JavaWeb学习笔记二 --- 会话机制、JSP、 EL+JSTL 总结(超详细的总结~~)
JavaWeb学习笔记第二章节总结,系列文章,博主会创作出更好的文章,希望能够帮助到你。
会话机制
会话技术分为:cookie技术、session技术,
Cookie技术
cookie技术为客户端技术,将数组保存在客户端浏览器上,每次访问服务器,随身携带数据

Cookie基本操作
服务器设置Cookie,响应给浏览器
Cookie cookie = new Cookie(key,value);
response.addCookie(cookie);
新建CookieServlet类测试
@WebServlet("/cookieTest")
public class CookieServlet extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
Cookie c1 = new Cookie("name", "zhangsan");
resp.addCookie(c1);
}
}
浏览器访问该地址

再次访问,浏览器会携带这cookie中数据去访问服务器

获取所有Cookie
@WebServlet("/getCookie")
public class GetCookieServlet extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
Cookie[] cookies = req.getCookies();
String name = null;
String age = null;
for (Cookie cookie : cookies) {
if (cookie.getName().equals("name")) {
name = cookie.getValue();
}
if (cookie.getName().equals("age")) {
age = cookie.getValue();
}
}
resp.getWriter().write("name:" + name + ", age:" + age);
}
}
浏览器访问该地址:

成功获取到所有cookie对象,cookie对象是键值对的,
一个name对应一个value
Cookie有效期设置
设置Cookie的有效期,默认cookie有效期关闭浏览器失效,通过setMaxAge方法设置cookie的有效期
@WebServlet("/cookieTest")
public class CookieServlet extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
Cookie c1 = new Cookie("name", "zhangsan");
Cookie c2 = new Cookie("age", "34");
//通过setMaxAge方法设置cookie的有效期,参数为秒
c1.setMaxAge(60);
c2.setMaxAge(60);
resp.addCookie(c1);
resp.addCookie(c2);
}
}
Session技术
session技术为服务器技术,将会话过程产生的数据保存到服务器内存中

浏览器第一次访问服务器时,服务器会在服务器端创建session文件
然后,将session文件名称(想象成钥匙)以cookie的形式响应给浏览器
当浏览器第二次访问服务器时,只需要随身携带钥匙(session文件名),再通过该钥匙找到内容
session基本操作
服务器创建session
@WebServlet("/sessionTest")
public class SessionServlet extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取session(就是session文件)
HttpSession s1 = req.getSession();
//向session存储数据
s1.setAttribute("name", "张三");
}
}
浏览器访问该地址:
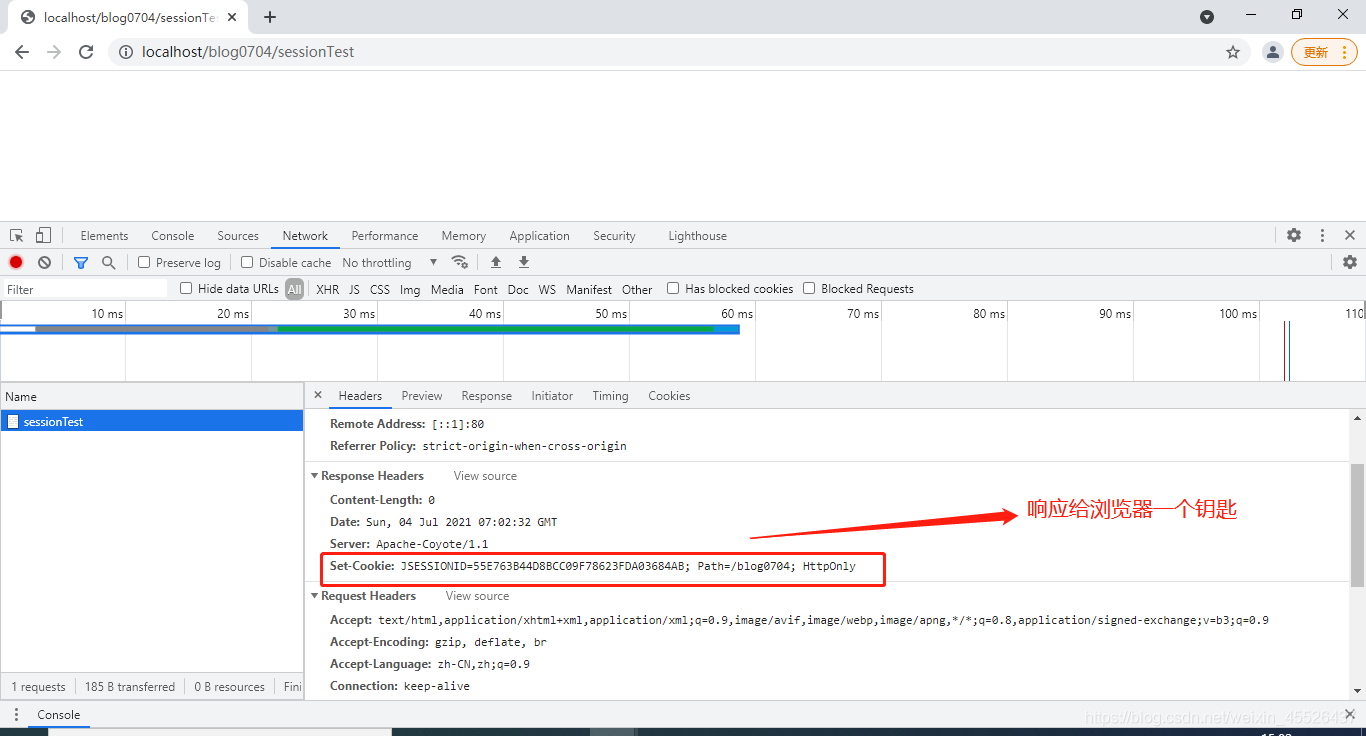
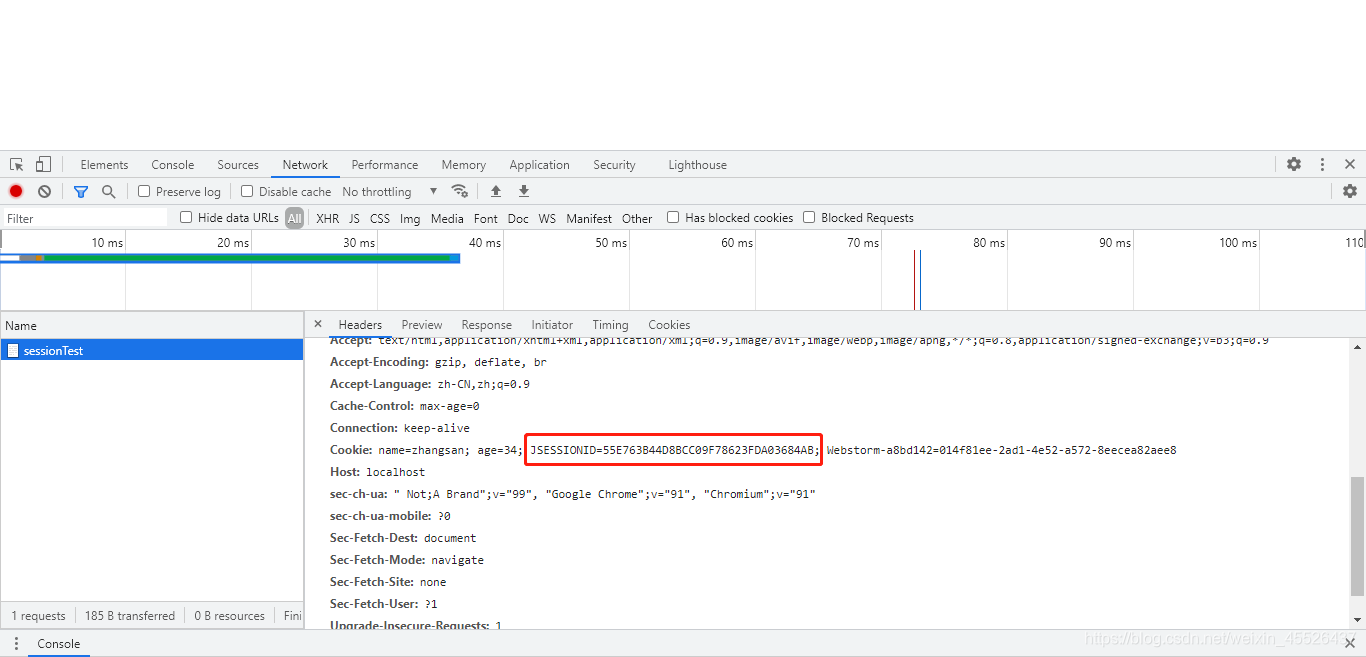
再次访问请求头中会有服务器响应给浏览器的钥匙
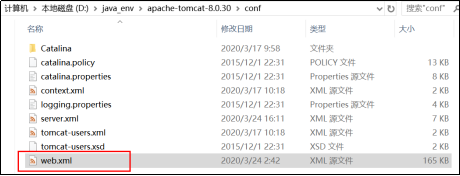
设置Session有效期:
1.在web.xml文件中配置
2.在tomcat服务器配置文件中配置
session-config,默认值为:30分钟
<session-config>
<session-timeout>30</session-timeout>
</session-config>
在java程序中设置
s1.setMaxInactiveInterval(10);
参数为秒
JSP
JSP,Java Server Pages,Java服务器端页面(网页)技术
在JSP页面中,Java代码可以和HTML代码共存,其中Java代码负责处理数据,HTML代码负责显示数据
jsp就是一个Servlet
创建JSP页面
右击WebContent—New—JSP File—输入文件名
或者:右击WebContent—New—Other—Web—JSP File—输入文件名
修改jsp页面的编码为UTF-8
Window—Preferences----搜索JSP—Templates----
JSP基本语法
代码块
在JSP页面中可以将Java代码块写到:
<% Java代码块 %>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8"
pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html >
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<% out.write("helloword") %>
</body>
</html>
输出变量/表达式结果:
<%=变量 或 表达式%>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8"
pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html >
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<%
out.write("helloword")
int a = 12;
int b = 30;
%>
<p>输出表达式结果</p>
<%=a+b %>
<p>输出变量结果</p>
<%=b %>
</body>
</html>
JSP注释
HTML代码注释:
JSP代码注释: <%-- 注释的内容 --%>
注释的快捷键:ctrl + shift + /
JSP指令
在jsp2.0中共定义了page、include和taglib三种指令。
page指令, 配置JSP页面信息的。
include指令,页面包含的,导入页面的。
<%@include file=“top.jsp”%>
taglib指令, 导入资源,格式:
<%@ taglib prefix=“c” uri=“http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core” %>
* prefix:前缀,自定义的
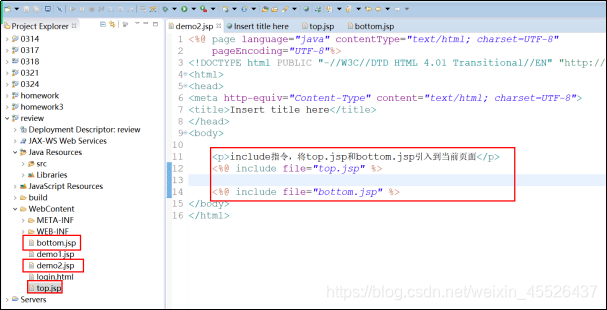
JSP内置对象
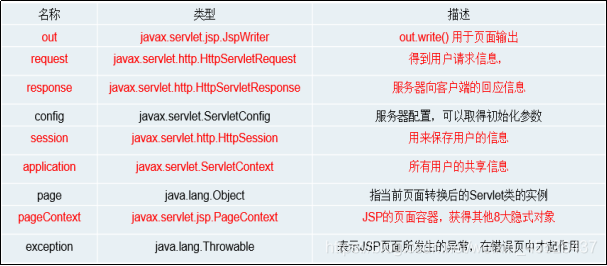
为了提升开发效率,JSP给我们提供了9大内置对象,不需要定义,我们在JSP脚本中可以直接使用。
4大域对象:
request域对象
session域对象
application域对象
pageContext域对象
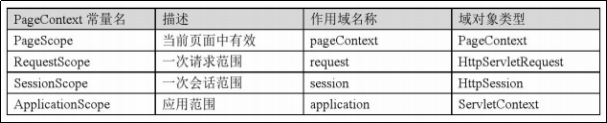
四大域对象的作用范围:从大到小
application > session > request > pageContext
四大域对象的作用优先级范围:从大到小:
pageContext > request > session > application
EL+JSTL
EL
在JSP页面开发中,为了获取Servlet域对象中存储的数据,经常需要书写很多Java代码,这样的做法会使JSP页面混乱,难以维护,为此,在JSP2.0规范中提供了EL表达式。
EL是Expression Language的缩写,它是一种简单的数据访问语言。
EL的目的:简化JSP脚本的书写。
EL语法格式:${EL表达式}
EL表达式获取数据
使用EL表达式获取四大域对象中的数据
${key}
如果获取域中的数据时,如果没有指定所在的域,会按照下面的顺序依次查找
—依次从pageContext域,request域,session域,application域中获取属性,在某个域中获取后将不在向后寻找
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 四大域对象 -->
<%
/*pageContext 对象只能在本页面才能访问到*/
pageContext.setAttribute("name", "pageContext");
request.setAttribute("name", "request");
session.setAttribute("name", "session");
application.setAttribute("name", "application");
%>
<!-- 使用EL表达式取出域对象中的数据 -->
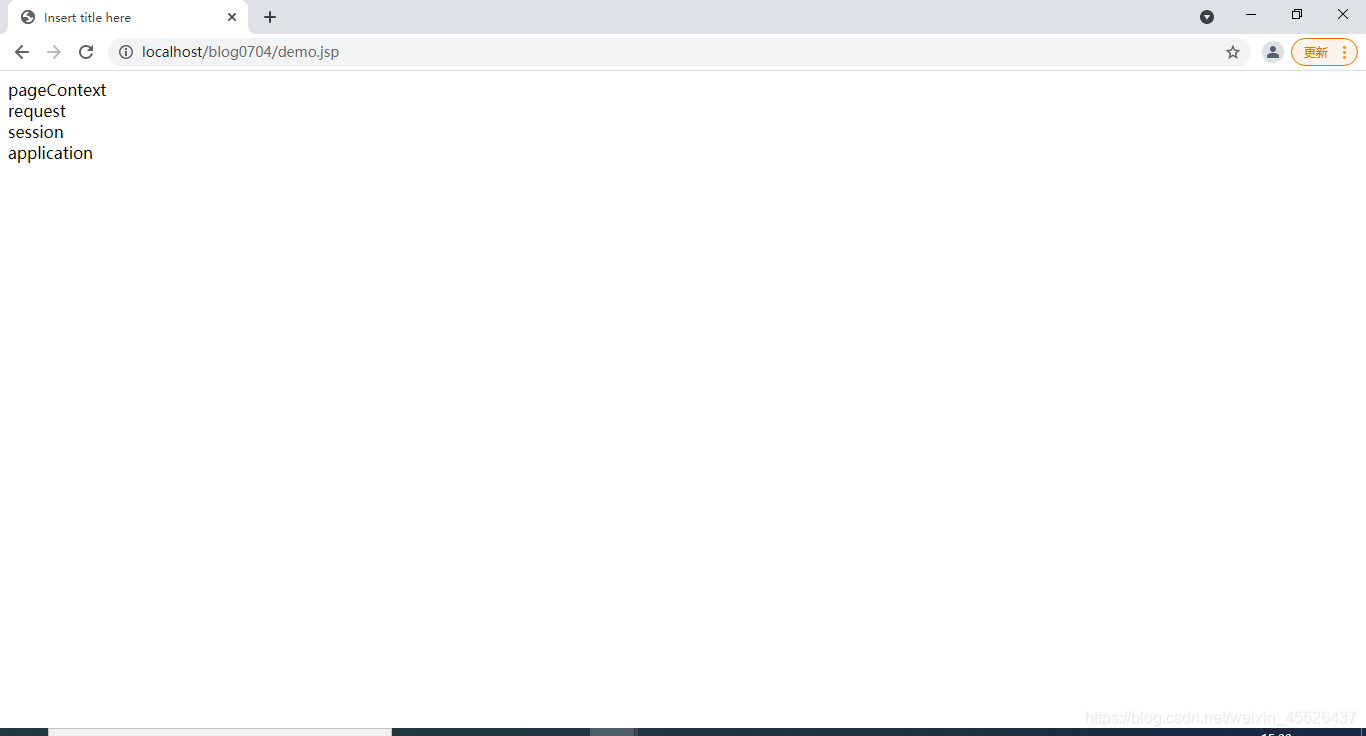
${pageScope.name}<br/>
${requestScope.name}<br/>
${sessionScope.name}<br/>
${applicationScope.name}<br/>
</body>
</html>
浏览器访问该地址:
EL表达式获取基本数据类型
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 四大域对象 -->
<%
request.setAttribute("name", "张三");
%>
${name }
</body>
</html>
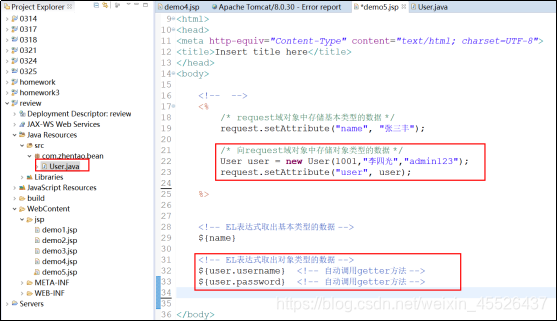
EL表达式获取对象类型数据
对象:${域名称.键名.属性名}
- 本质上会去调用对象的getter方法

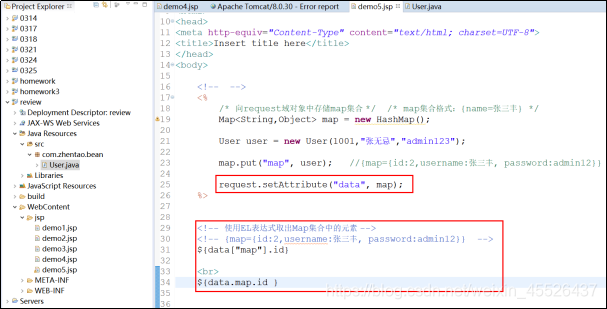
获取List集合中的数据
List集合: {域名称.键名.key名称}
${域名称.键名[“key名称”]}
JSTL介绍
JSTL,JSP Standard Tag Lib,JSP标准标签库,提供了一些标签(<c:if> <c:forEach>),能够在JSP页面完成更加复杂的业务逻辑,总之用于简化和替换jsp页面上的java代码
使用步骤:
- 导入jstl相关jar包
- 引入标签库:taglib指令: <%@ taglib %>
<%@ taglib uri=“http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core” prefix=“c”%> - 使用标签:
Java的标签库,常见的标签有:
<c:if></c:if>
<c:forEach></c:forEach>
<c:choose></c:choose>
利用jstl循环遍历用户集合:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 四大域对象 -->
<%
java.util.List<com.blog.bean.User> users = new java.util.ArrayList<com.blog.bean.User>();
users.add(new com.blog.bean.User("张三", 23));
users.add(new com.blog.bean.User("李四", 32));
users.add(new com.blog.bean.User("王五", 33));
request.setAttribute("users", users);
%>
<c:forEach items="${users }" var="user">
${user.name } ${user.age }
</c:forEach>
</body>
</html>
好了,总结到此结束,博主会创作更好的文章,一起探讨技术,努力前进,终有一日会实现自己的目标,加油,打好基础!!!
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)