚本导出onnx模型:
python export.py --weights yolov7-tiny.pt --img-size [320,320]
如果你并不是使用预训练模型而是使用自己训练的模型,可以直接导出模型,重写后处理功能单元。如果想复用本项目后处理功能单元,需要查看训练配置文件(如YOLOv7/cfg/training/yolov7-tiny.yaml),按照上述方式修改对应输出层(如IDetect)forward/fushforward函数,删除后处理部分,只保留卷积层再导出模型。
得到onnx模型后只需参考我们RK3568模型转换验证案例第二部分即可得到rknn模型。当然在我们的资源包中包含了转换好的模型,如果对模型转换的部分不感兴趣,可以迈着优雅的步伐前往下一节。
应用开发
使用 VS Code 连接到ModelBox SDK所在目录或者远程开发板进行应用开发。
创建工程
在SDK目录下使用create.py脚本创建工程,我决定为工程取名为surpass_detection:
rock@rock-3a:~/███$ ./create.py -t server -n surpass_detection
sdk version is modelbox-rk-aarch64-1.0.9.1
success: create surpass_detection in /home/rock/███/workspace
dos2unix: converting file /home/rock/███/workspace/surpass_detection/graph/modelbox.conf to Unix format...
dos2unix: converting file /home/rock/███/workspace/surpass_detection/graph/surpass_detection.toml to Unix format...
dos2unix: converting file /home/rock/███/workspace/surpass_detection/bin/mock_task.toml to Unix format...
build success: you can run main.sh in ./bin folder
ok,创建工程一小步,人类一大步。
创建推理功能单元
依然是万能的create.py脚本:
rock@rock-3a:~/███$ ./create.py -t infer -n surpass -p surpass_detection
sdk version is modelbox-rk-aarch64-1.0.9.1
success: create infer surpass in /home/rock/███/workspace/surpass_detection/model/surpass
可以看到推理功能单元创建在了项目工程的model目录下面:
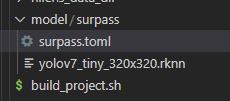
将我们转换好的模型yolov7_tiny_320x320.rknn拖到surpass目录下,接着编辑.toml配置文件,主要修改模型路径与输入输出,由于我们的模型有一个来自cpu的uint8类型输入与三个float类型的输出,所以对配置文件编辑如下:
# Copyright (C) 2020 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
[base]
name = "surpass"
device = "rknpu"
version = "1.0.0"
description = "your description"
entry = "./yolov7_tiny_320x320.rknn" # model file path, use relative path
type = "inference"
virtual_type = "rknpu2" # inference engine type: rockchip now support rknpu, rknpu2(if exist)
group_type = "Inference" # flowunit group attribution, do not change
is_input_contiguous = "false" # rk do not support memory combine, fix, do not change
[input]
[input.input1]
name = "input"
type = "uint8"
device = "cpu"
[output]
[output.output1]
name = "output1"
type = "float"
[output.output2]
name = "output2"
type = "float"
[output.output3]
name = "output3"
type = "float"
创建前后处理功能单元
我们需要一个推理前处理功能单元来实现letterbox功能,一个后处理功能单元来对模型推理结果进行解码,所以首先创建两个功能单元。
rock@rock-3a:~/███$ ./create.py -t python -n surpass_pre -p surpass_detection
sdk version is modelbox-rk-aarch64-1.0.9.1
success: create python surpass_pre in /home/rock/███/workspace/surpass_detection/etc/flowunit/surpass_pre
rock@rock-3a:~/███$ ./create.py -t python -n surpass_post -p surpass_detection
sdk version is modelbox-rk-aarch64-1.0.9.1
success: create python surpass_post in /home/rock/███/workspace/surpass_detection/etc/flowunit/surpass_post
可以看到在项目工程的etc/flowunit目录下面已经生成了两个功能单元, 每个功能单元下有.toml配置文件与.py功能代码文件:
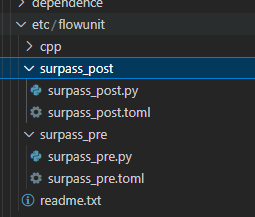
接下来我们要补充每个功能单元的逻辑代码,如果对具体实现过程不感兴趣,同样可以将我们资源包中的代码轻巧一个CtrlC+V速通本节。
首先补充前处理功能单元的配置文件内容,对于前处理功能单元,我们需要知道模型推理的shape,因此要对config字段进行配置,此外,我们希望得到原图与resize后的图两个输出,因为也要对输入输出进行修改:
# Copyright (c) Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2022. All rights reserved.
# Basic config
[base]
name = "surpass_pre" # The FlowUnit name
device = "cpu" # The flowunit runs on cpu
version = "1.0.0" # The version of the flowunit
type = "python" # Fixed value, do not change
description = "description" # The description of the flowunit
entry = "surpass_pre@surpass_preFlowUnit" # Python flowunit entry function
group_type = "generic" # flowunit group attribution, change as input/output/image ...
# Flowunit Type
stream = false # Whether the flowunit is a stream flowunit
condition = false # Whether the flowunit is a condition flowunit
collapse = false # Whether the flowunit is a collapse flowunit
collapse_all = false # Whether the flowunit will collapse all the data
expand = false # Whether the flowunit is a expand flowunit
# The default Flowunit config
[config]
net_h = 320
net_w = 320
# Input ports description
[input]
[input.input1] # Input port number, the format is input.input[N]
name = "in_image" # Input port name
type = "uint8" # Input port type
# Output ports description
[output]
[output.output1] # Output port number, the format is output.output[N]
name = "out_image" # Output port name
type = "uint8" # Output port type
[output.output2] # Output port number, the format is output.output[N]
name = "resized_image" # Output port name
type = "uint8" # Output port type
对于前处理的逻辑代码,只需要简单的实现letterbox功能即可:
# Copyright (c) Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2022. All rights reserved.
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import _flowunit as modelbox
import numpy as np
import cv2
import json
class surpass_preFlowUnit(modelbox.FlowUnit):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def open(self, config):
self.net_h = config.get_int('net_h', 320)
self.net_w = config.get_int('net_w', 320)
return modelbox.Status.StatusCode.STATUS_SUCCESS
def process(self, data_context):
# 获取输入输出
in_image = data_context.input("in_image")
out_image = data_context.output("out_image")
resized_out = data_context.output("resized_image")
for buffer_img in in_image:
# 根据meta信息将image reshape
width = buffer_img.get('width')
height = buffer_img.get('height')
channel = buffer_img.get('channel')
img_data = np.array(buffer_img.as_object(), copy=False)
img_data = img_data.reshape((height, width, channel))
# resize
resized_image, ratio, (dw, dh) = self.letterbox(img_data)
h, w, c = resized_image.shape
resized_image = resized_image.flatten()
# 由resized_image构建输出的buffer
img_buffer = modelbox.Buffer(self.get_bind_device(), resized_image)
img_buffer.copy_meta(buffer_img)
img_buffer.set("pix_fmt", "bgr")
img_buffer.set("width", w)
img_buffer.set("height", h)
img_buffer.set("width_stride", w * 3)
img_buffer.set("height_stride", h)
resized_out.push_back(img_buffer)
# 在原图附上buffer_meta信息,在接收节点可以读取到meta信息
buffer_meta = {"ratio": ratio, "dh": dh, "dw": dw,
"net_h": self.net_h, "net_w": self.net_w}
buffer_img.set("buffer_meta", json.dumps(buffer_meta))
out_image.push_back(buffer_img)
return modelbox.Status.StatusCode.STATUS_SUCCESS
def letterbox(self, img, color=(114, 114, 114)):
shape = img.shape[:2]
new_shape = (self.net_h, self.net_w)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1]
dw /= 2
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad:
img = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color)
return img, r, (dw, dh)
def close(self):
return modelbox.Status()
对于后处理功能单元的配置文件,我们在config中配置参数,接收三个float类型的推理结果与一个uint8类型的原图,输出画好检测框的图:
# Copyright (c) Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2022. All rights reserved.
# Basic config
[base]
name = "surpass_post" # The FlowUnit name
device = "cpu" # The flowunit runs on cpu
version = "1.0.0" # The version of the flowunit
type = "python" # Fixed value, do not change
description = "description" # The description of the flowunit
entry = "surpass_post@surpass_postFlowUnit" # Python flowunit entry function
group_type = "generic" # flowunit group attribution, change as input/output/image ...
# Flowunit Type
stream = false # Whether the flowunit is a stream flowunit
condition = false # Whether the flowunit is a condition flowunit
collapse = false # Whether the flowunit is a collapse flowunit
collapse_all = false # Whether the flowunit will collapse all the data
expand = false # Whether the flowunit is a expand flowunit
# The default Flowunit config
[config]
class_path = "data/classes.txt"
strides = ["8", "16", "32"]
masks = ["0", "1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8"]
anchors = ["12", "16", "19", "36", "40", "28", "36", "75", "76", "55", "72", "146", "142", "110", "192", "243", "459", "401"]
conf_threshold = 0.4
iou_threshold = 0.45
[input]
[input.input1]
name = "in_feat1"
type = "float"
[input.input2]
name = "in_feat2"
type = "float"
[input.input3]
name = "in_feat3"
type = "float"
[input.input4]
name = "in_image"
type = "uint8"
[output]
[output.output1]
name = "out_image"
type = "uint8"
后处理代码:
# Copyright (c) Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2022. All rights reserved.
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import _flowunit as modelbox
import json
import numpy as np
from utils import YOLO7, draw
class surpass_postFlowUnit(modelbox.FlowUnit):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def open(self, config):
label_path = config.get_string("label_path", "data/classes.txt")
with open(label_path) as f:
self.labels = f.readlines()
self.labels = [x.strip() for x in self.labels]
masks = np.array(config.get_int_list("masks", [])).reshape(3, 3)
anchors = np.array(config.get_int_list("anchors", [])).reshape(-1, 2)
self.strides = np.array(config.get_int_list("strides", []))
conf_threshold = config.get_float("conf_threshold", 0.5)
iou_threshold = config.get_float("iou_threshold", 0.4)
self.yolov7 = YOLO7(conf_threshold, iou_threshold, anchors=anchors, masks=masks, strides=self.strides)
return modelbox.Status.StatusCode.STATUS_SUCCESS
def process(self, data_context):
modelbox.info("Yolo7Post")
input_feat1 = data_context.input("in_feat1")
input_feat2 = data_context.input("in_feat2")
input_feat3 = data_context.input("in_feat3")
input_image = data_context.input("in_image")
out_image = data_context.output("out_image")
for buffer_feat1, buffer_feat2, buffer_feat3, buffer_img in zip(input_feat1, input_feat2, input_feat3, input_image):
feat_data_1 = np.array(buffer_feat1.as_object(), copy=False)
feat_data_2 = np.array(buffer_feat2.as_object(), copy=False)
feat_data_3 = np.array(buffer_feat3.as_object(), copy=False)
width = buffer_img.get("width")
height = buffer_img.get("height")
channel = buffer_img.get("channel")
img_data = np.array(buffer_img.as_object(), copy=False)
img_data = img_data.reshape((height, width, channel))
# 获取pre单元传入的buffer_meta信息
buffer_meta = json.loads(buffer_img.get("buffer_meta"))
feats = [np.transpose(feat.reshape(3, -1, buffer_meta["net_h"] // self.strides[idx],
buffer_meta["net_w"] // self.strides[idx]), (2, 3, 0, 1))
for idx, feat in enumerate([feat_data_1, feat_data_2, feat_data_3])]
# 解码
bboxes, classes, scores = self.yolov7.yolov7_post_process(feats)
draw(img_data, bboxes, scores, classes, self.labels, buffer_meta)
add_buffer = modelbox.Buffer(self.get_bind_device(), img_data)
add_buffer.copy_meta(buffer_img)
out_image.push_back(add_buffer)
return modelbox.Status.StatusCode.STATUS_SUCCESS
def close(self):
return modelbox.Status()
其中,utils中YOLO7与draw如下:
import numpy as np
import cv2
class YOLO7:
def __init__(self, conf_threshold, iou_threshold, anchors, masks, strides):
self.conf_threshold = conf_threshold
self.iou_threshold = iou_threshold
self.anchors = anchors
self.masks = masks
self.strides = strides
@staticmethod
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
@staticmethod
def make_grid(nx=20, ny=20):
xv, yv = np.meshgrid(np.arange(ny), np.arange(nx))
return np.stack((xv, yv), 2).reshape((ny, nx, -1, 2)).astype(np.float32)
def process(self, inputs, mask, anchors, stride):
anchors = [anchors[i] for i in mask]
ny, nx = map(int, inputs.shape[0:2])
grid = self.make_grid(nx, ny)
inputs = self.sigmoid(inputs)
box_confidence = inputs[..., 4]
box_confidence = np.expand_dims(box_confidence, axis=-1)
box_class_probs = inputs[..., 5:]
box_xy = (inputs[..., :2] * 2. - 0.5 + grid) * stride
box_wh = (inputs[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * anchors
box = np.concatenate((box_xy, box_wh), axis=-1)
return box, box_confidence, box_class_probs
def filter_boxes(self, boxes, box_confidences, box_class_probs):
box_scores = box_confidences * box_class_probs
box_classes = np.argmax(box_scores, axis=-1)
box_class_scores = np.max(box_scores, axis=-1)
pos = np.where(box_class_scores >= self.conf_threshold)
boxes = boxes[pos]
classes = box_classes[pos]
scores = box_class_scores[pos]
return boxes, classes, scores
def nms_boxes(self, boxes, scores):
x = boxes[:, 0]
y = boxes[:, 1]
w = boxes[:, 2]
h = boxes[:, 3]
areas = w * h
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x[i], x[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y[i], y[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x[i] + w[i], x[order[1:]] + w[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y[i] + h[i], y[order[1:]] + h[order[1:]])
w1 = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1)
h1 = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1)
inter = w1 * h1
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
inds = np.where(ovr <= self.iou_threshold)[0]
order = order[inds + 1]
keep = np.array(keep)
return keep
def yolov7_post_process(self, input_data):
boxes, classes, scores = [], [], []
for input, mask, stride in zip(input_data, self.masks, self.strides):
b, c, s = self.process(input, mask, self.anchors, stride)
b, c, s = self.filter_boxes(b, c, s)
boxes.append(b)
classes.append(c)
scores.append(s)
boxes = np.concatenate(boxes)
classes = np.concatenate(classes)
scores = np.concatenate(scores)
nboxes, nclasses, nscores = [], [], []
for c in set(classes):
inds = np.where(classes == c)
b = boxes[inds]
c = classes[inds]
s = scores[inds]
keep = self.nms_boxes(b, s)
nboxes.append(b[keep])
nclasses.append(c[keep])
nscores.append(s[keep])
if not nclasses and not nscores:
return [], [], []
boxes = np.concatenate(nboxes)
classes = np.concatenate(nclasses)
scores = np.concatenate(nscores)
return boxes, classes, scores
def draw(image, boxes, scores, classes, labels, buffer_meta):
r, dw, dh = buffer_meta["ratio"], buffer_meta["dw"], buffer_meta["dh"]
for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):
x, y, w, h = box
x = (x - dw) / r
y = (y - dh) / r
w = w / r
h = h / r
top = max(0, (x - w / 2).astype(int))
left = max(0, (y - h / 2).astype(int))
right = min(image.shape[1], (x + w / 2).astype(int))
bottom = min(image.shape[0], (y + h / 2).astype(int))
cv2.rectangle(image, (top, left), (right, bottom), (255, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(labels[cl], score), (top, left - 6),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (0, 0, 255), 2)
至此,我们所有的功能代码都准备好啦。
搭建流程图
准备好了每个功能单元,接下来要在流程图中将功能单元连接起来。创建工程时默认生成的流程图在工程目录graph文件夹下:
修改surpass_detection.toml内容:
# Copyright (C) 2020 Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
[driver]
dir = ["${HILENS_APP_ROOT}/etc/flowunit",
"${HILENS_APP_ROOT}/etc/flowunit/cpp",
"${HILENS_APP_ROOT}/model",
"${HILENS_MB_SDK_PATH}/flowunit"]
skip-default = true
[profile]
profile=true
trace=true
dir="${HILENS_DATA_DIR}/mb_profile"
[graph]
format = "graphviz"
graphconf = """digraph surpass_detection {
node [shape=Mrecord]
queue_size = 4
batch_size = 4
input1[type=input,flowunit=input,device=cpu,deviceid=0]
data_source_parser[type=flowunit, flowunit=data_source_parser, device=cpu, deviceid=0]
video_demuxer[type=flowunit, flowunit=video_demuxer, device=cpu, deviceid=0]
video_decoder[type=flowunit, flowunit=video_decoder, device=rknpu, deviceid=0, pix_fmt=bgr]
surpass_pre[type=flowunit, flowunit=surpass_pre, device=cpu, deviceid=0]
surpass[type=flowunit, flowunit=surpass, device=rknpu, deviceid=0, batch_size=1]
surpass_post[type=flowunit, flowunit=surpass_post, device=cpu, deviceid=0]
video_out[type=flowunit, flowunit=video_out, device=rknpu, deviceid=0]
input1:input -> data_source_parser:in_data
data_source_parser:out_video_url -> video_demuxer:in_video_url
video_demuxer:out_video_packet -> video_decoder:in_video_packet
video_decoder:out_video_frame -> surpass_pre:in_image
surpass_pre:resized_image -> surpass:input
surpass:output1 -> surpass_post:in_feat1
surpass:output2 -> surpass_post:in_feat2
surpass:output3 -> surpass_post:in_feat3
surpass_pre:out_image -> surpass_post:in_image
surpass_post:out_image -> video_out:in_video_frame
}"""
[flow]
desc = "surpass_detection run in modelbox-rk-aarch64"
其中,profile字段设为true启用性能统计功能,毕竟我们要看看surpass detectioin究竟是不是surpass。性能统计具体加载方式可以参考ModelBox文档相关章节。
运行应用
应用的输入输出可以在项目工程的bin/mock_task.toml中进行配置:
将资源包中的测试视频拷贝到data目录下,配置应用输入输出:
# 用于本地mock文件读取任务,脚本中已经配置了IVA_SVC_CONFIG环境变量, 添加了此文件路径
########### 请确定使用linux的路径类型,比如在windows上要用 D:/xxx/xxx 不能用D:\xxx\xxx ###########
# 任务的参数为一个压缩并转义后的json字符串
# 直接写需要转义双引号, 也可以用 content_file 添加一个json文件,如果content和content_file都存在content会被覆盖
# content_file支持绝对路径或者相对路径,不支持解析环境变量(包括${HILENS_APP_ROOT}、${HILENS_DATA_DIR}等)
[common]![Uploading file..._m9v3q47eo]()
content = "{\"param_str\":\"string param\",\"param_int\":10,\"param_float\":10.5}"
# 任务输入,mock模拟目前仅支持一路rtsp或者本地url
# rtsp摄像头,type = "rtsp", url里面写入rtsp地址
# 其它用"url",比如可以是本地文件地址, 或者httpserver的地址,(摄像头 url = "0")
[input]
type = "url"
url = "../data/car_test_video.mp4"
# 任务输出,目前仅支持"webhook", 和本地输出"local"(输出到屏幕,url="0", 输出到rtsp,填写rtsp地址)
# (local 还可以输出到本地文件,这个时候注意,文件可以是相对路径,是相对这个mock_task.toml文件本身)
[output]
type = "local"
url = "../hilens_data_dir/surpass_result.mp4"
之后就可以进入项目目录对应用进行构建与运行了:
rock@rock-3a:~/███/workspace/surpass_detection$ ./build_project.sh
dos2unix: converting file /home/rock/███/workspace/surpass_detection/graph/modelbox.conf to Unix format...
dos2unix: converting file /home/rock/███/workspace/surpass_detection/graph/surpass_detection.toml to Unix format...
dos2unix: converting file /home/rock/███/workspace/surpass_detection/etc/flowunit/surpass_post/surpass_post.toml to Unix format...
dos2unix: converting file /home/rock/███/workspace/surpass_detection/etc/flowunit/surpass_pre/surpass_pre.toml to Unix format...
dos2unix: converting file /home/rock/███/workspace/surpass_detection/model/surpass/surpass.toml to Unix format...
dos2unix: converting file /home/rock/███/workspace/surpass_detection/bin/mock_task.toml to Unix format...
build success: you can run main.sh in ./bin folder
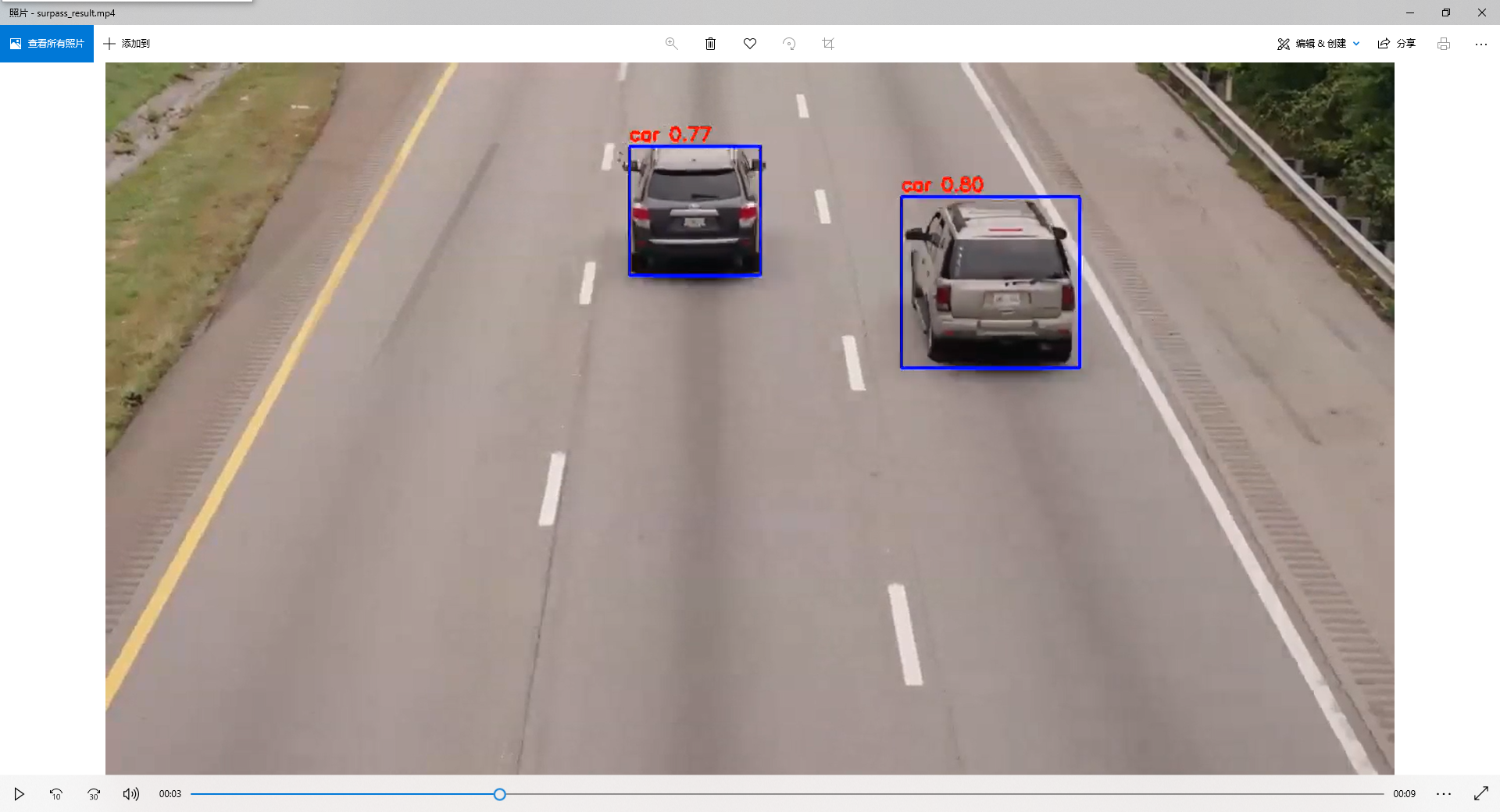
执行bin/main.sh运行应用(如果运行报错请切换到root账号再运行,本应用需要事先使用pip安装好OpenCV和NumPy),运行结束后在hilens_data_dir目录下生成了surpass_result.mp4文件与性能评估结果文件夹mb_profile:

可以右键下载查看:
查看性能统计文件:
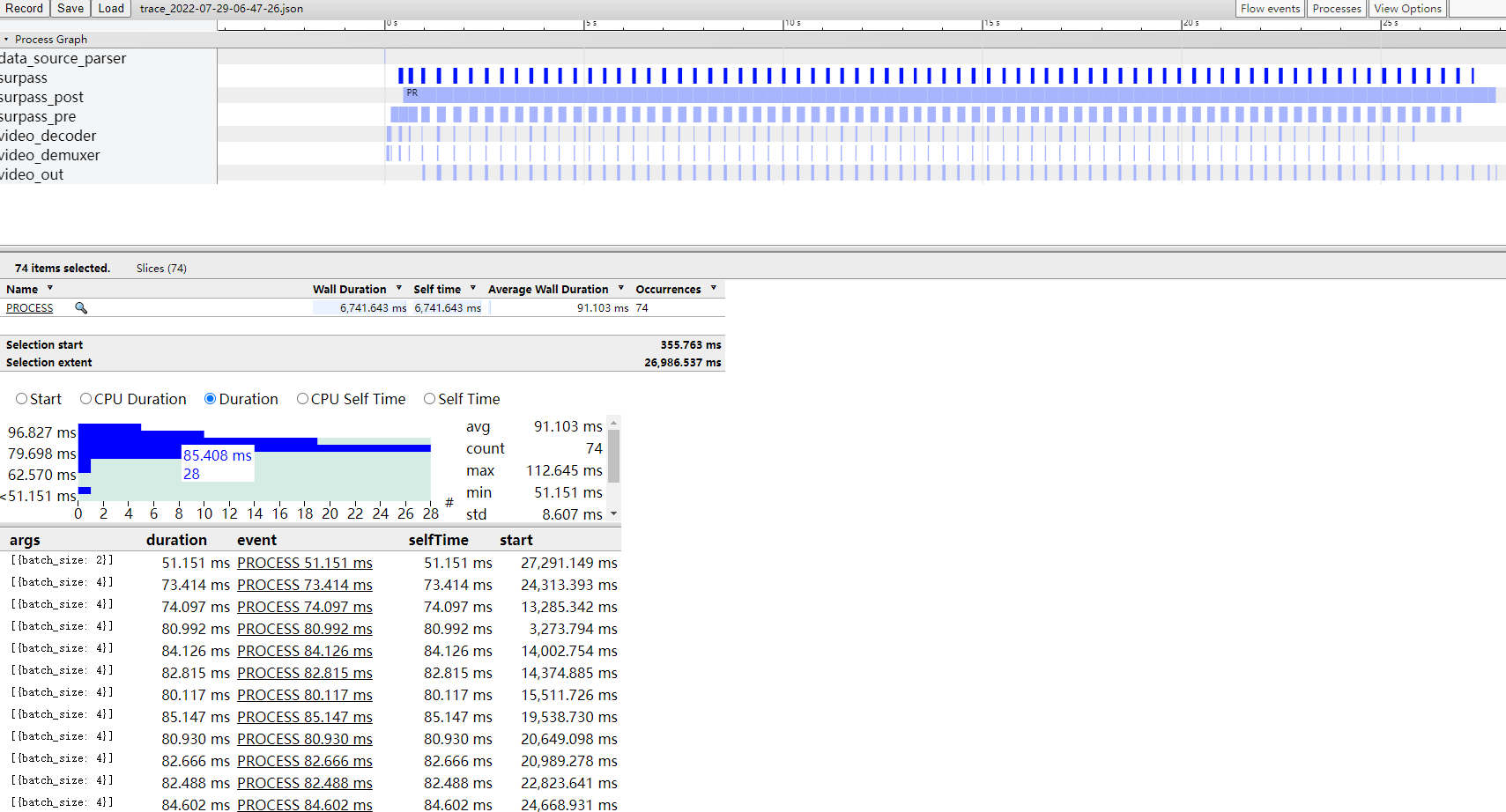
可以看到模型推理确实很快,平均每4次推理耗时90ms,我们应用的性能瓶颈其实是前后处理。
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)