SpringBoot中使用Swagger详解
在Spring Boot中规范的使用Swagger进行接口测试
Swagger是什么?
Swagger是一套基于OpenAPI规范构建的开源工具,可以帮助我们设计、构建、记录以及使用Rest API。Swagger主要包括了一下三个部分:
- Swagger Editor: 基于浏览器的编辑器,我们可以使用它来编写我们的OpenAPI文档。
- Swagger UI: 它会将我们编写的OpenAPI规范呈现为交互式的API文档。后文我们将使用浏览器来查看并且操作我们的Rest API。
- Swagger CodeGen:它可以通过为OpenAPI规范定义的任何API生成服务器存根和客户端SDK来简化构建过程。
简单点来讲就是说,swagger是一款可以根据resutful风格生成的生成的接口开发文档,并且支持做测试的一款中间软件。
为什么要用Swagger?
后端:
- 不用再手写WiKi接口拼大量的参数,避免手写错误
- 对代码侵入性低,采用全注解的方式,开发简单
- 方法参数名修改、增加、减少参数都可以直接生效,不用手动维护
- 缺点:增加了开发成本,写接口还得再写一套参数配置
前端:
- 后端只需要定义好接口,会自动生成文档,接口功能、参数一目了然
- 联调方便,如果出问题,直接测试接口,实时检查参数和返回值,就可以快速定位是前端还是后端的问题
测试:
- 对于某些没有前端界面UI的功能,可以用它来测试接口
- 操作简单,不用了解具体代码就可以操作
准备工作
使用的环境:
springboot: 2.7.8-SNAPSHOT
Java:1.8
swagger:2.9.2
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
创建项目
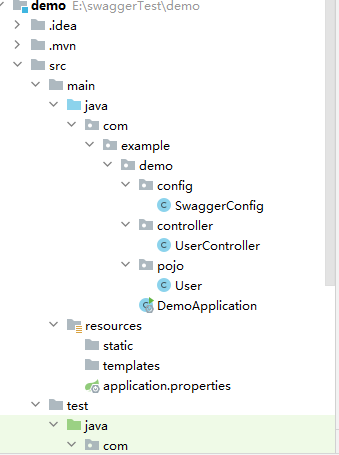
添加依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
编写接口
UserController提供了用户的增、删、改、查四个接口,TestController提供了一个测试接口
pojo.user源码:
package com.example.demo.pojo;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
/**
* @Author 秋名山码神
* @Date 2023/1/9
* @Description
*/
@ApiModel("用户实体类")
public class User {
@ApiModelProperty("用户名")
private String username;
@ApiModelProperty("密码")
private String password;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
UserController源码:
package com.example.demo.controller;
import com.example.demo.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
/**
* @Author 秋名山码神
* @Date 2023/1/9
* @Description
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@PostMapping("/add")
public boolean addUser(User user){
return false;
}
@GetMapping("/find/{id}")
public User findById(@PathVariable("id") int id) {
return new User();
}
@PutMapping("/update")
public boolean update(@RequestBody User user) {
return true;
}
@DeleteMapping("/delete/{id}")
public boolean delete(@PathVariable("id") int id) {
return true;
}
}
SwaggerConfig源码
package com.example.demo.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
/**
* @Author 秋名山码神
* @Date 2023/1/9
* @Description
*/
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean
// 配置Swagger的Docket的bean实例
public Docket api(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.select()
// RequestHandlerSelectors配置扫描接口的方式
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.any())
// path过滤什么路径
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
@Configuration是告诉Spring Boot需要加载这个配置类;@EnableSwagger2是启用Swagger2.
验证
启动一下项目,然后在浏览器中访问http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
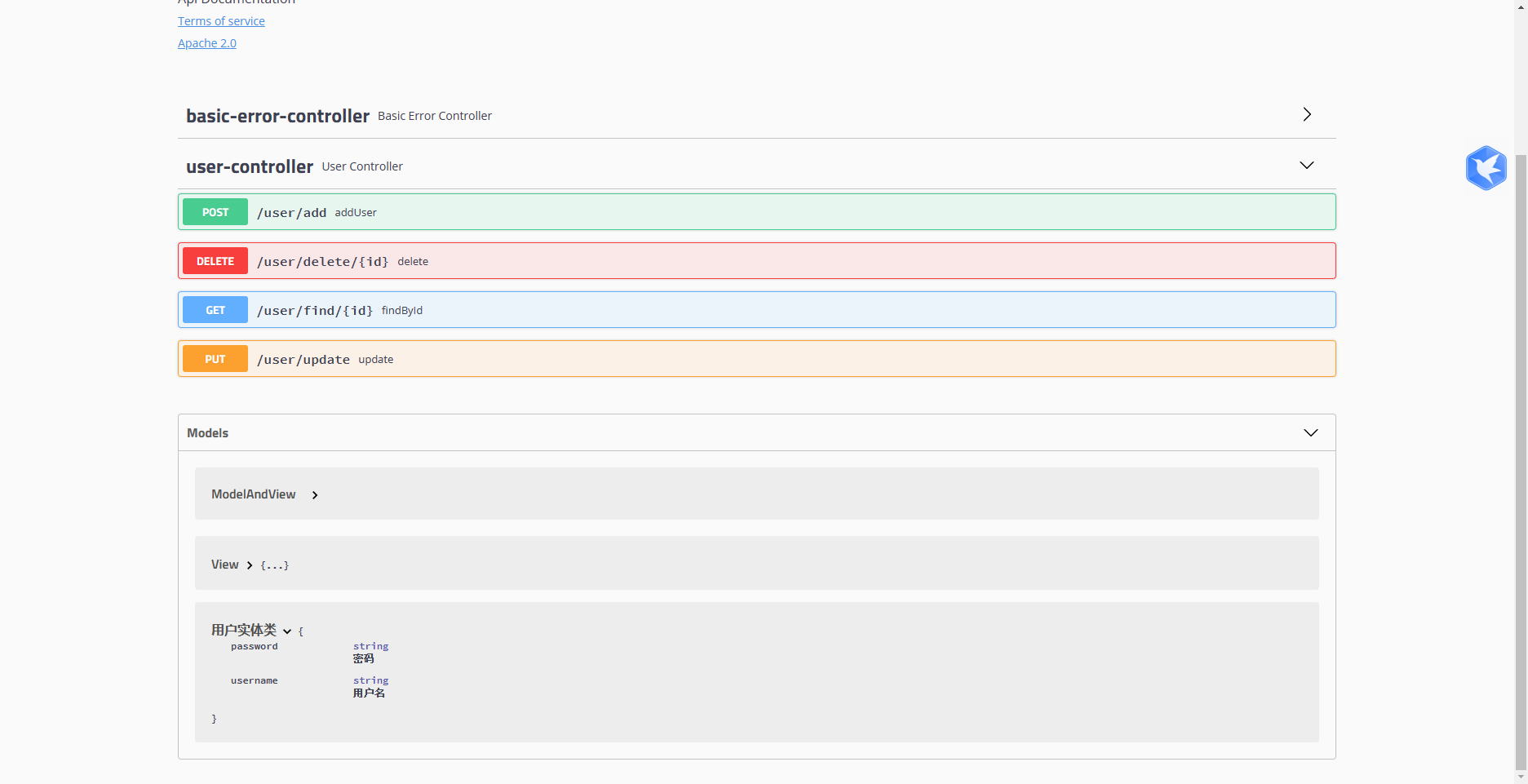
到此项目已经跑起来了,我们来解释一下,Swagger中的高级配置**(代码注释写的也很清楚)**
高级配置
文档注释
- 通过在控制器类上添加@Api注解,可以给控制器增加描述和标签信息
@Api(tags = "用户相关接口",description = "提供用户相关的Rest API")
public class UserController {
- 通过在接口方法上添加@ApiOperation注解来展开对接口的描述
@ApiOperation("添加用户操作")
@PostMapping("/add")
public boolean addUser(User user){
return false;
}
- 通过在实体类上添加@ApiModel和@ApiModelProperty注解来对我们的API所涉及到的对象做描述
@ApiModel("用户实体类")
public class User {
@ApiModelProperty("用户名")
private String username;
@ApiModelProperty("密码")
private String password;
- 文档信息配置,Swagger还支持设置一些文档的版本号、联系人邮箱、网站、版权、开源协议等等信息,但与上面几条不同的是这些信息不能通过注解配置,而是通过创建一个ApiInfo对象,并且使用appInfo()方法来设置,我们在SwaggerConfig.java类中新增如下内容即可:
@Bean
// 配置Swagger的Docket的bean实例
public Docket api(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.select()
// RequestHandlerSelectors配置扫描接口的方式
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.any())
// path过滤什么路径
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfo(
"Spring Boot 项目集成 Swagger 实例文档",
"欢迎",
"API V1.0",
"Terms of service",
new Contact("名字想好没", "csdn", "163.com"),
"Apache", "http://www.apache.org/", Collections.emptyList());
}
接口过滤
- 加注解:如果想在文档中屏蔽掉某个接口方法,只需要在该接口方法上添加@ApiIgnore即可
- 在Docket上增加筛选。Docket提供了apis()和paths()两个方法来帮助我们在不同级别上过滤接口:
apis(): 这种方式我们可以通过指定包名的方式,让Swagger 只去某些包下扫描。
paths(): 这种方式可以通过筛选API的 url 来进行过滤。
自定义响应
Docket的globalResponseMessage()方法全局覆盖HTTP方法的响应消息,但是我们首先得通过Docket的useDefaultResponseMessage()方法告诉Swagger不适用默认的HTTP响应消息 ,假设我们需要覆盖所有GET方法的 500 和 403 错误的响应消息。我们只需要在SwaggerConfig.java 类种的Docket Bean下添加如下内容:
.useDefaultResponseMessages(false)
.globalResponseMessage(RequestMethod.GET, newArrayList(
new ResponseMessageBuilder()
.code(500)
.message("服务器发生异常")
.responseModel(new ModelRef("Error"))
.build(),
new ResponseMessageBuilder()
.code(403)
.message("资源不可用")
.build()
));
SwaggerUI的使用
接口调用
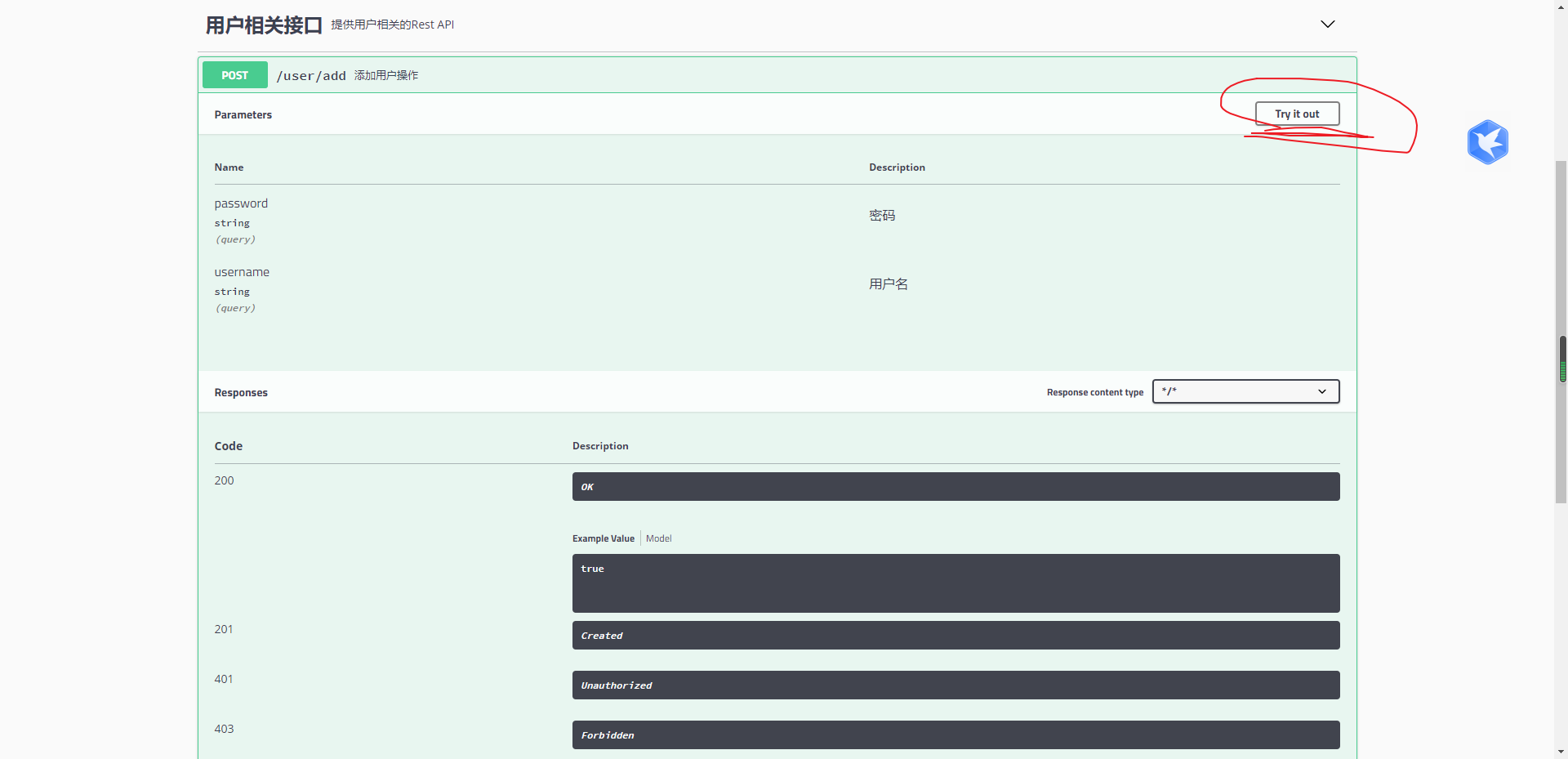
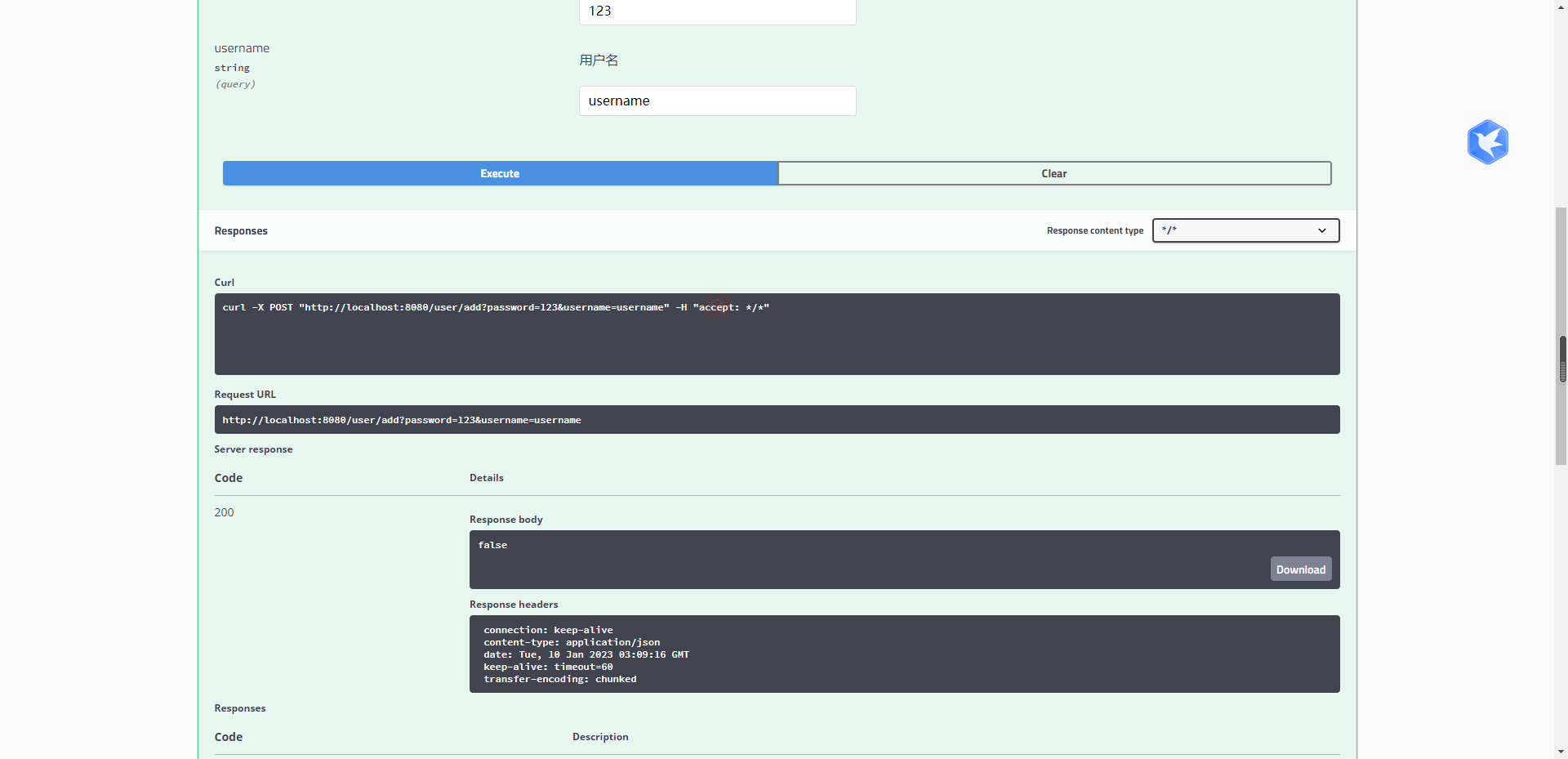
遇到的问题:
启动项目报空指针异常
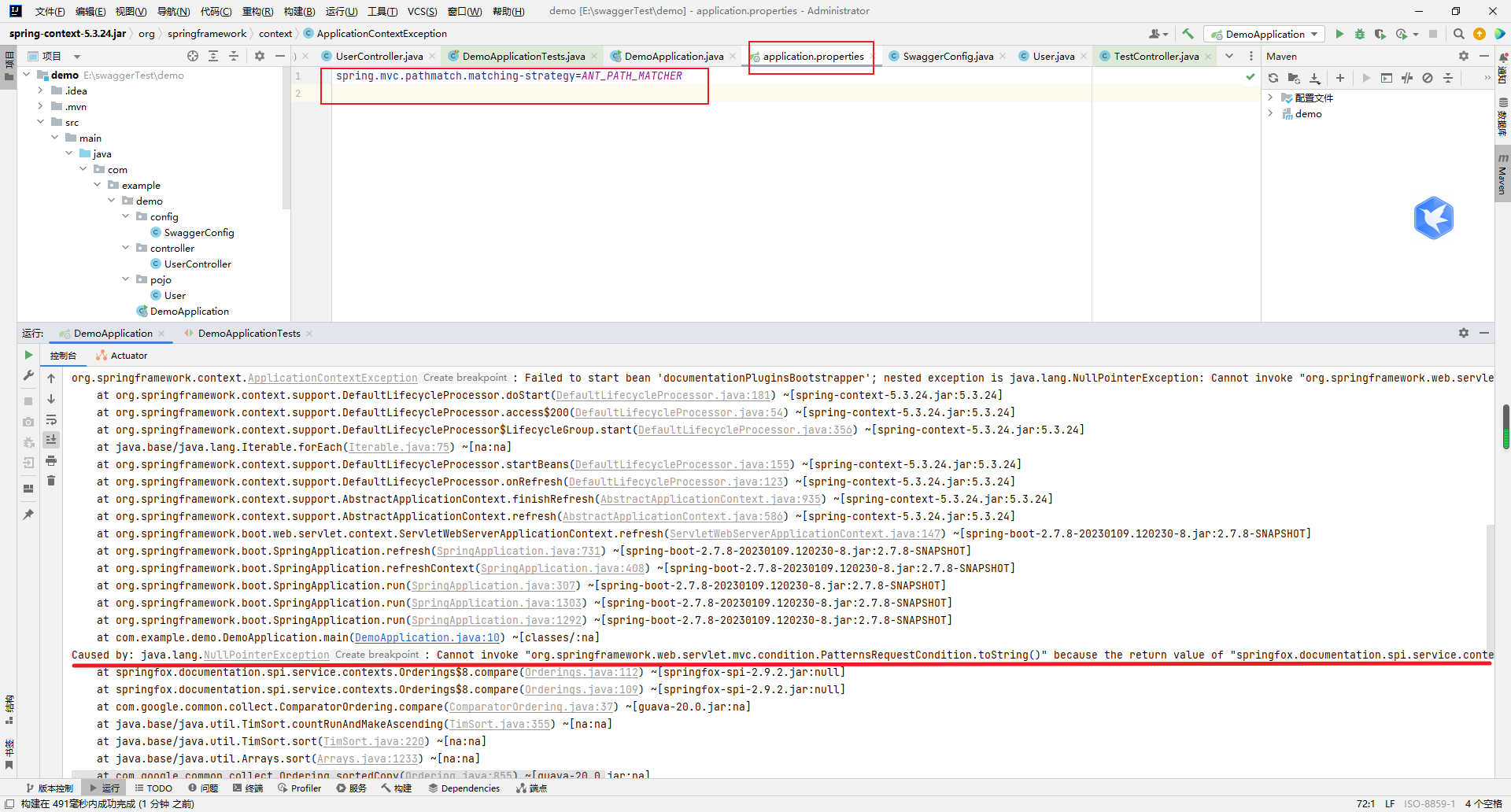
添加这个代码:spring.mvc.pathmatch.matching-strategy=ANT_PATH_MATCHER
- 点赞
- 收藏
- 关注作者


评论(0)